Abstract
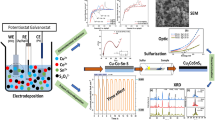
We have synthesized CuInSe2 (CIS) thin films from an aqueous electrolyte by potentiostatic electrochemical technique at room temperature. The effects of pH and selenization on the properties of CIS layer have been thoroughly investigated. The studies were carried out on the samples prepared in as-prepared bath with pH 2.5 and later adjusted to 1.2. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was studied at slow scan rate to optimize the deposition parameters. The prepared thin films were selenized in a tubular furnace at 400 °C for 20 min in selenium atmosphere. Structural, optical, compositional, morphological, and electrical properties were studied with the help of X-ray diffractometer, Uv-vis absorption spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDAX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and current–voltage (I–V) measurements. The prominent reflections (112), (204/220), and (312/116) of tetragonal CIS have been exhibited for all as-deposited and selenized samples. The energy band gap of the selenized CIS thin film was found to be ~1.03 eV. Granular, uniform, and densely packed surface morphology was observed for as-deposited and selenized samples electrodeposited at −0.6 and −0.8 V versus Ag/AgCl for the pH of bath 1.2 and 2.5, respectively. EDAX result reveals the stoichiometric CIS films can be electrodeposited at −0.6 and −0.8 V with pH of the bath 1.2 and 2.5, respectively. The ideality factor (η) deducted from I–V measurements was found to be reduced from 1.6 to 1.3 and 1.9 to 1.2 after selenization of samples grown at −0.6 and −0.8 V, respectively, revealing the formation of ideal diode due to elimination of surface leakage current. Photoelectrochemical (PEC) measurement confirms the growth of p-type CIS thin film.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaure NB, Young J, Samantilleke AP, Dharmadasa IM (2004) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 81:125–133
Jackson P, Hariskos D, Lotter E, Paetel S, Wuerz R, Menner R, Wischmann W, Powalla M (2011) Prog Photovolt Res Appl 19:894–897
Lakhe M, Chaure NB (2014) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 123:122–129
Moharram A, Hafiz MM, Salem A (2001) Appl Surf Sci 172:1–2
Repins IM, Contreras B, Egaas D, Scharf J, Perkins C, To B, Noufi R (2008) Prog Photovolt Res Appl 16:235–239
Terasako T, Uno Y, Kariya T (2006) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90:262–275
Niki S, Yamada A, Hunger R (2002) J Cryst Growth 237–239:1993–1999
Tiwari AN, Krejci M, Haug FJ, Zogg H (1999) Prog Photovolt Res Appl 7:393–397
Ashida A, Hachiuma Y, Yamamoyo N, Cho Y (1994) J Math Sci Lett 13:1181–1184
Wang XL, Wang GJ, Tian BL, Du ZL (2010) Chin Sci Bull 55:1854–1858
Lee H, Lee W, Kim J, Ko M, Kim K, Seo K, Lee D, Kim H (2013) Electrochim Acta 87:450–456
Chaure NB, Samantilleke AP, Burton RP, Young J, Dharmadasa IM (2005) Thin Solid Films 472:212–216
Yang J, Liu L, Li J, Liu Y (2012) Electrochem Solid State Lett 15:D19–D21
Padros A, Briones F, Sanz F (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:1025–1029
Dhanwate VN, Chaure NB (2012) Appl Nanosci 3:1–5
Maldes M, Vazquez M, Goossens A (2008) Electrochim Acta 54:524–529
Schon JH, Alberts V, Bucher E (1999) Semicond Sci Technol 14:657–659
Mandati S, Sarada BV, Dey SR, Joshi SV (2013) J Electrochem Soc 160:D173–D177
Bouraiou A, Aida MS, Meglali O, Attaf N (2011) Curr Appl Phys 11:1173–1178
Calixto ME, Sebastian PJ, Bhattacharya RN, Noufi R (1999) Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 59:75–84
Bao-Ping S, Shan P, Bin-Bin H, Guang-Hong Y, Shao-Ming W, Zu-Liang D (2013) J Inorg Mater 28:141–145
Harris TM, Wilson JL, Bleakley M (1999) J Electrochem Soc 146:1461–1464
Pourbiax M (1966) Atlas of electrochemical equlibra. Pergamon Press, New York
Kemell M, Ritala M, Leskela M (2005) Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 30:1–31
Oda Y, Matsubayashi M, Minemoto T (2009) J Cryst Growth 311:738–741
Culliti BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of x-ray diffraction. NJ Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliff
Nawale S, Ravi V, Mulla IS (2009) Sensors Actuators B 139:466–170
Kulkurni SK (2007) Nanotechnology, principles and applications. Capital publishing Co., India
Gupta S, Patidar D, Saxena NS, Sharma K (2009) Chalcogenide Lett 6:723–731
Tung RT (1992) Phys Rev B 45:13509–13523
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the finacial support from Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), New Delhi under the major project grant ERIP/ER/10003866/M/01/1388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohom, A.B., Londhe, P.U. & Chaure, N.B. The effect of pH and selenization on the properties of CuInSe2 thin films prepared by electrodeposition technique for device applications. J Solid State Electrochem 19, 201–210 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2582-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2582-0