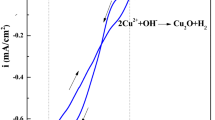
Abstract
Thin films of Cu2CoSnS4 (CCTS) are electrodeposited onto fluorine tin oxide substrate using pulsed electrodeposition mode for various time periods followed by sulfurization treatment at 500 °C. The pulse potential (V1) is held constant at 0 V vs. Ag/AgCl, while (V2) is set at − 1.1 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The effect of pulse duration on the CCTS proprietress is being investigated. Cyclic voltammetry was used to study the electrochemical behaviors of Cu–Co–Sn–S precursors, while in situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy investigated the electrical properties of the system during electrodeposition of CCTS at − 1.10 V. The impedance spectra revealed a capacitive loop pattern along with Warburg diffusion. The samples were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy, and UV–visible spectroscopy. Both XRD data and Raman spectra indicated that the CCTS thin films have a stannite structure. The films deposited for 20 min and 30 min exhibit a predominantly pure CCTS phase. Moreover, deposition for 20 min exhibits a homogeneous morphology with a nearly stoichiometric composition along with an optical band gap energy of 1.54 eV. Apart from the CCTS phase, noticeable secondary phases are present in films deposited at both low and high pulse durations, and they have been observed to slightly affect the gap energy.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murali B, Krupanidhi SB (2013) Facile synthesis of Cu2CoSnS4 nanoparticles exhibiting red-edge-effect: application in hybrid photonic devices. J Appl Phys 114:144312. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4825070
Green MA, Dunlop ED, Yoshita M, Kopidakis N, Bothe K, Siefer G, Hao X (2023) Solar cell efficiency tables (version 62). Prog Photovolt 31:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3726
Hammami H, Marzougui M, Oueslati H, Rabeh MB, Kanzari M (2021) Synthesis, growth and characterization of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films via thermal evaporation method. Optik 227:166054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.166054
Zaberca O, Gillorin A, Durand B, Chane-Ching JY (2011) A general route to the synthesis of surfactant-free, solvent-dispersible ternary and quaternary chalcogenide nanocrystals. J Mater Chem 21:6483. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10894h
Gillorin A, Balocchi A, Marie X, Dufour P, Chane-Ching JY (2011) Synthesis and optical properties of Cu2CoSnS4 colloidal quantum dots. J Mater Chem 21:5615. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm03964k
Cui Y, Deng R, Wang G, Pan D (2012) A general strategy for synthesis of quaternary semiconductor Cu2MSnS4 (M = Co2+, Fe2+, Ni2+, Mn2+) nanocrystals. J Mater Chem 22:23136. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm33574c
Azmi S, Layachi OA, Ouardi ME, Khoumri EM, Moujib A, Brouzi AE, Nohair M, Pezzato L, Dabala M (2022) Growth of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film absorber layer on transparent conductive oxides and molybdenum substrates by electrodeposition for photovoltaic application. Optik 250:168320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168320
Wang T, Zhan Q, Cheng W (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films prepared via radio-frequency (RF) magnetron sputtering. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:2285–2291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0499-6
Moriya K, Tanaka K, Uchiki H (2007) Fabrication of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin-film solar cell prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Jpn J Appl Phys 46:5780–5781. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.46.5780
Ansari MZ, Khare N (2017) Effect of intrinsic strain on the optical band gap of single phase nanostructured Cu2ZnSnS4. Mater Sci Semicond Process 63:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2017.02.011
Krishnaiah M, Bhargava P, Mallick S (2015) Low-temperature synthesis of Cu2CoSnS4 nanoparticles by thermal decomposition of metal precursors and the study of its structural, optical and electrical properties for photovoltaic applications. RSC Adv 5:96928–96933. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA18679J
Ansari MZ, Khare N (2014) Structural and optical properties of CZTS thin films deposited by ultrasonically assisted chemical vapour deposition. J Phys D Appl Phys 47:185101. https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/47/18/185101
Maldar PS, Gaikwad MA, Mane AA, Nikam SS, Desai SP, Giri SD, Sarkar A, Moholkar AV (2017) Fabrication of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films by a facile spray pyrolysis for photovoltaic application. Sol Energy 158:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.09.036
Maldar PS, Mane AA, Nikam SS, Giri SD, Sarkar A, Moholkar AV (2017) Temperature dependent properties of spray deposited Cu2CoSnS4 (CCTS) thin films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 28:18891–18896. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7842-1
López-Vergara F, Galdámez A, Manríquez V, González G (2015) Crystal structure and Raman scattering characterization of Cu2Fe1-xCoxSnS4 chalcogenide compounds. Solid State Sci 49:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2015.09.010
Zhang X, Bao N, Lin B, Gupta A (2013) Colloidal synthesis of wurtzite Cu2CoSnS4 nanocrystals and the photoresponse of spray-deposited thin films. Nanotechnology 24:105706. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/24/10/105706
Oubakalla M, Beraich M, Taibi M, Majdoubi H, Guenbour A, Bellaouchou A, Addou M, Bentiss F, Zarrouk A, Fahoume M (2022) Effects of co-electrodeposition potential on the physicochemical properties of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films enriched by a theoretical calculation. Int J Light Electron Opt. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168886
Beraich M, Taibi M, Guenbour A, Zarrouk A, Boudalia M, Bellaouchou A, Tabyaoui M, Sekkat Z, Fahoume M (2019) Synthesis and characterization of Cu2CoSnS4 thin film via electrodeposition technique for solar cells. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:12487–12492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01608-2
El Ouardi M, Ait Layachi O, Amaterz E, El Idrissi A, Taoufyq A, Bakiz B, Benlhachemi A, Arab M, BaQais A, Ahsaine HA (2023) Photo-electrochemical degradation of rhodamine B using electrodeposited Mn3(PO4)2.3H2O thin films. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 444:115011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2023.115011
Azmi S, Moujib A, Layachi OA, Matei E, Galca AC, Zaki MY, Secu M, Rusu MI, Grigorescu CEA, Khoumri EM (2020) Towards phase pure kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber layers growth via single step free sulfurization electrodeposition under a fix applied potential on Mo substrate. J Alloy Compd 842:155821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155821
Bryden KJ, Ying JY (1998) Pulsed electrodeposition synthesis and hydrogen absorption properties of nanostructured palladium-iron alloy films. J Electrochem Soc 145:3339–3346. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.1838809
Gurav KV, Yun JH, Pawar SM, Shin SW, Suryawanshi MP, Kim YK, Agawane GL, Patil PS, Kim JH (2013) Pulsed electrodeposited CZTS thin films: effect of duty cycle. Mater Lett 108:316–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2013.06.062
Termsaithong P, Munprom R, Shah A, Rodchanarowan A (2018) Pulsed current co-electrodeposition of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber material on fluorinated tin oxide (FTO) glass substrate. Surf Coat Technol 350:807–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.04.045
Gurav KV, Kim YK, Shin SW, Suryawanshi MP, Tarwal NL, Ghorpade UV, Pawar SM, Vanalakar SA, Kim IY, Yun JH, Patil PS, Kim JH (2015) Pulsed electrodeposition of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films: effect of pulse potentials. Appl Surf Sci 334:192–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.09.079
Jeon M, Shimizu T, Shingubara S (2011) Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films and nanowires prepared by different single-step electrodeposition method in quaternary electrolyte. Mater Lett 65:2364–2367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.05.003
Azmi S, Nohair M, Khoumri EM, El Marrakchi M, Dabala M (2018) Effect of the complexing agents on the properties of electrodeposited CZTS thin films. 7th international conference on renewable energy research and Applications, Paris, France. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRERA.2018.8566894
Boudouma A, Ait Layachi O, Hrir H, Khoumri E (2023) A one-step electrodeposition method was used to produce monoclinic Cu2SnS3 thin films for the development of solar cells. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 34:1903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11390-x
Layachi OA, Azmi S, Moujib A, El Khoumri MN (2023) Investigation of nucleation and growth mechanism of Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber layer electrodeposition on Indium Tin Oxide coated glass. Thin Solid Films 782:140019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2023.140019
Tsai H-W, Chen C-W, Thomas SR, Hsu C-H, Tsai W-C, Chen Y-Z, Wang Y-C, Wang ZM, Hong H-F, Chueh Y-L (2016) Facile growth of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin-film by one-step pulsed hybrid electrophoretic and electroplating deposition. Sci Rep 6:19102. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19102
Chang B-Y, Park S-M (2010) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Ann Rev Anal Chem 3:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.anchem.012809.102211
Herrera Hernández H, Ruiz Reynoso AM, Trinidad González JC, González Morán CO, Miranda Hernández JG, Mandujano Ruiz A, Morales Hernández J, Orozco Cruz R (2020) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): a review study of basic aspects of the corrosion mechanism applied to steels. In: El-Azazy M, Min M, Annus P (eds) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.94470
Yuan Y, Luo G, Li N (2021) New in situ description of electrodepositing multiple nucleation processes under galvanostatic stimuli. RSC Adv 11:31526–31532. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04988G
Ordine AP, Díaz SL, Margarit ICP, Barcia OE, Mattos OR (2006) Electrochemical study on Ni–P electrodeposition. Electrochim Acta 51:1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2005.02.129
Korjenic A, Raja KS (2019) Electrochemical stability of fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) coating at different pH conditions. J Electrochem Soc 166:C169–C184. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0811906jes
Hsu CH, Mansfeld F (2001) Technical Note: concerning the conversion of the constant phase element parameter Y0 into a capacitance. Corrosion 57:747–748. https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3280607
Hirschorn B, Orazem ME, Tribollet B, Vivier V, Frateur I, Musiani M (2010) Determination of effective capacitance and film thickness from constant-phase-element parameters. Electrochim Acta 55:6218–6227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2009.10.065
Valahia L, Olteanu RM, Ion IA, Bucurică IV, Gurgu ID, Dulamă ST (2020) ITO and FTO coated glass characterization using SEM and AFM techniques. Bull Transilv Univ Brasov Ser 12(61):41–46
Ahmadi M, Guinel MJ-F (2013) Synthesis, characterization and understanding of the mechanisms of electroplating of nanocrystalline–amorphous nickel–tungsten alloys using in situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J Alloy Compd 574:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.04.033
I. Fotsing Etude Par voltammétrie cyclique des conditions d’électrodéposition de phosphure de zinc pour des applications photovoltaïques, (n.d.) 145
Liu K, Wei A, Zhang W, Xiao Z, Zhao Y, Liu J (2019) Synthesis of vertically aligned CoS prismatic nanorods as counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:1541–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0425-y
Sheng X, Wang L, Chen G, Yang D (2011) Simple synthesis of flower-like ln 2 S 3 structures and their use as templates to prepare CuS particles. J Nanomater 2011:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/280216
Oubakalla M, Beraich M, Taibi M, Majdoubi H, Aichi Y, Guenbour A, Bellaouchou A, Bentiss F, Zarrouk A, Fahoume M (2022) The choice of the copper concentration favoring the production of stoichiometric CuSbS2 and Cu12Sb4S13 thin films co-electrodeposited on FTO. J Alloy Compd 908:164618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164618
Chaki SH, Tailor JP, Deshpande MP (2014) Covellite CuS—single crystal growth by chemical vapour transport (CVT) technique and characterization. Mater Sci Semicond Process 27:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2014.07.038
Harinipriya S, Cassian H, Sudha V (2021) Colloidal CCTS nanoparticle synthesis by solution method for solar photovoltaic applications. J Market Res 15:3558–3569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.134
Tang Y-Q, Ge Z-H, Feng J (2017) Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of copper sulfides via solution phase methods and spark plasma sintering. Crystals 7:141. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst7050141
Tlemçani TS, Benamar EB, Moursli FCE, Hajji F, Edfouf Z, Taibi M, Labrim H, Belhorma B, Aazou S, Schmerber G, Bouras K, Sekkat Z, Dinia A, Ulyashin A, Slaoui A, Abd-Lefdil M (2015) Deposition time effect on the physical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films obtained by electrodeposition route onto mo-coated glass substrates. Energy Procedia 84:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.12.305
Azmi S, Pezzato L, Sturaro M, Khoumri EM, Martucci A, Dabalà M (2019) A green and low-cost synthetic approach based on deep eutectic choline-urea solvent toward synthesis of CZTS thin films. Ionics 25:2755–2761. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2719-8
Beraich M, Taibi M, Guenbour A, Zarrouk A, Boudalia M, Bellaouchou A, Tabyaoui M, Mansouri S, Sekkat Z, Fahoume M (2019) Preparation and characterization of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films for solar cells via co-electrodeposition technique: effect of electrodeposition time. Optik 193:162996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.162996
Oubakalla M, Beraich M, Taibi M, Majdoubi H, Guenbour A, Bellaouchou A, Addou M, Bentiss F, Zarrouk A, Fahoume M (2022) Effects of copper concentration on the properties of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films co-electrodeposited on the FTO substrate. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:12016–12025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-08162-4
Ait Layachi O, Moujib A, El Khouja O, CatalinGalca A, Boudouma A, Azmi S, Nini M, Nohair M, Khoumri E (2024) Electrodeposition mechanism of Cu2CoSnS4 thin films onto FTO-coated glass: effect of some additives. J Electroanal Chem 959:118177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2024.118177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Omar Ait Layachi: wrote the main manuscript text and prepared figures All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ait Layachi, O., Boudouma, A., Lasri, M. et al. Pulsed potential co-electrodeposition of Cu2CoSnS4 absorber layer on fluorinated tin oxide (FTO)-coated glass. J Appl Electrochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-024-02131-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-024-02131-x