Abstract
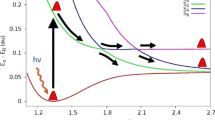
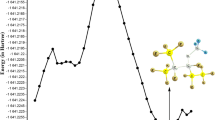
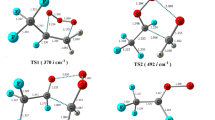
The photo dissociation of nitrosyl fluorite, FONO, a potential source of atmospheric fluorine, underlies its active role in ozone depletion and other activities in the troposphere. In the present work, the electronic structure of FONO is revisited at high level of ab initio and density functional theory (DFT) theoretical levels. Several different post SCF methods were used to compute excited states, vertical excitation energies and intensities, namely configuration interaction with single excitations (CIS), equation of motion coupled cluster with single and double excitations (EOM-CCSD), and symmetry adopted cluster configuration interaction (SAC-CI) methods. The potential energy functions along two internal coordinates, namely the F-ONO bond and the FONO dihedral angle, have been computed on the ground state relaxed potential energy surface (PES) for the ground, 5A′ and 5A″ excited states using the EOM-CCSD method. In the gas phase, the decay of the excited states of FONO was examined closely by calculating the UV photoabsorption cross-section spectrum and by nonadiabatic dynamics simulations. Nonadiabatic dynamics were simulated by sampling 300 trajectories in two spectral windows at 3.0 ± 0.25 and 4.5 ± 0.25 eV using the surface hopping method. Two different photodissociation reaction pathways with two main products, including multifragmentation (FO+NO) and atomic elimination (F) mechanisms were identified. For the cis-isomer, the main photochemical channel is F+NO2, representing 67% of all processes. For the trans-isomer, however, the main dissociation pathway is (FO+NO).

Photodisscociation of nitrosyl fluorite (FONO) seems to underlie its active role in ozone depletion and other activities in the troposphere. The present research revisits the electronic structure of FONO at high level of ab initio and DFT theoretical levels. Cis-trans isomerization and dissociation in the ground and low lying excited states were examined. Photoabsorption cross-section spectra were computed and nonadiabatic dynamics were launched for both cis and trans FONO isomers.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smardzewski RR, Fox WB (1974) Infrared spectroscopic evidence for matrix isolated “nitrosyl hypofluorite”, an isomer of nitryl luoride. J Chem Phys 60:2980
Sorenson SA, Noble PN (1982) Vibrational potential function and structure of nitrosyl hypofluorite by normal coordinate analysis. J Chem Phys 77:2483
Ganguli PS, McGee HA Jr (1972) Synthesis and stability of nitrogen-oxygen-fluorine compounds from a MINDO [modified intermediate neglect of differential overlap] molecular orbital perspective. Inorg Chem 11:3071
Linett JW (1961) A modification of the Lewis-Langmuir Octet rule. J Am Chem Soc 83:2645
Noble PN (1991) Structures and vibrational frequencies of FOOF and FONO using density functional theory. J Phys Chem 95:4695
Dixon DA, Christe KO (1992) Nitrosyl hypofluorite: local density functional study of a problem case for theoretical methods. J Phys Chem 96:1018
Peña-Gallego P, Martinez-Núñez E, Vázquez SA (1998) Classical trajectory study of the Cis-Trans isomerization and F-O dissociation of FONO. J Phys Chem A 102:8708
Bauerfeldt GF, Arbilla G, da Silva EC (2001) Theoretical study and rate constants for the unimolecular isomerization of YONO (Y= F, Cl and Br). J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 539:223
Ellison GB, Herbert JM, McCoy AB, Stanton JF, Szalay PG (2004) Unimolecular rearrangement of trans-FONO to FNO2. A possible model system for atmospheric nitrate formation. J Phys Chem A 108:7639
Oberhammer H (2002) The N-O bond in covalent nitrates and nitrites. J Mol Struct 605:177
Papayannis DK, Kosmas AM (2006) Ab initio investigation of isomeric and conformeric structures of halogen nitrites, XONO (X = Cl, Br, I). Mol Phys 104:2561
Lee TJ, Rice JE (1992) FONO: a difficult case for theory and experiment. J Chem Phys 97:4223
Lee TJ, Bauschlicher CW Jr, Dateo CE, Rice JE (1994) The molecular structure of cis-FONO. Chem Phys Lett 228:583
Lee TJ, Rice JE, Dateo CE (1996) The varying nature of fluorine oxygen bonds. Mol Phys 89:1359
Lee TJ, Bauschlicher CW Jr, Jayatilaka D (1997) Theor Chem Accounts 97:185
Raghavachari K, Trucks GW, Pople JA, Head-Gordon M (1989) A fifth-order perturbation comparison of electron correlation theories. Chem Phys Lett 157:479
Berski S, Latajka Z, Gordon AJ (2010) Quantum chemical topology study on the electronic structure of cis- and trans-FONO. J Chem Phys 133:034304
Aziz SG, Alyoubi AO, Elroby SA, Hilal RH (2016) Photochemical dissociation of HOBr. A nonadiabatic dynamics study. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 324:8–13
Weigend F, Ahlrichs R (2005) Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: design and assessment of accuracy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 7:3297–3305
Weigend F (2006) Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys Chem Chem Phys 8:1057–1065
Barbatti M, Ruckenbauer M, Plasser F, Pittner J, Granucci G, Persico M, Lischka H (2014) Newton-X: a surface-hopping program for nonadiabatic molecular dynamics. WIREs: Comp Mol Sci 4:26–33
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA et al (2013) Gaussian 09, revision D.01. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford
Foresman JB, Head-Gordon M, Pople JA, Frisch MJ (1992) Toward a systematic molecular orbital theory for excited states. J Phys Chem 96:135–149
Kállay M, Gauss J (2004) Calculation of excited-state properties using general coupled-cluster and configuration-interaction models. J Chem Phys 121:9257
Barbatti M, Granucci G, Ruckenbauer M, Plasser F, Crespo-Otero R, Pittner J, Persico M, Lischka H (2013) NEWTON-X: a package for Newtonian dynamics close to the crossing seam. Available via the Internet at www.newtonx.org
Crespo-Otero R, Barbatti M (2012) Spectrum simulation and decomposition with nuclear ensemble: formal derivation and application to Benzene, Furan and 2-Phenylfuran. Theor Chem Accounts 131:1237
Tully JC (1990) Molecular-dynamics with electronic-transitions. J Chem Phys 93:1061–1071
Barbatti M (2011) Nonadiabatic dynamics with trajectory surface hopping method. WIREs: Comp Mol Sci 1:620–633
Granucci G, Persico M (2007) Critical appraisal of the fewest switches algorithm for surface hopping. J Chem Phys 126:134114–134114-11
Hammes-Schiffer S, Tully JC (1994) Proton-transfer in solution—molecular-dynamics with quantum transitions. J Chem Phys 101:4657–4667
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2006) Comparative DFT study of van der Waals complexes: rare-gas dimers, alkaline-earth dimers, zinc dimer, and zinc-rare-gas dimers. J Phys Chem 110:5121–5129
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG (2008) The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor Chem Accounts 120(1):215–241
Hallou A, Schriver-Mazzuoli L, Schriver A, Chaquin P (1998) Matrix photochemistry of nitrosyl chloride: interconversion of ClNO and ClON species by irradiation and tunneling effect. Chem Phys 237(3):251–264
Coangaa JM, Schriver-Mazzuolia L, Schrivera A, Dahoo PR (2002) Matrix infrared spectroscopic studies of the photo-dissociation, at 266 nm of ClNO2 and of ClONO. Chem Phys 276:309–320
Pena-Gallego A, Martinez-Nunez E, Vazquez SA (1998) Classical trajectory study of the cis-trans isomerization and F-O dissociation of FONO. J Phys Chem A 102(45):8708–8715
Chai J-D, Head-Gordon M (2008) Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom-atom dispersion corrections. Phys Chem Chem Phys 10:6615–6620
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilal, A.R., Hilal, R. Photodissociation of FONO: an excited state nonadiabatic dynamics study. J Mol Model 23, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3238-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3238-7