Abstract
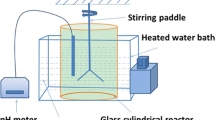
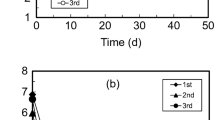
The microbial leaching process was evaluated for the treatment of synthetic sediments contaminated with cadmium and nickel sulfides. A series of batch leaching experiments was conducted to compare metal solubilization in sediment inoculated with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans -inoculated sediments to that in sterile control sediment. The rate and extent of metal solubilization were significantly higher in A. ferrooxidans -inoculated reactors than in acidified sterile reactors. The efficiency of cadmium (Cd) solubilization (80) in the bioleaching process was higher than that of nickel (Ni) solubilization (60). The performance of leaching reactors containing only culture supernatants was comparable to that of A. ferrooxidans -inoculated reactors, indicating that indirect non-contact leaching by the products of microbial metabolism is the predominant mechanism for metal solubilization rather than direct microbial sulfide oxidation. Moreover, the similar (60–75%) extents of Cd2+ leaching with A. ferrooxidans , cell-free filtrate, and Fe3+ suggest that abiotic oxidation of CdS by Fe3+ controls the overall leaching rate, and the role of A.␣ferrooxidans is most likely not to oxidize CdS mineral directly but to regenerate Fe3+ as an oxidant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
JF Blais RD Tyagi JC. Auclair (1992a) ArticleTitleBioleaching of trace metals from sewage sludge by sulfur-oxidizing bacteria J␣Environ Eng 118 690–707
JF Blais RD Tyagi JC Auclair CP. Huang (1992b) ArticleTitleComparison of acid and microbial leaching for metal removal from municipal sludge Water Sci Technol 26 197–206
M Boon JJ. Heijnen (1998) ArticleTitleChemical oxidation kinetics of pyrite in bioleaching processes Hydrometallurgy 48 27–41 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-386X(97)00072-8
M Boon M Snijder GS Hansford JJ. Heijnen (1998) ArticleTitleThe oxidation kinetics of zinc sulphide leaching by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 48 171–186 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-386X(97)00081-9
SY Chen JG. Lin (2001) ArticleTitleBioleaching of heavy metals from sediment: significance of pH Chemosphere 44 1093–1102 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00334-9 Occurrence Handle11513396
DM Di Toro JD Mahony DJ Hansen KJ Scott MB Hicks SM Maya MS. Redmond (1990) ArticleTitleToxicity of cadmium in sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide Environ Toxicol Chem 9 1487–1502
TA Fowler FK. Crundwell (1998) ArticleTitleLeaching of zinc sulfide by Thibacillus ferrooxidans : experiments with a controlled redox potential indicate no direct bacterial mechanism Appl Environ Microbiol 64 3570–3575 Occurrence Handle9758769
SR Hutchins MS Davison JA Brierley CL. Brierley (1986) ArticleTitleMicroorganisms in reclamation of metals Ann Rev Microbiol 40 311–336 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001523
DP Kelly AP. Wood (2000) ArticleTitleReclassification of some speices of Thibacillus to the newly designated genera Acidithiobacillus gen. nov., Halothiobacillus gen.nov. and Thermithiobacillus gen. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50 511–516 Occurrence Handle10758854
K Kinzler T Gehrke J Telegdi W. Sand (2003) ArticleTitleBioleaching – a result of interfacial processes caused by extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) Hydrometallurgy 71 83–88 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-386X(03)00176-2
Y Konishi H Kubo S. Asai (1992) ArticleTitleBioleaching of zinc sulfide concentrate by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Bioeng 39 66–74 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260390111
HM Lizama I. Suzuki (1989) ArticleTitleRate equations and kinetic parameters of the reactions involved in pyrite oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 55 2918–2913
G Mercier M Chartier D. Couillard (1996) ArticleTitleStrategies to maximize the microbial leaching of lead from metal-contaminated aquatic sediments Water Res 30 2452–2464 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(96)00118-2
BR Ravishankar JF Blais H Benmoussa RD. Tyagi (1994) ArticleTitleBioleaching of metals from sewage sludge: Elemental sulfur recovery J Environ Eng 120 462–470
W Sand T Gehrke PG Jozsa A. Schippers (2001) ArticleTitle(Bio)chemistry of bacterial leaching -direct vs. indirect bioleaching Hydrometallurgy 59 159–175 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00180-8
H Seidel J Ondruschka P Morgenstern U. Stottmeister (1998) ArticleTitleBioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated aquatic sediments using indigenous sulfur-oxidizing bacteria: a feasibility study Water Sci Technol 37 387–394 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00222-4
J Shrihari M Modak R Kumar KS. Gandhi (1995) ArticleTitleDissolution of particles of pyrite mineral by direct attachment of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 38 175–187 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-386X(94)00053-6
Smith EE, Shumate KS. 1970 The sulphide to sulphate reaction mechanism: a study of the sulphide to sulphate reaction mechanism as it relates to the formation of acid mine waters. Water Pollut Control Res Series , Ohio State University Research Foundation.
W Stumm JJ. Morgan (1996) Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters John Wiley and Sons New York
AE Torma IJ. Itzkovitch (1976) ArticleTitleInfluence of organic solvents on chalcopyrite oxidation ability of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol 32 102–107
AE Torma CC Walden RMR. Branion (1970) ArticleTitleMicrobiological leaching of a zinc sulfide concentrate Biotechnol Bioeng 12 501–517 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260120403 Occurrence Handle5482892
H. Tributsch (2001) ArticleTitleDirect versus indirect bioleaching Hydrometallurgy 59 177–185 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-386X(00)00181-X
LJ Tsai KC Yu SF Chen PY. Kung (2003) ArticleTitleEffect of temperature on removal of heavy metals from contaminated river sediments via bioleaching Water Res 37 2449–2457 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00634-6 Occurrence Handle12727257
OH Tuovinen SI Niemela HG. Gyllenberg (1971) ArticleTitleEffect of mineral nutrients and organic substances on the development of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Bioeng 13 517–527 Occurrence Handle10.1002/bit.260130406
RD Tyagi D. Couillard (1989) ArticleTitleBacterial leaching of metals from sludge Encyclopedia of Environ Control Technol 3 557–560
RD Tyagi D Couillard F. Tran (1988) ArticleTitleHeavy metals removal from anaerobically digested sludge by chemical and microbiological methods Environ Pollut 50 295–316 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0269-7491(88)90194-7 Occurrence Handle15092644
L Wong JG. Henry (1983) ArticleTitleBacterial leaching of heavy metals from anaerobically digested sewage sludge Water Pollut Res J Canada 18 151–162
L Wong JG. Henry (1984) ArticleTitleDecontaminating biological sludge for agricultural use Water Sci Technol 17 575–586
Y Zhuang HE Allen G. Fu (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of aeration of sediment on cadmium binding Environ Toxicol Chem 13 717–724
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.D., Bae, J.E., Park, H.S. et al. Bioleaching of cadmium and nickel from synthetic sediments by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Environ Geochem Health 27, 229–235 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-3479-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-004-3479-0