Abstract
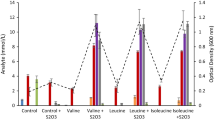
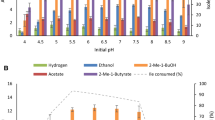
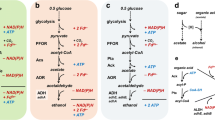
Fifty-six thermophilic strains including members of Caldanaerobacter, Caldicellulosiruptor, Caloramator, Clostridium, Thermoanaerobacter, and Thermoanaerobacterium, were investigated for branched-chain amino acid degradation in the presence of thiosulfate in batch culture. All of the Thermoanaerobacter and Caldanaerobacter strains (24) degraded the branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) to a mixture of their corresponding branched-chain fatty acids and branched-chain alcohols. Only one Caloramator strain degraded the branched-chain amino acids to the corresponding branched-chain fatty acids. The ratio of branched-chain fatty acid production over branched-chain alcohol production for Thermoanaerobacter was 7.15, 6.61, and 11.53 for leucine, isoleucine, and valine, respectively. These values for Caldanaerobacter were 3.49, 4.13, and 7.31, respectively. This indicates that members within Caldanaerobacter produce proportionally more of the alcohols as compared with Thermoanaerobacter. No species within other genera investigated produced branched-chain alcohols from branched-chain amino acids in the presence of thiosulfate.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S, Madden T, Schaffer A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Andreesen JR, Bahl H, Gottschalk G (1989) Introduction to the physiology and biochemistry of the genus Clostridium. In: Minton NP, Clarke DJ (eds) Clostridia. Plenum Press, New York, pp 27–62
Barker HA (1981) Amino acid degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 50:23–40
Beck HC, Hansen AM, Lauritsen FR (2004) Catabolism of leucine to branched-chain fatty acids in Staphylococcus xylosus. J Appl Microbiol 96:1185–1193
Cann IKO, Stroot PG, Mackie KR, White BA, Mackie RI (2001) Characterization of two novel saccharolytic, anaerobic thermophiles, Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum sp. nov. and Thermoanaerobacterium zeae sp. nov., and emendation of the genus Thermoanaerobacterium. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol 51:293–302
Chang T, Yao S (2011) Thermophilic, lingocellulolytic bacteria for ethanol production: current state and perspectives. Appl Micorbiol Biotechnol 92:13–27
Choi KY, Wernick DG, Tat CA, Liao JC (2014) Consolidated conversion of protein waste into biofuels and ammonia using Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 23:53–61
Cord-Ruwisch R (1985) A quick method for determination of dissolved and precipitated sulphides in cultures of sulphate-reducing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 4:33–36
Ehrlich F (1907) Uber die Bedingungen der Fuselöbildung und uber ihren Zusammenhang mit dem Eiweissaufbau der Hefe. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges 40:1027–1047
Elsden SR, Hilton MG (1978) Volatile acid production from threonine, valine, leucine and isoleucine by clostridia. Arch Microbiol 117:165–172
Euzéby JP (1997) List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder available on the internet. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 47:590–592
Fardeau M-L, Patel BKC, Magot M, Ollivier B (1997) Utilization of serine, leucine, isoleucine, and valine by Thermoanaerobacter brockii in the presence of thiosulfate or Methanobacterium sp. as electron acceptors. Anaerobe 3:405–410
Fardeau M-L, Salinas MB, L’Haridon S, Jeanthon C, Verhé F, Cayol J-L, Patel BKC, Garcia J-L, Ollivier B (2004) Isolation from oil resevoirs of novel thermophilic anaerobes phylogenetically related to Thermoanaerobacter subterraneus: reassignment of T. subterraneus, Thermoanaerobacter yonseiensis, Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis and Carboxydibrachium pacificum to Caldanaerobacter subterraneous gen. nov., sp. nov., com. nov. as four novel subspecies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:467–474
Faudon C, Fardeau ML, Heim J, Patel B, Magot M, Ollivier B (1995) Peptide and amino acid oxidation in the presence of thiosulfate by members of the genus Thermoanaerobacter. Curr Microbiol 31:152–157
Gutsche KA, Tran TBT, Vogel RF (2012) Production of volatile compounds by Lactobacillus sakei from branched chain alpha-keto acids. Food Microbiol 29:224–228
Hazelwood LA, Daran J-M, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT, Dickinson JR (2008) The Ehrlich pathway for fusel alcohol production: a century of research on Saccharomyces cerevisae. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2259–2266
Hungate RE (1969) A roll tube method for cultivation of strict anaerobes. In: Norris JR, Ribbons DW (eds) Methods in microbiology, vol 3B. Academic Press, New York, pp 117–132
Huo YX, Cho KM, Rivera JGL, Monte E, Shen CR, Yan YJ, Liao JC (2011) Conversion of proteins into biofuels by engineering nitrogen flux. Nat Biotechnol 29:346–351
Kozianowski G, Canganella F, Rainey FA, Hippe H, Antranikian G (1997) Purification and characterization of thermostable pectate-lyases from a newly isolated thermophilic bacterium, Thermoanaerobacter italicus sp. nov. Extremophiles 1:171–182
Lee YE, Jain MK, Lee CY, Lowe SE, Zeikus JG (1993) Taxonomic distinction of saccharolytic thermophilic anaerobes—description of Thermoanaerobacterium xylanolyticum gen-nov, sp-nov, and Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum gen-nov, sp-nov - reclassification of Thermoanaerobium brockii, Clostridium thermosulfurogenes, and Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum E100-69 as Thermoanaerobacter brockii comb-nov, Thermoanaerobacterium thermosulfurigenes comb-nov, and Thermoanaerobacter thermohydrosulfuricus comb-nov, respectively—and transfer of Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum 39E to Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:41–51
Lee Y-J, Dashti M, Prange A, Rainey FA, Rohde M, Whitman WB, Wiegel J (2007) Thermoanaerobacter sulfurigignens sp. nov., an anaerobic thermophilic bacterium that reduces 1 M thiosulfate to elemental sulfur and tolerates 90 mM sulfite. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1429–1434
McInerney MJ (1988) Anaerobic hydrolysis and fermentation of fats and proteins. In: Zehnder AJB (ed) Biology of anarobic microorganisms. Wiley, New York, pp 373–415
Orlygsson J, Baldursson SRB (2007) Phylogenetic and physiological studies of four hydrogen-producing thermoanaerobes from Icelandic geothermal areas. Icelandic Agric Sci 20:93–106
Orlygsson J, Houwen FP, Svensson BH (1994) Influence of hydrogenotrophic methane formation on the thermophilic anaerobic degradation of proteins and amino acids. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 13:327–334
Orlygsson J, Houwen FP, Svensson BH (1995) Thermophilic anaerobic amino acid degradation–deamination rates and end product formation. Appl Microbiol Biot 43:235–241
Orlygsson J, Sigurbjornsdottir MA, Bakken HE (2010) Bioprospecting thermophilic ethanol and hydrogen producing bacteria from hot springs in Iceland. Icelandic Agricult Sci 23:73–85
Parte AC (2014) LPSN—list of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. Nucl Acid Res 42:D613–D616
Peralta-Yahya PP, Keasling JD (2010) Advanced biofuel production in microbes. Biotechnol J 5:147–162
Ren N, Wang A, Cao G, Xu J, Gao L (2009) Bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to hydrogen: potential and challenges. Biotechnol Adv 27:1051–1060
Sakuragi H, Kuroda K, Ueda M (2011) Molecular breeding of advanced microorganism for biofuel production. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2011/416931
Scully SM, Orlygsson J (2014) Branched-chain alcohol formation from branched-chain amino acids by Thermoanaerobacter brockii and Thermoanaerobacter yonseiensis. Anaerobe 30:82–84
Scully SM, Orlygsson J (2015) Recent advances in second generation ethanol production by thermophilic bacteria. Energies 8:1–30
Skirnisdottir S, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjorleifsdottir S, Marteinsson VT, Petursdottir SK, Holst O, Kristjansson JK (2000) Influence of sulfide and temperature on species composition and community structure of hot spring microbial mats. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2835–2841
Smit G, Smit A, Engels WJM (2005) Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavor profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:591–610
Smit BA, Engels WJM, Smit G (2009) Branched chain aldehydes: production and breakdown pathways and relevance for flavor in foods. Appl Microbil Biot 81:987–999
Stams AJM, Hansen JA (1984) Fermentation of glutamate and other compounds by Acidaminobacter hydrogenoformans gen. nov. sp. nov., an obligate anaerobe isolated from black mud. Studies with pure cultures and mixed cultures with sulfate-reducing and methanogenic bacteria. Arch Microbiol 137:329–337
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Bio Evol 10:512–526
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetic analysis. Version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Taylor MP, Eley KL, Martin S, Tuffin M, Burton SG, Cowan DA (2009) Thermophilic ethanologenesis: future prospects for second-generation bioethanol production. Trends Biotechnol 27:398–405
Ward DE, Ross P, van der Weijden CC, Snoep JL, Claiborne A (1999) Catabolism of branched-chain alpha-keto acids in Entercoccus faecalis: the bkd gene cluster, enzymes, and metabolic route. J Bacteriol 181:5433–5442
Westley J (1987) Thiocyanate and thiosulfate. Methods in Enzym 143:22–25
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Margret Auður Sigurbjörnsdóttir for her assistance constructing the phylogenetic tree and Eva María Ingvadóttir for her helpful feedback during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Atomi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scully, S.M., Iloranta, P., Myllymaki, P. et al. Branched-chain alcohol formation by thermophilic bacteria within the genera of Thermoanaerobacter and Caldanaerobacter . Extremophiles 19, 809–818 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0756-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0756-z