Abstract
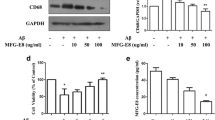
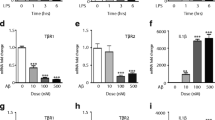
Deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptides has been shown to induce the release of inflammatory factors by activated microglia and brain infiltrating monocytes/macrophages. Interestingly, the enzyme transglutaminase 2 (TG2) has been shown to play a key role in neuroinflammation and regulation of transcription factors involved in immunomodulation. In this study, we aimed to better elucidate the mechanisms underlying TG2 involvement in the pro-inflammatory signaling pathway activated by fibrillar Aβ1–42 in THP-1 monocytes. Cell exposure for 24 h to 500 nM Aβ1–42, induced the up-regulation of CD14, CD16, and TG2, suggesting THP-1 cell functional activation. Aβ1–42 also increased the production of reactive oxygen species, that was reduced by the pre-incubation with genistein (25 µg/ml), a soy isoflavone with antioxidant properties. Moreover, IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA transcript and protein levels were eightfold increased in Aβ1–42-treated THP-1 monocytes. Interestingly, these effects were significantly reduced by R283 (~45%), a specific inhibitor of TG activity, and genistein (~40%). Aβ1–42 induced the activation of p54/p46 JNK, as well as ERK 1/2 at a lower extent. The inactivation of ERK1/2 signalling pathway, but not JNK, by either genistein or U0126, a MEK1/2 inhibitor, was not able to blunt Aβ1–42-induced TG2 up-regulation, that, instead, was significantly reduced by R283. Aβ1–42 also induced AP-1 activation that was not significantly affected by genistein or U0126, while was strongly reduced by R283. Our preliminary findings first suggest that TG2 up-regulation is involved in the pro-inflammatory activation of THP-1 monocytes induced by Aβ1–42 via AP1/JNK signalling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhter R, Sanphui P, Das H, Saha P, Biswas SC (2015) The regulation of p53 up-regulated modulator of apoptosis by JNK/c-Jun pathway in β-amyloid-induced neuron death. J Neurochem 134(6):1091–1103
Bergamini CM, Collighan RJ, Wang Z, Griffin M (2011) Structure and regulation of type 2 transglutaminase in relation to its physiological functions and pathological roles. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 78:1–46
Bianchi R, Giambanco I, Donato R (2010) S100B/RAGE-dependent activation of microglia via NF-kappaB and AP-1 co-regulation of COX-2 expression by S100B, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. Neurobiol Aging 31(4):665–677
Brown KD (2013) Transglutaminase 2 and NF-κB: an odd couple that shapes breast cancer phenotype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137(2):329–336
Caccamo D, Campisi A, Currò M, Aguennouz M, Li Volti G, Avola R, Ientile R (2005) Nuclear factor-kappab activation is associated with glutamate-evoked tissue transglutaminase up-regulation in primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci Res 82(6):858–865
Caccamo D, Condello S, Ferlazzo N, Currò M, Griffin M, Ientile R (2013) Transglutaminase 2 interaction with small heat shock proteins mediate cell survival upon excitotoxic stress. Amino Acids 44(1):151–159
Cameron B, Landreth GE (2010) Inflammation, microglia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 37(3):503–509
Cazareth J, Guyon A, Heurteaux C, Chabry J, Petit-Paitel A (2014) Molecular and cellular neuroinflammatory status of mouse brain after systemic lipopolysaccharide challenge: importance of CCR2/CCL2 signaling. J Neuroinflamm 11(1):132
Currò M, Ferlazzo N, Condello S, Caccamo D, Ientile R (2010) Transglutaminase 2 silencing reduced the beta-amyloid-effects on the activation of human THP-1 cells. Amino Acids 39(5):1427–1433
Currò M, Risitano R, Ferlazzo N, Cirmi S, Gangemi C, Caccamo D, Ientile R, Navarra M (2016) Citrus bergamia juice extract attenuates β-amyloid-induced pro-inflammatory activation of THP-1 cells through MAPK and AP-1 pathways. Sci Rep 6:20809
Eckert RL, Kaartinen MT, Nurminskaya M, Belkin AM, Colak G, Johnson GV, Mehta K (2014) Transglutaminase regulation of cell function. Physiol Rev 94(2):383–417
Elli L, Ciulla MM, Busca G, Roncoroni L, Maioli C, Ferrero S, Bardella MT, Bonura A, Paliotti R, Terrani C, Braidotti P (2011) Beneficial effects of treatment with transglutaminase inhibitor cystamine on the severity of inflammation in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Lab Investig 91(3):452–461
Ganai AA, Farooqi H (2015) Bioactivity of genistein: a review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Biomed Pharmacother 76:30–38
Giri RK, Selvaraj SK, Kalra VK (2003) Amyloid peptide-induced cytokine and chemokine expression in THP-1 monocytes is blocked by small inhibitory RNA duplexes for early growth response-1 messenger RNA. J Immunol 170(10):5281–5294
Hong H, Jang BC (2014) Prednisone inhibits the IL-1β-induced expression of COX-2 in HEI-OC1 murine auditory cells through the inhibition of ERK-1/2, JNK-1 and AP-1 activity. Int J Mol Med 34(6):1640–1646
Ientile R, Currò M, Caccamo D (2015) Transglutaminase 2 and neuroinflammation. Amino Acids 47(1):19–26
Jeitner TM, Battaile K, Cooper AJ (2013) γ-Glutamylamines and neurodegenerative diseases. Amino Acids 44(1):129–142
Ji Q, Xu X, Zhang Q, Kang L, Xu Y, Zhang K, Li L, Liang Y, Hong T, Ye Q, Wang Y (2016) The IL-1β/AP-1/miR-30a/ADAMTS-5 axis regulates cartilage matrix degradation in human osteoarthritis. J Mol Med (Berl) 94(7):771–785
Kim SH, Kim SH, Kim YB, Jeon YT, Lee SC, Song YS (2009) Genistein inhibits cell growth by modulating various mitogen-activated protein kinases and AKT in cervical cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:495–500
Kim DY, Park BS, Hong GU, Lee BJ, Park JW, Kim SY, Ro JY (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of the R2 peptide, an inhibitor of transglutaminase 2, in a mouse model of allergic asthma, induced by ovalbumin. Br J Pharmacol 162(1):210–225
Kramer PR, Winger V, Kramer SF (2007) 17beta-Estradiol utilizes the estrogen receptor to regulate CD16 expression in monocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 279(1–2):16–25
Lee YW, Lee WH (2008) Protective effects of genistein on proinflammatory pathways in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Nutr Biochem 19(12):819–825
Lee J, Kim YS, Choi DH, Bang MS, Han TR, Joh TH, Kim SY (2004) Transglutaminase 2 induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a novel pathway in BV-2 microglia. J Biol Chem 279(51):53725–53735
Lee YJ, Han SB, Nam SY, Oh KW, Hong JT (2010) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 33:1539–1556
Li Z, Xu X, Bai L, Chen W, Lin Y (2011) Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated tissue transglutaminase overexpression couples acquired tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand resistance and migration through c-FLIP and MMP-9 proteins in lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem 286(24):21164.e1556–21172.e1556
Liu Y, Walter S, Stagi M, Cherny D, Letiembre M, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Heine H, Penke B, Neumann H, Fassbender K (2005) LPS receptor (CD14): a receptor for phagocytosis of Alzheimer’s amyloid peptide. Brain 128:1778–1789
Lu S, Saydak M, Gentile V, Stein JP, Davies PJA (1995) Isolation and characterization of the human tissue transglutaminase gene promoter. J Biol Chem 270(17):9748–9756
Luft T, Jefford M, Luetjens P, Hochrein H, Masterman KA, Maliszewski C, Shortman K, Cebon J, Maraskovsky E (2002) IL-1 beta enhances CD40 ligand-mediated cytokine secretion by human dendritic cells (DC): a mechanism for T cell-independent DC activation. J Immunol 168(2):713–722
Mehta K, Lopez-Berestein G (1986) Expression of tissue transglutaminase in cultured monocytic leukemia (THP-1) cells during differentiation. Cancer Res 46(3):1388–1394
Monsonego A, Shani Y, Friedmann I, Paas Y, Eizenberg O, Schwartz M (1997) Expression of GTP-dependent and GTP-independent tissue-type transglutaminase in cytokine-treated rat brain astrocytes. J Biol Chem 272(6):3724–3732
Park MK, Lee HJ, Shin J, Noh M, Kim SY, Lee CH (2011) Novel participation of transglutaminase-2 through c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced keratin reorganization of PANC-1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1811(12):1021–1029
Park MK, You HJ, Lee HJ, Kang JH, Oh SH, Kim SY, Lee CH (2013) Transglutaminase-2 induces N-cadherin expression in TGF-β1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via c-Jun-N-terminal kinase activation by protein phosphatase 2A down-regulation. Eur J Cancer 49(7):1692–1705
Rivest S (2009) Regulation of innate immune responses in the brain. Nat Rev Immunol 9(6):429–439
Robitaille K, Daviau A, Lachance G, Couture JP, Blouin R (2008) Calphostin C-induced apoptosis is mediated by a tissue transglutaminase-dependent mechanism involving the DLK/JNK signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ 15(9):1522–1531
Sai X, Kawamura Y, Kokame K, Yamaguchi H, Shiraishi H, Suzuki R, Suzuki T, Kawaichi M, Miyata T, Kitamura T, De Strooper B, Yanagisawa K, Komano H (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-inducible protein, Herp, enhances presenilin-mediated generation of amyloid beta-protein. J Biol Chem 277(15):12915–12920
Szczepanik AM, Rampe D, Ringheim GE (2001) Amyloid-beta peptide fragments p3 and p4 induce pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production in vitro and in vivo. J Neurochem 77(1):304–317
Tseng HC, Lee IT, Lin CC, Chi PL, Cheng SE, Shih RH, Hsiao LD, Yang CM (2013) IL-1β promotes corneal epithelial cell migration by increasing MMP-9 expression through NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent pathways. PLoS One 8(3):e57955
Vukic V, Callaghan D, Walker D, Lue LF, Liu QY, Couraud PO, Romero IA, Weksler B, Stanimirovic DB, Zhang W (2009) Expression of inflammatory genes induced by beta-amyloid peptides in human brain endothelial cells and in Alzheimer’s brain is mediated by the JNK-AP1 signaling pathway. Neurobiol Dis 34:95–106
Wang Z, Griffin M (2012) TG2, a novel extracellular protein with multiple functions. Amino Acids 42(2–3):939–949
Yamada A, Akimoto H, Kagawa S, Guillemin GJ, Takikawa O (2009) Proinflammatory cytokine interferon-gamma increases induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in monocytic cells primed with amyloid beta peptide 1–42: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 110:791–800
Yang CM, Hsieh HL, Yu PH, Lin CC, Liu SW (2015) IL-1β induces MMP-9-dependent brain astrocytic migration via transactivation of PDGF receptor/NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species signals. Mol Neurobiol 52(1):303–317
Yates SL, Burgess LH, Kocsis-Angle J, Antal JM, Dority MD, Embury PB, Piotrkowski AM, Brunden KR (2000) Amyloid beta and amylin fibrils induce increases in proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine production by THP-1 cells and murine microglia. J Neurochem 74(3):1017–1025
Zhang F, Jiang L (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:243–256
Zhang K, Tian L, Liu L, Feng Y, Dong YB, Li B, Shang DS, Fang WG, Cao YP, Chen YH (2013) CXCL1 contributes to beta-amyloid-induced transendothelial migration of monocytes in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 8:e72744
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Departmental funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editors: S. Beninati, M. Piacentini, C. M. Bergamini.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Currò, M., Gangemi, C., Giunta, M.L. et al. Transglutaminase 2 is involved in amyloid-beta1–42-induced pro-inflammatory activation via AP1/JNK signalling pathways in THP-1 monocytes. Amino Acids 49, 659–669 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2366-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2366-1