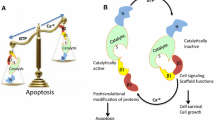
Abstract
Owing to numerous pro-survival target genes, aberrant activation of the NF-κB transcription factor is associated with a drug-resistant phenotype and aggressive breast tumor behavior. Transglutaminase 2 (TG2), a ubiquitously expressed protein cross-linking enzyme, activates NF-κB through a non-conventional mechanism that disables the IκBα inhibitor. Our group has recently documented that the TG2 gene (termed TGM2) is a direct transcriptional target of NF-κB. These developments uncover a novel self-reinforcing molecular feedback loop where TG2 activates NF-κB and, in turn, NF-κB directly upregulates the transcription of TGM2. This manuscript reviews the literature that supports the existence of the TG2/NF-κB signaling loop, the nature of the signal transduction that activates this loop, and the phenotypic consequences stemming from the aberrant activation of this novel signaling mechanism in breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lorand L, Conrad SM (1984) Transglutaminases. Mol Cell Biochem 58(1–2):9–35
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(2):140–156
Greenberg CS, Birckbichler PJ, Rice RH (1991) Transglutaminases: multifunctional cross-linking enzymes that stabilize tissues. FASEB J 5(15):3071–3077
Kitchens CS, Newcomb TF (1979) Factor XIII. Medicine (Baltimore) 58(6):413–429
Tamaki T, Aoki N (1982) Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin catalyzed by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem 257(24):14767–14772
Greenberg CS, Enghild JJ, Mary A, Dobson JV, Achyuthan KE (1988) Isolation of a fibrin-binding fragment from blood coagulation factor XIII capable of cross-linking fibrin (ogen). Biochem J 256(3):1013–1019
Hohl D (1990) Cornified cell envelope. Dermatologica 180(4):201–211
Jiang WG, Ablin RJ (2011) Prostate transglutaminase: a unique transglutaminase and its role in prostate cancer. Biomark Med 5(3):285–291
Williams-Ashman HG (1984) Transglutaminases and the clotting of mammalian seminal fluids. Mol Cell Biochem 58(1–2):51–61
Satchwell TJ, Shoemark DK, Sessions RB, Toye AM (2009) Protein 4.2: a complex linker. Blood Cells Mol Dis 42(3):201–210
Candi E, Paradisi A, Terrinoni A, Pietroni V, Oddi S, Cadot B, Jogini V, Meiyappan M, Clardy J, Finazzi-Agro A, Melino G (2004) Transglutaminase 5 is regulated by guanineadenine nucleotides. Biochem J 381(Pt 1):313–319
Ahvazi B, Boeshans KM, Idler W, Baxa U, Steinert PM, Rastinejad F (2004) Structural basis for the coordinated regulation of transglutaminase 3 by guanine nucleotides and calcium/magnesium. J Biol Chem 279(8):7180–7192
Nakaoka H, Perez DM, Baek KJ, Das T, Husain A, Misono K, Im MJ, Graham RM (1994) Gh: a GTP-binding protein with transglutaminase activity and receptor signaling function. Science 264(5165):1593–1596
Stephens P, Grenard P, Aeschlimann P, Langley M, Blain E, Errington R, Kipling D, Thomas D, Aeschlimann D (2004) Crosslinking and G-protein functions of transglutaminase 2 contribute differentially to fibroblast wound healing responses. J Cell Sci 117(Pt 15):3389–3403
Baek KJ, Kang S, Damron D, Im M (2001) Phospholipase Cdelta1 is a guanine nucleotide exchanging factor for transglutaminase II (Galpha h) and promotes alpha 1B-adrenoreceptor-mediated GTP binding and intracellular calcium release. J Biol Chem 276(8):5591–5597
Chen JS, Mehta K (1999) Tissue transglutaminase: an enzyme with a split personality. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31(8):817–836
Aeschlimann D, Thomazy V (2000) Protein crosslinking in assembly and remodelling of extracellular matrices: the role of transglutaminases. Connect Tissue Res 41(1):1–27
Telci D, Griffin M (2006) Tissue transglutaminase (TG2): a wound response enzyme. Front Biosci 11:867–882
Haroon ZA, Hettasch JM, Lai TS, Dewhirst MW, Greenberg CS (1999) Tissue transglutaminase is expressed, active, and directly involved in rat dermal wound healing and angiogenesis. FASEB J 13(13):1787–1795
Raghunath M, Hopfner B, Aeschlimann D, Luthi U, Meuli M, Altermatt S, Gobet R, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Steinmann B (1996) Cross-linking of the dermo-epidermal junction of skin regenerating from keratinocyte autografts. Anchoring fibrils are a target for tissue transglutaminase. J Clin Invest 98(5):1174–1184
Huang L, Haylor JL, Hau Z, Jones RA, Vickers ME, Wagner B, Griffin M, Saint RE, Coutts IG, El Nahas AM, Johnson TS (2009) Transglutaminase inhibition ameliorates experimental diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 76(4):383–394
Van Herck JL, Schrijvers DM, De Meyer GR, Martinet W, Van Hove CE, Bult H, Vrints CJ, Herman AG (2010) Transglutaminase 2 deficiency decreases plaque fibrosis and increases plaque inflammation in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice. J Vasc Res 47(3):231–240
Abadie V, Sollid LM, Barreiro LB, Jabri B (2011) Integration of genetic and immunological insights into a model of celiac disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 29:493–525
Ai L, Kim WJ, Demircan B, Dyer LM, Bray KJ, Skehan RR, Massoll NA, Brown KD (2008) The transglutaminase 2 gene (TGM2), a potential molecular marker for chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity, is epigenetically silenced in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 29(3):510–518
Mehta K, Fok J, Miller FR, Koul D, Sahin AA (2004) Prognostic significance of tissue transglutaminase in drug resistant and metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10(23):8068–8076
Cheadle C, Vawter MP, Freed WJ, Becker KG (2003) Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. J Mol Diagn 5(2):73–81
Jones PA, Baylin SB (2007) The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 128(4):683–692
Kumar A, Xu J, Brady S, Gao H, Yu D, Reuben J, Mehta K (2010) Tissue transglutaminase promotes drug resistance and invasion by inducing mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One 5(10):e13390
Kumar A, Gao H, Xu J, Reuben J, Yu D, Mehta K (2011) Evidence that aberrant expression of tissue transglutaminase promotes stem cell characteristics in mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One 6(6):e20701
Dyer LM, Schooler KP, Ai L, Klop C, Qiu J, Robertson KD, Brown KD (2011) The transglutaminase 2 gene is aberrantly hypermethylated in glioma. J Neurooncol 101(3):429–440
Shao M, Cao L, Shen C, Satpathy M, Chelladurai B, Bigsby RM, Nakshatri H, Matei D (2009) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and ovarian tumor progression induced by tissue transglutaminase. Cancer Res 69(24):9192–9201
Verma A, Guha S, Diagaradjane P, Kunnumakkara AB, Sanguino AM, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Aggarwal BB, Krishnan S, Gelovani JG, Mehta K (2008) Therapeutic significance of elevated tissue transglutaminase expression in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(8):2476–2483
Mehta K (1994) High levels of transglutaminase expression in doxorubicin-resistant human breast carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 58(3):400–406
Yuan L, Choi K, Khosla C, Zheng X, Higashikubo R, Chicoine MR, Rich KM (2005) Tissue transglutaminase 2 inhibition promotes cell death and chemosensitivity in glioblastomas. Mol Cancer Ther 4(9):1293–1302
Chen JS, Agarwal N, Mehta K (2002) Multidrug-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells contain deficient intracellular calcium pools. Breast Cancer Res Treat 71(3):237–247
Han JA, Park SC (1999) Reduction of transglutaminase 2 expression is associated with an induction of drug sensitivity in the PC-14 human lung cancer cell line. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 125(2):89–95
Herman JF, Mangala LS, Mehta K (2006) Implications of increased tissue transglutaminase (TG2) expression in drug-resistant breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Oncogene 25(21):3049–3058
Yuan L, Siegel M, Choi K, Khosla C, Miller CR, Jackson EN, Piwnica-Worms D, Rich KM (2007) Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor, KCC009, disrupts fibronectin assembly in the extracellular matrix and sensitizes orthotopic glioblastomas to chemotherapy. Oncogene 26(18):2563–2573
Cao L, Petrusca DN, Satpathy M, Nakshatri H, Petrache I, Matei D (2008) Tissue transglutaminase protects epithelial ovarian cancer cells from cisplatin-induced apoptosis by promoting cell survival signaling. Carcinogenesis 29(10):1893–1900
Ai L, Skehan RR, Saydi J, Lin T, Brown KD (2012) Ataxia-Telangiectasia, Mutated (ATM)/Nuclear Factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells (NFkappaB) signaling controls basal and DNA damage-induced transglutaminase 2 expression. J Biol Chem 287(22):18330–18341
Kim DS, Park SS, Nam BH, Kim IH, Kim SY (2006) Reversal of drug resistance in breast cancer cells by transglutaminase 2 inhibition and nuclear factor-kappaB inactivation. Cancer Res 66(22):10936–10943
Mann AP, Verma A, Sethi G, Manavathi B, Wang H, Fok JY, Kunnumakkara AB, Kumar R, Aggarwal BB, Mehta K (2006) Overexpression of tissue transglutaminase leads to constitutive activation of nuclear factor-{kappa}B in cancer cells: delineation of a novel pathway. Cancer Res 66(17):8788–8795
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18(49):6853–6866
Gilmore TD (2006) Introduction to NF-kappaB: players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 25(51):6680–6684
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18(18):2195–2224
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30(1):43–52
Mabb AM, Miyamoto S (2007) SUMO and NF-kappaB ties. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(15):1979–1996
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2012) NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev 26(3):203–234
Chen LF, Greene WC (2004) Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5(5):392–401
Brantley DM, Yull FE, Muraoka RS, Hicks DJ, Cook CM, Kerr LD (2000) Dynamic expression and activity of NF-kappaB during post-natal mammary gland morphogenesis. Mech Dev 97(1–2):149–155
Clarkson RW, Heeley JL, Chapman R, Aillet F, Hay RT, Wyllie A, Watson CJ (2000) NF-kappaB inhibits apoptosis in murine mammary epithelia. J Biol Chem 275(17):12737–12742
Brantley DM, Chen CL, Muraoka RS, Bushdid PB, Bradberry JL, Kittrell F, Medina D, Matrisian LM, Kerr LD, Yull FE (2001) Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) regulates proliferation and branching in mouse mammary epithelium. Mol Biol Cell 12(5):1445–1455
Cao Y, Bonizzi G, Seagroves TN, Greten FR, Johnson R, Schmidt EV, Karin M (2001) IKKalpha provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 107(6):763–775
Demicco EG, Kavanagh KT, Romieu-Mourez R, Wang X, Shin SR, Landesman-Bollag E, Seldin DC, Sonenshein GE (2005) RelB/p52 NF-kappaB complexes rescue an early delay in mammary gland development in transgenic mice with targeted superrepressor IkappaB-alpha expression and promote carcinogenesis of the mammary gland. Mol Cell Biol 25(22):10136–10147
Baxter FO, Came PJ, Abell K, Kedjouar B, Huth M, Rajewsky K, Pasparakis M, Watson CJ (2006) IKKbeta/2 induces TWEAK and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells. Development 133(17):3485–3494
Connelly L, Barham W, Pigg R, Saint-Jean L, Sherrill T, Cheng DS, Chodosh LA, Blackwell TS, Yull FE (2010) Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in mammary epithelium promotes milk loss during mammary development and infection. J Cell Physiol 222(1):73–81
Dejardin E, Bonizzi G, Bellahcene A, Castronovo V, Merville MP, Bours V (1995) Highly-expressed p100/p52 (NFKB2) sequesters other NF-kappa B-related proteins in the cytoplasm of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 11(9):1835–1841
Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Martin DA, Goulet RJ Jr, Sledge GW Jr (1997) Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 17(7):3629–3639
Biswas DK, Shi Q, Baily S, Strickland I, Ghosh S, Pardee AB, Iglehart JD (2004) NF-kappa B activation in human breast cancer specimens and its role in cell proliferation and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(27):10137–10142
Kim DW, Sovak MA, Zanieski G, Nonet G, Romieu-Mourez R, Lau AW, Hafer LJ, Yaswen P, Stampfer M, Rogers AE, Russo J, Sonenshein GE (2000) Activation of NF-kappaB/Rel occurs early during neoplastic transformation of mammary cells. Carcinogenesis 21(5):871–879
Zhou Y, Yau C, Gray JW, Chew K, Dairkee SH, Moore DH, Eppenberger U, Eppenberger-Castori S, Benz CC (2007) Enhanced NF kappa B and AP-1 transcriptional activity associated with antiestrogen resistant breast cancer. BMC Cancer 7:59
Gu Z, Lee RY, Skaar TC, Bouker KB, Welch JN, Lu J, Liu A, Zhu Y, Davis N, Leonessa F, Brunner N, Wang Y, Clarke R (2002) Association of interferon regulatory factor-1, nucleophosmin, nuclear factor-kappaB, and cyclic AMP response element binding with acquired resistance to Faslodex (ICI 182,780). Cancer Res 62(12):3428–3437
Zhou Y, Eppenberger-Castori S, Marx C, Yau C, Scott GK, Eppenberger U, Benz CC (2005) Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NFkappaB) identifies a high-risk subset of hormone-dependent breast cancers. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(5):1130–1144
Wang CY, Cusack JC Jr, Liu R, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) Control of inducible chemoresistance: enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Nat Med 5(4):412–417
Ahmed KM, Cao N, Li JJ (2006) HER-2 and NF-kappaB as the targets for therapy-resistant breast cancer. Anticancer Res 26(6B):4235–4243
Lee J, Kim YS, Choi DH, Bang MS, Han TR, Joh TH, Kim SY (2004) Transglutaminase 2 induces nuclear factor-kappaB activation via a novel pathway in BV-2 microglia. J Biol Chem 279(51):53725–53735
Park SS, Kim JM, Kim DS, Kim IH, Kim SY (2006) Transglutaminase 2 mediates polymer formation of I-kappaBalpha through C-terminal glutamine cluster. J Biol Chem 281(46):34965–34972
Kim DS, Han BG, Park KS, Lee BI, Kim SY, Bae CD (2010) I-kappaBalpha depletion by transglutaminase 2 and mu-calpain occurs in parallel with the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399(2):300–306
Chiao PJ, Miyamoto S, Verma IM (1994) Autoregulation of I kappa B alpha activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(1):28–32
Ientile R, Caccamo D, Griffin M (2007) Tissue transglutaminase and the stress response. Amino Acids 33(2):385–394
Wu ZH, Miyamoto S (2007) Many faces of NF-kappaB signaling induced by genotoxic stress. J Mol Med 85(11):1187–1202
Shiloh Y (2003) ATM and related protein kinases: safeguarding genome integrity. Nat Rev Cancer 3(3):155–168
Wu ZH, Shi Y, Tibbetts RS, Miyamoto S (2006) Molecular linkage between the kinase ATM and NF-kappaB signaling in response to genotoxic stimuli. Science 311(5764):1141–1146
Wu ZH, Wong ET, Shi Y, Niu J, Chen Z, Miyamoto S, Tergaonkar V (2010) ATM- and NEMO-dependent ELKS ubiquitination coordinates TAK1-mediated IKK activation in response to genotoxic stress. Mol Cell 40(1):75–86
Niu J, Shi Y, Iwai K, Wu ZH (2011) LUBAC regulates NF-kappaB activation upon genotoxic stress by promoting linear ubiquitination of NEMO. EMBO J 30(18):3741–3753
Caccamo D, Campisi A, Curro M, Aguennouz M, Volti GL, Avola R, Ientile R (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation is associated with glutamate-evoked tissue transglutaminase up-regulation in primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci Res 82(6):858–865
Mirza A, Liu SL, Frizell E, Zhu J, Maddukuri S, Martinez J, Davies P, Schwarting R, Norton P, Zern MA (1997) A role for tissue transglutaminase in hepatic injury and fibrogenesis, and its regulation by NF-kappaB. Am J Physiol 272(2 Pt 1):G281–G288
Boehm JE, Singh U, Combs C, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA (2002) Tissue transglutaminase protects against apoptosis by modifying the tumor suppressor protein p110 Rb. J Biol Chem 277(23):20127–20130
Milakovic T, Tucholski J, McCoy E, Johnson GV (2004) Intracellular localization and activity state of tissue transglutaminase differentially impacts cell death. J Biol Chem 279(10):8715–8722
Yamaguchi H, Wang HG (2006) Tissue transglutaminase serves as an inhibitor of apoptosis by cross-linking caspase 3 in thapsigargin-treated cells. Mol Cell Biol 26(2):569–579
Fesus L, Szondy Z (2005) Transglutaminase 2 in the balance of cell death and survival. FEBS Lett 579(15):3297–3302
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2(6):442–454
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH, Sonenshein GE (2008) NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J Cell Biochem 104(3):733–744
Lilienbaum A, Paulin D (1993) Activation of the human vimentin gene by the Tax human T-cell leukemia virus. I. Mechanisms of regulation by the NF-kappa B transcription factor. J Biol Chem 268(3):2180–2188
Himelstein BP, Lee EJ, Sato H, Seiki M, Muschel RJ (1997) Transcriptional activation of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene in an H-ras and v-myc transformed rat embryo cell line. Oncogene 14(16):1995–1998
Kupferman ME, Fini ME, Muller WJ, Weber R, Cheng Y, Muschel RJ (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase 9 promoter activity is induced coincident with invasion during tumor progression. Am J Pathol 157(6):1777–1783
Verma A, Wang H, Manavathi B, Fok JY, Mann AP, Kumar R, Mehta K (2006) Increased expression of tissue transglutaminase in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its implications in drug resistance and metastasis. Cancer Res 66(21):10525–10533
Kang SK, Lee JY, Chung TW, Kim CH (2004) Overexpression of transglutaminase 2 accelerates the erythroid differentiation of human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell line through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 577(3):361–366
Guo Z, Kozlov S, Lavin MF, Person MD, Paull TT (2010) ATM activation by oxidative stress. Science 330(6003):517–521
Barzilai A, Biton S, Shiloh Y (2008) The role of the DNA damage response in neuronal development, organization and maintenance. DNA Repair (Amst) 7(7):1010–1027
Barzilai A, Rotman G, Shiloh Y (2002) ATM deficiency and oxidative stress: a new dimension of defective response to DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst) 1(1):3–25
Benz CC, Yau C (2008) Ageing, oxidative stress and cancer: paradigms in parallax. Nat Rev Cancer 8(11):875–879
Oberley LW, Buettner GR (1979) Role of superoxide dismutase in cancer: a review. Cancer Res 39(4):1141–1149
Li N, Karin M (2000) Signaling pathways leading to nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Methods Enzymol 319:273–279
Madrid LV, Wang CY, Guttridge DC, Schottelius AJ, Baldwin AS Jr, Mayo MW (2000) Akt suppresses apoptosis by stimulating the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 subunit of NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Biol 20(5):1626–1638
Romashkova JA, Makarov SS (1999) NF-kappaB is a target of AKT in anti-apoptotic PDGF signalling. Nature 401(6748):86–90
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401(6748):82–85
Smethurst PA, Griffin M (1996) Measurement of tissue transglutaminase activity in a permeabilized cell system: its regulation by Ca2+ and nucleotides. Biochem J 313(Pt 3):803–808
Kiraly R, Demeny M, Fesus L (2010) Protein transamidation by transglutaminase 2 in cells: a disputed Ca2+ -dependent action of a multifunctional protein. FEBS J 278(24):4717–4739
Tate PH, Bird AP (1993) Effects of DNA methylation on DNA-binding proteins and gene expression. Curr Opin Genet Dev 3(2):226–231
Gilmore TD, Herscovitch M (2006) Inhibitors of NF-kappaB signaling: 785 and counting. Oncogene 25(51):6887–6899
Keillor JW, Chabot N, Roy I, Mulani A, Leogane O, Pardin C (2011) Irreversible inhibitors of tissue transglutaminase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 78:415–447
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Drs. Lingbao Ai and Kapil Mehta for insightful discussions before the drafting of this manuscript. Work in our lab has been supported by grants from the NIH (R01-CA102289), the Ocala Royal Dames for Cancer Research, and the Florida Department of Health.
Conflict of interest
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brown, K.D. Transglutaminase 2 and NF-κB: an odd couple that shapes breast cancer phenotype. Breast Cancer Res Treat 137, 329–336 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2351-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2351-7