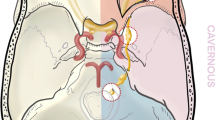
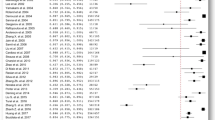
Abstract
Background
Non-vestibular schwannomas are relatively rare, with trigeminal and jugular foramen schwannomas being the most common. This is a heterogenous group which requires detailed investigation and careful consideration to management strategy. The optimal management for these tumours remains unclear, and there are several controversies. The aim of this paper is to provide insight into the main principles defining management and surgical strategy, in order to formulate a series of recommendations.
Methods
A task force was created by the EANS skull base section committee along with its members and other renowned experts in the field to generate recommendations for the surgical management of these tumours on a European perspective. To achieve this, the task force performed an extensive systematic review in this field and had discussions within the group. This article is the third of a three-part series describing non-vestibular schwannomas (IX, X, XI, XII).
Results
A summary of literature evidence was proposed after discussion within the EANS skull base section. The constituted task force dealt with the practice patterns that exist with respect to preoperative radiological investigations, ophthalmological assessments, optimal surgical and radiotherapy strategies and follow-up management.
Conclusion
This article represents the consensually derived opinion of the task force with respect to the treatment of non-vestibular schwannomas. For each of these tumours, the management paradigm is shifting towards the compromise between function preservation and progression free survival.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara K, Morita A (2005) Dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma in an elderly woman: a clinical dilemma. Surg Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.07.045
Bartal AD, Djaldetti MM, Mandel EM, Lerner MA (1973) Dumb bell neurinoma of the hypoglossal nerve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.36.4.592
Berger MS, Edwards MSB, Bingham WG (1982) Hypoglossal neurilemoma: case report and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198205000-00013
Bindal S, El Ahmadieh TY, Plitt A, Aoun SG, Neeley OJ, El Tecle NE, Barnett S, Gluf W (2019) Hypoglossal schwannomas: a systematic review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.11.037
Bulsara KR, Sameshima T, Friedman AH, Fukushima T (2008) Microsurgical management of 53 jugular foramen schwannomas: lessons learned incorporated into a modified grading system - Clinical article. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/11/0794
Carvalho GA, Tatagiba M, Samii M (2000) Cystic schwannomas of the jugular foramen: clinical and surgical remarks. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200003000-00007
Chang KC, Leu YS (2002) Hypoglossal schwannoma in the submandibular space. J Laryngol Otol. https://doi.org/10.1258/0022215021910177
Chibbaro S, Mirone G, Makiese O, Bresson D, George B (2009) Dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas: surgical management, outcome and complications on a series of 16 patients. Neurosurg Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-009-0188-2
D.D. C, N.L. M, K. V, S. S-A, R.W. P, N. T, V.K.H. S, C.A. D, R.F. S (2011) Surgical management and outcome of schwannomas in the craniocervical region: clinical article. J. Neurosurg.
Dolan EJ, Tucker WS, Rotenberg D, Chui M (1982) Intracranial hypoglossal schwannoma as an unusual cause of facial nerve palsy Case report. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1982.56.3.0420
Eldevik OP, Gabrielsen TO, Jacobsen EA (2000) Imaging findings schwannomas of the jugular foramen. Am. J. Neuroradiol.
Elsharkawy M, Xu Z, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2012) Gamma Knife surgery for nonvestibular schwannomas: radiological and clinical outcomes: clinical article. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.8.JNS11215
Goel A, Desai K (2000) Cystic Schwannomas of the jugular foramen: clinical and surgical remarks. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1093/neurosurgery/47.6.1470
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Kida Y et al (2016) Gamma Knife surgery for patients with jugular foramen schwannomas: a multiinstitutional retrospective study in Japan. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.8.JNS151156
Ichimura S, Yoshida K, Kawase T (2009) Surgical approach for hypoglossal schwannomas to prevent deformity of the atlanto-occipital joint. Acta Neurochir (Wien). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0284-7
Ichimura S, Yoshida K, Sutiono AB, Horiguchi T, Sasaki H, Kawase T (2010) Greater petrosal nerve schwannomas—analysis of four cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-010-0277-2
Inoue T, Nonaka Y, Hirai H, Shima A, Suzuki F, Matsuda M, Fukushima T (2018) Single-stage total resection of giant dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma: a case report. Acta Neurochir (Wien). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3431-6
Jean WC, Felbaum D (2016) Evolution of the intracranial approaches to jugular foramen tumors: a surgeon’s personal perspective through three illustrative cases. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.530
Kadri PAS, Al-Mefty O (2004) Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas. Neurosurg Focus. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.2004.17.2.9
Kankane VK, Warade AC, Misra BK (2019) Nonvestibular schwannoma tumors in the cerebellopontine angle: a single-surgeon experience. Asian J Neurosurg 14(1):154. https://doi.org/10.4103/ajns.ajns_335_17
Kano H, Meola A, Yang HC et al (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery for jugular foramen schwannomas: an international multicenter study. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.5.JNS162894
Kaye AH, Hahn JF, Kinney SE, Hardy RW, Bay JW (1984) Jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1984.60.5.1045
Kuo LT, Huang APH, Kuo KT, Tseng HM (2008) Extradural dumbbell schwannoma of the hypoglossal nerve: a case report with review of the literature. Surg Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2007.11.023
Lee MK, Sidell DR, Mendelsohn AH, Blackwell KE (2012) Hypoglossal schwannoma masquerading as a carotid body tumor. Case Rep Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/842761
Lee M, Tong K (2016) Jugular foramen schwannoma mimicking paraganglioma: case report and review of imaging findings. Radiol Case Reports. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radcr.2015.12.002
Li Y, Lou J, Qiu S, Guo Y, Pan M (2016) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannomas: two cases of long-term follow-up and a review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2016.922
Lunsford LD, Sheehan JP (2015) Intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery, 2nd edn. Thieme
Mathiesen T, Svensson M, Lundgren J, Kihlström L, Parisotto R, Bagger-Sjöbäck D (2009) Hypoglossal schwannoma—successful reinnervation and functional recovery of the tongue following tumour removal and nerve grafting. Acta Neurochir (Wien). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0226-4
Mazzoni A, Saleh E, Sanna M, Achilli V (1997) Lower cranial nerve schwannomas involving the jugular foramen. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. https://doi.org/10.1177/000348949710600503
Nonaka Y, Grossi PM, Bulsara KR, Taniguchi RM, Friedman AH, Fukushima T (2011) Microsurgical management of hypoglossal schwannomas over 3 decades: a modified grading scale to guide surgical approach. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822a547b
Di Pascuale I, Brito N, Zerpa J, Roa C, Faria G (2020) Hypoglossal nerve schwannoma: case report and literature review. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.12.006
Pellet W, Cannoni M, Pech A (1988) The widened transcochlear approach to jugular foramen tumors. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1988.69.6.0887
Ryu SM, Il LJ, Park K, Choi JW, Kong DS, Nam DH, Jeong HS, Cho YS, Seol HJ (2017) Optimal treatment of jugular foramen schwannomas: long-term outcome of a multidisciplinary approach for a series of 29 cases in a single institute. Acta Neurochir (Wien). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3230-0
Samii M, Alimohamadi M, Gerganov V (2015) Surgical treatment of jugular foramen schwannoma: surgical treatment based on a new classification. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000831
Samii M, Babu RP, Tatagiba M, Sepehrnia A (1995) Surgical treatment of jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.82.6.0924
Samii M, Migliori MM, Tatagiba M, Babu R (1995) Surgical treatment of trigeminal schwannomas. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.82.5.0711
Sanna M, Bacciu A, Falcioni M, Taibah A (2006) Surgical management of jugular foramen schwannomas with hearing and facial nerve function preservation: a series of 23 cases and review of the literature. Laryngoscope. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000246193.84319.e5
Santander XA, Cotúa CE, Saldaña C (2017) Spontaneous regression of a hypoglossal neurinoma: case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.06.004
Sarma S, Sekhar LN, Schessel DA (2002) Nonvestibular schwannomas of the brain: a 7-year experience. Neurosurgery 50(3):437–449
Sedney CL, Nonaka Y, Bulsara KR, Fukushima T (2013) Microsurgical management of jugular foramen schwannomas. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182770e74
Shinya Y, Hasegawa H, Shin M, Sugiyama T, Kawashima M, Katano A, Kashio A, Kondo K, Saito N (2021) Long-term outcomes of stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal facial and jugular foramen schwannoma in comparison with vestibular schwannoma. Cancers (Basel) 13(5):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051140
Suri A, Bansal S, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK, Kale SS, Chandra PS, Singh M, Kumar R, Sharma MS (2014) Management of hypoglossal schwannomas: single institutional experience of 14 cases. J Neurol Surgery, Part B Skull Base. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1356924
Suri A, Bansal S, Singh M, Mahapatra AK, Sharma BS (2014) Jugular foramen schwannomas: a single institution patient series. J Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.02.029
Sutay S, Tekinsoy B, Ceryan K, Aksu Y (1993) Submaxillary hypoglossal neurilemmoma. J Laryngol Otol. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215100124892
Sutiono AB, Kawase T, Tabuse M, Kitamura Y, Arifin MZ, Horiguchi T, Yoshida K (2011) Importance of preserved periosteum around jugular foramen neurinomas for functional outcome of lower cranial nerves: anatomic and clinical studies. Neurosurgery. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822a19a3
Tan LC, Bordi L, Symon L, Cheesman AD (1990) Jugular foramen neuromas: a review of 14 cases. Surg Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0090-3019(90)90130-H
Wang X, Long W, Liu D, Yuan J, Xiao Q, Liu Q (2020) Optimal surgical approaches and treatment outcomes in patients with jugular foramen schwannomas: a single institution series of 31 cases and a literature review. Neurosurg Rev 43(5):1339–1350
Weindling SM, Wood CP, Hoxworth JM (2017) Hypoglossal canal lesions: distinctive imaging features and simple diagnostic algorithm. Am J Roentgenol. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.17.18102
Yasumatsu R, Nakashima T, Miyazaki R, Segawa Y, Komune S (2013) Diagnosis and management of extracranial head and neck schwannomas: a review of 27 cases. Int J Otolaryngol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/973045
Zeng XJ, Li D, Hao SY et al (2016) Long-term functional and recurrence outcomes of surgically treated jugular foramen schwannomas: a 20-year experience. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.09.104
Zhang Q, Kong F, Guo H, Chen G, Liang J, Li M, Ling F (2012) Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped hypoglossal schwannoma via a pure endoscopic transoral approach. Acta Neurochir (Wien). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1193-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the local Ethical Committee (Geneva Ethics Committee Board no. 11-233R, NAC 11-085R) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
For this retrospective type of study, formal consent is not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Comments
This is yet another excellent attempt by the EANS skull base section to produce a consensus statement and review the literature regarding the non-vestibular schwannomas in adults. I congratulate the Editor as well the EANS skull base section for this exercise. The statements made are reasonable, and this manuscript will be value addition to the literature. A more comprehensive review of the literature is desirable. We have published our operative experience with the management of 224 consecutive non-vestibular schwannoma C P Angle tumours between 2001 and 2014.(1) The series had 34 trigeminal schwannoma and 26 jugular foramen schwannomas. Treatment strategy of jugular foramen schwannoma is best individualised and depends on the age of the patient, size of the tumour and lower cranial nerve involvement. Retrosigmoid approach was employed in 77 per cent of cases, and gross total excision was achieved in 62 per cent of cases. We recommend a more radical approach with an attempt at total excision in young patients with large tumours, especially with compromised lower cranial nerve function and a more conservative approach leaving the tumour in the jugular foramen for adjunct radiosurgery in patients with intact lower cranial function preoperatively. A similar conservative approach is preferred in elderly patients and patients with co morbidity. A period of observation is recommended in elderly patients with small tumours or incidental pick up of tumours.
Basant Misra.
India.
Reference:
1. Kankane VK, Warade AC, Misra BK. Non-vestibular schwannoma tumors in the cerebellopontine angle: A single-surgeon experience. Asian J Neurosurg (2019) 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_335_17.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Tumor - Schwannoma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bal, J., Bruneau, M., Berhouma, M. et al. Management of non-vestibular schwannomas in adult patients: a systematic review and consensus statement on behalf of the EANS skull base section Part III: Lower cranial nerve schwannomas, jugular foramen (CN IX, X, XI) and hypoglossal schwannoma (XII). Acta Neurochir 164, 321–329 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-05072-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-021-05072-y