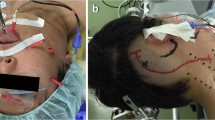
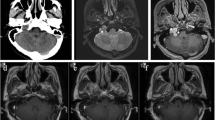
Abstract
Complete resection of jugular foramen schwannomas (JFSs) with minimal cranial nerve complications remains difficult even for skilled neurosurgeons. Between November 2011 and November 2017, 31 consecutive patients diagnosed with JFSs underwent a single-stage operation performed by the same neurosurgeon. We retrospectively analyzed clinical characteristics, surgical approaches, treatment outcomes, and follow-up data for these patients. JFSs were classified according to the Samii classification system. A retrosigmoid approach was used to resect type A tumors, while a suboccipital transjugular process (STJP) approach was used to resect type B tumors. Notably, the present study is the first to report the use of a paracondylar-lateral cervical (PCLC) approach for the treatment of type C and D tumors. Type A-D tumors were observed in seven, four, four, and 16 patients, respectively. Gross-total resection was achieved in 29 patients (93.5%). There were no cases of intracranial hematoma, re-operation, tracheotomy, or death. Adjunctive gamma knife treatment was used to manage residual tumors in two patients. Neurological deficits relieved in half of patients at the last follow-up. By reviewing the studies published on PubMed, the approaches gradually be more conservative, rather than widely expose the skull base. Nonetheless, endoscope and stereotactic radiosurgery plays an important role in the management of JFSs. Both tumor removal and neurological function retention can be obtained by choosing individual treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bejjani GK, Sullivan B, Salas-Lopez E, Abello J, Wright DC, Jurjus A, Sekhar LN (1998) Surgical anatomy of the infratemporal fossa: the styloid diaphragm revisited. Neurosurgery 43:842–852 discussion 852-843
Bulsara KR, Sameshima T, Friedman AH, Fukushima T (2008) Microsurgical management of 53 jugular foramen schwannomas: lessons learned incorporated into a modified grading system. J Neurosurg 109:794–803. https://doi.org/10.3171/JNS/2008/109/11/0794
Cavalcanti DD, Martirosyan NL, Verma K, Safavi-Abbasi S, Porter RW, Theodore N, Sonntag VK, Dickman CA, Spetzler RF (2011) Surgical management and outcome of schwannomas in the craniocervical region. J Neurosurg 114:1257–1267. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.5.JNS0966
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Kida Y, Sasaki A, Iwai Y, Kondoh T, Tsugawa T, Sato M, Sato M, Nagano O, Nakaya K, Nakazaki K, Kano T, Hasui K, Nagatomo Y, Yasuda S, Moriki A, Serizawa T, Osano S, Inoue A (2016) Gamma knife surgery for patients with jugular foramen schwannomas: a multiinstitutional retrospective study in Japan. J Neurosurg 125:822–831. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.8.JNS151156
Kadri PA, Al-Mefty O (2004) Surgical treatment of dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas. Neurosurg Focus 17:E9
Kano H, Meola A, Yang HC, Guo WY, Martinez-Alvarez R, Martinez-Moreno N, Urgosik D, Liscak R, Cohen-Inbar O, Sheehan J, Lee JYK, Abbassy M, Barnett GH, Mathieu D, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2018) Stereotactic radiosurgery for jugular foramen schwannomas: an international multicenter study. J Neurosurg 129:928–936. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.5.JNS162894
Katsuta T, Rhoton AL Jr, Matsushima T (1997) The jugular foramen: microsurgical anatomy and operative approaches. Neurosurgery 41:149–201 discussion 201-142
Kaye AH, Hahn JF, Kinney SE, Hardy RW Jr, Bay JW (1984) Jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg 60:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1984.60.5.1045
Komune N, Matsushima K, Matsushima T, Komune S, Rhoton AL Jr (2016) Surgical approaches to jugular foramen schwannomas: an anatomic study. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1041–E1053. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.24156
Ryu SM, Lee JI, Park K, Choi JW, Kong DS, Nam DH, Jeong HS, Cho YS, Seol HJ (2017) Optimal treatment of jugular foramen schwannomas: long-term outcome of a multidisciplinary approach for a series of 29 cases in a single institute. Acta Neurochir 159:1517–1527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-017-3230-0
Samii M, Alimohamadi M, Gerganov V (2015) Surgical treatment of jugular foramen schwannoma: surgical treatment based on a new classification. Neurosurgery 77:424–432; discussion 432. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000000831
Samii M, Alimohamadi M, Gerganov V (2016) Endoscope-assisted retrosigmoid infralabyrinthine approach to jugular foramen tumors. J Neurosurg 124:1061–1067. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.3.JNS142904
Samii M, Babu RP, Tatagiba M, Sepehrnia A (1995) Surgical treatment of jugular foramen schwannomas. J Neurosurg 82:924–932. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.82.6.0924
Sanna M, Bacciu A, Falcioni M, Taibah A (2006) Surgical management of jugular foramen schwannomas with hearing and facial nerve function preservation: a series of 23 cases and review of the literature. Laryngoscope 116:2191–2204. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000246193.84319.e5
Sedney CL, Nonaka Y, Bulsara KR, Fukushima T (2013) Microsurgical management of jugular foramen schwannomas. Neurosurgery 72:42–46; discussion 46. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3182770e74
Song MH, Lee HY, Jeon JS, Lee JD, Lee HK, Lee WS (2008) Jugular foramen schwannoma: analysis on its origin and location. Otol Neurotol 29:387–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e318164cb83
Suri A, Bansal S, Singh M, Mahapatra AK, Sharma BS (2014) Jugular foramen schwannomas: a single institution patient series. J Clin Neurosci 21:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.02.029
Sutiono AB, Kawase T, Tabuse M, Kitamura Y, Arifin MZ, Horiguchi T, Yoshida K (2011) Importance of preserved periosteum around jugular foramen neurinomas for functional outcome of lower cranial nerves: anatomic and clinical studies. Neurosurgery 69:ons230–ons240; discussion ons240. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822a19a3
Wan JH, Wu YH, Li ZJ, Li XJ, Qian HP, Meng XL, Xu ZG (2012) Triple dumbbell-shaped jugular foramen schwannomas. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2011.05.012
Wen HT, Rhoton AL Jr, Katsuta T, de Oliveira E (1997) Microsurgical anatomy of the transcondylar, supracondylar, and paracondylar extensions of the far-lateral approach. J Neurosurg 87:555–585. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.4.0555
Wilson MA, Hillman TA, Wiggins RH, Shelton C (2005) Jugular foramen schwannomas: diagnosis, management, and outcomes. Laryngoscope 115:1486–1492. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mlg.0000172196.76865.a1
Zeng XJ, Li D, Hao SY, Wang L, Tang J, Xiao XR, Meng GL, Jia GJ, Zhang LW, Wu Z, Zhang JT (2016) Long-term functional and recurrence outcomes of surgically treated jugular foramen schwannomas: a 20-year experience. World Neurosurg 86:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.09.104
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Dr. Wenya Linda Bi for her suggestions on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant number 2014BAI04B01) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81802974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: X.W., W.L., Q.L. Do the surgery procedure: all authors. Acquisition of data: X.W. Analysis and interpretation of data: X.W, Q.X. Drafting the article: X.W. Critically revising the article: all authors. Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: all authors. Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: X.W. Study supervision: Q.L.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Xiangya Hospital, Central South University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals participants include in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Long, W., Liu, D. et al. Optimal surgical approaches and treatment outcomes in patients with jugular foramen schwannomas: a single institution series of 31 cases and a literature review. Neurosurg Rev 43, 1339–1350 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01165-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01165-6