Abstract
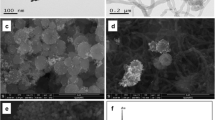
A novel magnetic Ti3C2Tx-MXene/Fe3O4 composite was prepared from Ti3C2Tx and magnetic Fe3O4. The characterizations by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) exhibited that the Ti3C2Tx/Fe3O4 nanomaterial presented an outstanding conductivity and a large specific area, which could improve the electron transfer rate, leading to the amplification of the sensor’s signal. Furthermore, an ultrasensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on MXene/Fe3O4 composites was fabricated for detecting methylmalonic acid (MMA) with high selectivity. The current intensity of differential pulse voltammetry of the sensor presented a good linear relationship with the logarithm of MMA concentration ranging from 9 × 10−15 mol L−1 to 9 × 10−13 mol L−1. The detection limit of the sensor was 2.33 × 10−16 mol L−1. The fabricated sensor was utilized for detecting MMA in human serum samples with excellent recoveries. Therefore, this method significantly improved the sensitivity of detection, and constitutes an affordable sensing platform for trace detection of organic carboxylic acid.
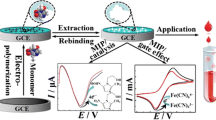
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almási T, Guey LT, Lukacs C, Csetneki K, Vokó Z, Zelei T (2019) Systematic literature review and meta-analysis on the epidemiology of methylmalonic acidemia (MMA) with a focus on MMA caused by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (mut) deficiency. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1063-z
Hang C, Xu S, Wu Q, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Xu Y (2021) mRNA-based therapies and their clinical prospects. Chin Sci Bull 66:3649–3666. https://doi.org/10.1360/TB-2021-0222
Du N, Chen M, Cui Y, Liu X, Li Y (2022) Fluorescent sensor array constructed by functionalized carbon nanodots for qualitative and quantitative analysis of urinary organic acids biomarkers. Sens Actuators B Chem 350:130825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130825
Cox EV, White AM (1962) Methylmalonic acid excretion: an index of vitamin-B12 deficiency. Lancet 280:853–856. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(62)90631-1
Bashir H, Hinterberger H, Jones B (1966) Methylmalonic acid excretion in vitamin B12 deficiency. Br J Haematol 12:704–711. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00156.x
Obeid R, Geisel J, Herrmann W (2015) Comparison of two methods for measuring methylmalonic acid as a marker for vitamin B12 deficiency. Diagnosis 2:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1515/dx-2014-0030
Babidge PJ, Babidge WJ (1994) Determination of methylmalonic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 216:424–426. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1994.1062
Pedersen TL, Keyes WR, Shahab-Ferdows S, Allen LH, Newman JW (2011) Methylmalonic acid quantification in low serum volumes by UPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:1502–1506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.039
Deepa JR, Anirudhan TS, Soman G (2020) Electrochemical sensing of methylmalonic acid based on molecularly imprinted polymer modified with graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchem J 159:105489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105489
Kumar J, Soomro RA, Neiber RR, Ahmed N, Medany SS, Albaqami MD, Nafady A (2022) Ni nanoparticles embedded Ti3C2Tx-MXene nanoarchitectures for electrochemical sensing of methylmalonic acid. Biosensors 12:231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040231
Rajeev R, Benny L, Roy M, Mathew AT, Akshaya KB, Varghese A, Hegde G (2022) A facile and economic electrochemical sensor for methylmalonic acid: a potential biomarker for vitamin B12 deficiency. New J Chem 46:4114–4125. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ05544E
Wulff G, Sarhan A, Zabrocki K (1973) Enzyme-analogue built polymers and their use for the resolution of racemates. Tetrahedron Lett 14:4329–4332. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4039(01)87213-0
Ashley J, Shahbazi MA, Kant K, Chidambara VA, Wolff A, Bang DD, Sun Y (2017) Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation and biosensing in food analysis: progress and perspectives. Biosens Bioelectron 91:606–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.018
Vidal L, Robin O, Parshintsev J, Mikkola J-P, Riekkola M-L (2013) Quaternary ammonium-functionalized silica sorbents for the solid-phase extraction of aromatic amines under normal phase conditions. J Chromatogr A 1285:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.003
Duan D, Yang H, Ding Y, Li L, Ma G (2019) A three-dimensional conductive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on MOF derived porous carbon/carbon nanotubes composites and prussian blue nanocubes mediated amplification for chiral analysis of cysteine enantiomers. Electrochim Acta 302:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.02.028
Liu G, Ling J, Li J (2021) Extremely sensitive molecularly imprinted ECL sensor with multiple probes released from liposomes immobilized by a light-triggered click reaction. ACS Sens 6:4185–4192. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.1c01763
Rostamizadeh K, Abdollahi H, Parsajoo C (2013) Synthesis, optimization, and characterization of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Int Nano Lett 3:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5326-3-20
Naguib M, Mochalin VN, Barsoum MW, Gogotsi Y (2014) 25th anniversary article: MXenes: a new family of two-dimensional materials. Adv Mater 26:992–1005. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201304138
Shahzada F, Iqbal A, Zaidi SA, Hwang SW, Koo CM (2019) Nafion-stabilized two-dimensional transition metal carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene) as a high-performance electrochemical sensor for neurotransmitter. Ind Eng Chem Res 79:338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.061
Xia T, Liu G, Wang J, Hou S, Hou S (2021) MXene-based enzymatic sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of cholesterol. Biosens Bioelectron 183:113243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113243
Liu G, Xia T, Wei J, Hou S, Hou S (2022) Ammonia modified MXene/aniline copolymers electrochemical sensors for ultrasensitive sensing glutathione. ChemElectroChem 9:e202200971. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202200971
Yu P, Cao G, Yi S, Zhang X, Li C, Sun X, Wang K, Ma Y (2018) Binder-free 2D titanium carbide (MXene)/carbon nanotube composites for high-performance lithium-ion capacitors. Nanoscale 10:5906–5913. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR00380G
Xie Y, Gao F, Tu X, Ma X, Xu Q, Dai R, Huang X, Yu Y, Lu L (2019) Facile synthesis of MXene/electrochemically reduced graphene oxide composites and their application for electrochemical sensing of carbendazim. J Electrochem Soc 166:B1673–B1680. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0091916jes
Wen M, Xing Y, Liu G, Hou S, Hou S (2022) Electrochemical sensor based on Ti3C2 membrane doped with UIO-66-NH2 for sensing dopamine. Microchim Acta 189:141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05222-8
Liu G, Xia T, Liang X, Hou S, Hou S (2022) Enzymatic electrochemical biosensor from Eu-doped SnO2 embedded in MXene for high performance sensing lactate. ChemElectroChem 9:e202200848. https://doi.org/10.1002/celc.202200848
Zhang D, Wang X, He LJ, Song W, Sun Z, Han B, Li J-X, Lei Q-Q (2013) Preparation and characteristic of magnetic LDPE/Fe3O4 nano-composite films. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 24:1796–1800. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-1014-0
Wei S, Liu Y, Hua T, Liu L, Wang H (2013) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the determination of ampicillin based on a gold nanoparticle and multiwalled carbon nanotube-coated Pt electrode. J Appl Polym Sci 131:40613. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.40613
Wang Y, Li Y, Qiu Z, Wu X, Zhou P, Zhou T, Zhao J, Miao Z, Zhou J, Zhuo S (2018) Fe3O4@ Ti3C2 MXene hybrids with ultrahigh volumetric capacity as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 6:11189–11197. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ta00122g
Liang Y, Qu C, Yang R, Qu L, Li J (2017) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for daidzein recognition and detection based on poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) functionalized graphene. Sens Actuators B Chem 251:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.05.044
Liu P, Zhang X, Xu W, Guo C, Wang S (2012) Electrochemical sensor for the determination of brucine in human serum based on molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine/SWNTs composite film. Sens Actuators B Chem 163:84–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.01.011
Mao H, Song S, Li Y, Zhuo Q, Huo J (2018) Determination of serun methylmalonic acid by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to evaluation of nutritional status of vitamin B12. J Prev Med Chin PLA 36:699–702. https://doi.org/10.13704/j.cnki.jyyx.2018.06.002
Aghamohammadi M, Shahdousti P, Harooni B (2016) Ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction followed by gas chromatography–flame ionization detection for urinary methylmalonic acid determination. Microchem J 124:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.07.028
Li N, Deng C, Zhang X (2007) Determination of methylmalonic acid and glutaric acid in urine by aqueous-phase derivatization followed by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 30:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200600296
Al-Dirbashi OY, Jacob M, Al-Hassnan Z, Chabayta RW, El-Badaoui F, Rashed MS (2006) Determination of methylmalonic acid in urine by HPLC with intramolecular excimer-forming fluorescence derivatization. Biomed Chromatogr 20:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.527
Funding
This work was supported by the Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent Special Project (No. 2021AC20002) and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Electrochemical and Magneto-chemical Functional Materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Supplementary data. (DOCX 2199 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Y., Ding, X., Liang, X. et al. Magnetic MXene–based molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for methylmalonic acid. Microchim Acta 190, 208 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05791-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05791-2