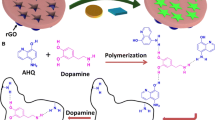
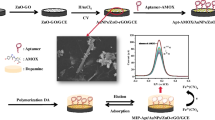
Abstract
A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor (MIECS) for trace determination of taurine was developed. The sensor was constructed by electropolymerizing dopamine and o-phenylenediamine as dual monomers on the surface of amino-functionalized iron-based MOFs and graphene composite-modified electrode. The porous structure and large specific surface area of amino-functionalized iron-based MOFs not only increase the number of imprinted sites, but also facilitate the binding of molecularly imprinted films. The presence of dual monomers can increase the binding sites during the formation of imprinted films. The linear range of this sensor for taurine detection is 1.00 × 10−14–1.00 × 10−8 mol L−1 with a determination limit of 3.20 × 10−15 mol L−1. The proposed MIECS was successfully applied to quantify the amount of taurine in human serum sample with good recovery values from 97.3 to 113%.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Hansen SH (2001) The role of taurine in diabetes and the development of diabetic complications. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17(5):330–346. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.229
Militante JD, Lombardini JB (2002) Treatment of hypertension with oral taurine: experimental and clinical studies. Amino Acids 23(4):381–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0212-0
Mas MR, Comert B, Oncu K, Vural SA, Akay C, Tasci I, Ozkomur E, Serdar M, Mas N, Alcigir G, Yener N (2004) The effect of taurine treatment on oxidative stress in experimental liver fibrosis. Hepatol Res 28(4):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.herpes.2003.11.012
De Curtis M, Santamaria F, Ercolini P, Vittoria L, De Ritis G, Garofalo V, Ciccimarra F (1992) Effect of taurine supplementation on fat and energy absorption in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child 67(9):1082. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.67.9.1082
Kimmel DW, Leblanc G, Meschievitz ME, Cliffel DE (2012) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 84(2):685–707. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac202878q
O'Brien C, Varty K, Ignaszak A (2021) The electrochemical detection of bioterrorism agents: a review of the detection, diagnostics, and implementation of sensors in biosafety programs for class A bioweapons. Microsyst Nanoeng 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-021-00242-5
Chai R, Wang Y, Kan X (2021) Sensitive and selective detection of glycoprotein based on dual-signal and dual-recognition electrochemical sensing platform. Food Chem 340:127944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127944
Li T, Liao C, An J, Zhou L, Tian L, Zhou Q, Li N, Wang X (2021) A highly sensitive bioelectrochemical toxicity sensor and its evaluation using immediate current attenuation. Sci Total Environ 766:142646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142646
Lee S, Ozlu B, Eom T, Martin DC, Shim BS (2020) Electrically conducting polymers for bio-interfacing electronics: from neural and cardiac interfaces to bone and artificial tissue biomaterials. Biosens Bioelectron 170:112620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112620
Temocin Z (2021) Designing of a stable and selective glucose biosensor by glucose oxidase immobilization on glassy carbon electrode sensitive to H2O2 via nanofiber interface. J Appl Electrochem 51(2):283–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-020-01502-4
Uzun L, Turner APF (2016) Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: realising their potential. Biosens Bioelectron 76:131–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.013
Gui R, Jin H, Guo H, Wang Z (2018) Recent advances and future prospects in molecularly imprinted polymers-based electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 100:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.058
Jiang Z, Li G, Zhang M (2016) A novel sensor based on bifunctional monomer molecularly imprinted film at graphene modified glassy carbon electrode for detecting traces of moxifloxacin. RSC Adv 6(39):32915–32921. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra01494a
Zhao W-R, Kang T-F, Lu L-P, Shen F-X, Cheng S-Y (2017) A novel electrochemical sensor based on gold nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer with binary functional monomers for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. J Electroanal Chem 786:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.01.003
Li J, Huang X, Ma J, Wei S, Zhang H (2020) A novel electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer with binary functional monomers at Fe-doped porous carbon decorated Au electrode for the sensitive detection of lomefloxacin. Ionics 26(8):4183–4192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-020-03554-0
Rawool CR, Srivastava AK (2019) A dual template imprinted polymer modified electrochemical sensor based on Cu metal organic framework/mesoporous carbon for highly sensitive and selective recognition of rifampicin and isoniazid. Sens Actuators, B Chem 288:493–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.032
Tung TT, Kim TY, Shim JP, Yang WS, Kim H, Suh KS (2011) Poly(ionic liquid)-stabilized graphene sheets and their hybrid with poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene). Org Electron 12(12):2215–2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2011.09.012
Zhou HC, Long JR, Yaghi OM (2012) Special thematic issue on metal organic frameworks. Chem Rev 112(2):673–1268
O’Keeffe M, Peskov MA, Ramsden SJ, Yaghi OM (2008) The Reticular Chemistry Structure Resource (RCSR) database of, and symbols for, crystal nets. Acc Chem Res 41(12):1782–1789. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar800124u
Yin C, Zhuang Q, Xiao Q, Wang Y, Xie J (2021) Electropolymerization of poly(methylene blue) on flower-like nickel-based MOFs used for ratiometric electrochemical sensing of total polyphenolic content in chrysanthemum tea. Anal Methods: Adv Methods Appl 13(9):1154–1163. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ay00028d
Guo H, Zhu Y, Qiu S, Lercher AJ, Zhang H (2010) Coordination modulation induced synthesis of nanoscale Eu 1-Tbxmetal-organic frameworks for luminescent thin films. Adv Mater 22(37):4190–4192. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201000844
Petit C, Bandosz TJ (2015) Engineering the surface of a new class of adsorbents: metal-organic framework/graphite oxide composites. J Colloid Interface Sci 447:139–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.08.026
Petit C, Bandosz TJ (2009) MOF–graphite oxide composites: combining the uniqueness of graphene layers and metal–organic frameworks. Adv Mater 21(46):4753–4757. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200901581
Wu X-Q, Feng P-Q, Guo Z, Wei X (2020) Water-Stable 1D Double-chain Cu metal–organic framework-based electrochemical biosensor for detecting l-tyrosine. Langmuir 36(46):14123–14129. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02799
Jiang T, Sun X, Wei L, Li M (2020) Determination of hydrogen peroxide released from cancer cells by a Fe-Organic framework/horseradish peroxidase-modified electrode. Anal Chim Acta 1135:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.09.040
Bauer S, Serre C, Devic T, Horcajada P, Marrot J, Férey G, Stock N (2008) High-throughput assisted rationalization of the formation of metal organic frameworks in the iron(III) aminoterephthalate solvothermal system. Inorg Chem 47(17):7568–7576. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic800538r
Yi X, He X, Yin F, Yang T, Chen B, Li G (2020) NH2–MIL-88B–Fe for electrocatalytic N2 fixation to NH3 with high Faradaic efficiency under ambient conditions in neutral electrolyte. J Mater Sci 55(26):12041–12052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04777-2
Li SJ, Hou LL, Chang MZ, Yan JJ, Liu L (2016) A novel enzyme-free hydrogen peroxide sensor based on electrode modified with gold nanoparticles-overoxidized polydopamine composites. Int J Electrochem Sci 11(4):2887–2896. https://doi.org/10.20964/110402887
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Doctoral Research Foundation project of Nanyang Institute of Technology (No. 510195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, D., Wang, J., Han, P. et al. Dual-monomer molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on amino-functionalized MOFs and graphene for trace determination of taurine. Microchim Acta 190, 162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05751-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05751-w