Abstract
A new ultrasensitive sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor has been successfully constructed to quantitatively detect carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) using blackberry-like mesoporous bismuth-based nanospheres NaBiOF (NBOF NSs) inlaid with Pt nanodots (NDs) (BiPt NSs) as the antibody capture and signal-amplifying probe. The growth of Pt NDs inside the holes of NBOF NSs formed the nanozyme inlay outside NBOF NSs, greatly increasing the specific surface area and exposure of the catalytic active sites by minimizing the particle size of the Pt to nanodot scale. Such a blackberry-shaped heterojunction structure of BiPt NSs was well-suited to antibody capture and improved the catalytic performance of BiPt NSs in reducing H2O2, amplifying the signal, and yielding highly sensitive detection of CEA. The use of Au nanoparticle-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes (Au@MWCNTs) as the electrode substrates significantly enhanced the electron transfer behavior over the electrode surface, further increasing the conductivity and sensitivity of the immunosensor. Remarkably, good compatibility with human body fluid was achieved using the newly developed BiPt-based immunosensor resulting from the favorable biocompatibility and stability of both BiPt NSs and Au@MWCNTs. Benefiting from the double signal amplification strategy and the high biocompatibility, the immunosensor responded linearly to CEA in a wide range from 50 fg/mL to 100 ng/ml with an extremely low detection limit of 3.52 fg/mL (S/N = 3). The excellent detection properties of this new immunosensor were evidenced by the satisfactory selectivity, reproducibility, and stability obtained, as well as the reliable and precise determination of CEA in actual human blood samples. This work provides a new strategy for the early clinical diagnosis of cancer.
Graphical Abstract

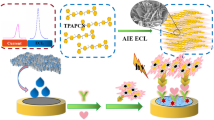
Novel blackberry-like mesoporous NaBiOF nanospheres with Pt nanodot inlay were successfully usedto construct a sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for the ultra-sensitive detection ofcarcinoembryonic antigen in human blood plasma based on a remarkable signal amplification strategy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li TT, Yi H, Liu Y, Wang ZL, Liu SQ et al (2018) One-Step Synthesis of DNA Templated Water-Soluble Au-Ag Bimetallic Nanoclusters for Ratiometric Fluorescence Detection of DNA. J Biomed Nanotechnol 14(1):150–160
Liu Y, Li TT, Ling CX, Wang ZL, Jin L et al (2019) A simple visual method for DNA detection based on the formation of gold nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett 30(12):2359–2362
Ju HX (2017) Signal Amplification for Highly Sensitive Immunosensing. J Anal Test 1(1):7
Ju HX (2011) Sensitive biosensing strategy based on functional nanomaterials. Sci China Chem 54(8):1202–1217
Lei JP, Ju HX (2012) Signal amplification using functional nanomaterials for biosensing. Chem Soc Rev 41(6):2122–2134
Lan QC, Shen HF, Li J, Ren CLH, Yang XY, Z. J. (2020) Facile synthesis of novel reduced graphene oxide@polystyrene nanospheres for sensitive label-free electrochemical immunoassay. Chem Commun 56(5):699–702
Cao J, Ouyang P, Yu S, Shi F, Ren C, Wang C et al (2021) Hedgehog-like Bi2S3 nanostructures: a novel composite soft template route to the synthesis and sensitive electrochemical immunoassay of the liver cancer biomarker. Chem Commun 57(14):1766–1769
Lan Q, Ren C, Lambert A, Zhang G, Li J, Cheng Q et al (2020) Platinum Nanoparticle-decorated Graphene Oxide@Polystyrene Nanospheres for Label-free Electrochemical Immunosensing of Tumor Markers. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(11):4392–4399
Shi F, Xu J, Hu Z, Ren C, Xue Y, Zhang Y et al (2021) Bird nest-like zinc oxide nanostructures for sensitive electrochemical glucose biosensor. Chin Chem Lett 32(10):3185–3188
Dong X, Zhao GH, Li YY, Zeng QZ, Ma HM et al (2022) Dual-Mechanism Quenching of Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on a Novel ECL Emitter Polyoxomolybdate-Zirconia for 17 beta-Estradiol Detection. Anal Chem 94(37):12742–12749
Wu TT, Song XZ, Ren X, Dai L, Ma HM et al (2022) Catalytic Decomposition of the Hole-Derived H2O2 by AgBiS2@Ag Nanozyme to Enhance the Photocurrent of Z-Scheme BiVO4/ZnIn2S4 Photoelectrode in Microfluidic Immunosensing Platform. Anal Chem 94:12127–12135
Xu QN, Yan F, Lei JP, Leng C, Ju HX (2012) Disposable Electrochemical Immunosensor by Using Carbon Sphere/Gold Nanoparticle Composites as Labels for Signal Amplification. Chem Eur J 18(16):4994–4998
Cui ZT, Wu D, Zhang Y, Ma HM, Li H et al (2014) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensors for multiplexed determination using mesoporous platinum nanoparticles as nonenzymatic labels. Anal Chim Acta 807:44–50
Wang C, Li ZH, Ju HX (2021) Copper-Doped Terbium Luminescent Metal Organic Framework as an Emitter and a Co-reaction Promoter for Amplified Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay. Anal Chem 93(44):14878–14884
Jordan W (2005) Competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Methods Mol Biol 295:215–226
Huang X, Lin QY, Lu LL, Li MJ, Tang DP (2022) In2O3/CdIn2S4 heterojunction-based photoelectrochemical immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen with enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation for signal amplification. Anal Chim Acta 1228:340358
Hajdu SI (2021) Pathfinders in oncology from the time the causal relation between tobacco use and lung cancer was established to publication of the first Cancer Staging Manual by the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer 127(16):2828–2854
Li L, Liu C, Cao XW, Wang Y, Dong J et al (2017) Determination of Carcinoembryonic Antigen by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Using Gold Nanobowl Arrays. Anal Lett 50(6):982–998
Zou K, Gao ZG, Deng QF, Luo Y, Zou LJ et al (2016) Picomolar detection of carcinoembryonic antigen in whole blood using microfluidics and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Electrophoresis 37(5-6):786–789
Zhao S (2019) Aptamer-Based Microchip Electrophoresis Assays for Amplification Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Methods Mol Biol 1972:251–259
Li J, Wu J, Cui L, Liu MM, Yan F et al (2016) Proximity hybridization-regulated electrochemical stripping of silver nanoparticles via nanogold induced deposition for immunoassay. Analyst 141(1):131–136
Wang LS, Leng C, Tang S, Lei JP, Ju HX (2012) Enzyme-free signal amplification for electrochemical detection of Mycobacterium lipoarabinomannan antibody on a disposable chip. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):421–424
Ge YQ, Wu J, Ju HX, Wu S (2014) Ultrasensitive enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor based on hybridization chain reaction triggered double strand DNA@Au nanoparticle tag. Talanta 120:218–223
Lai GS, Wang LL, Wu J, Ju HX, Yan F (2012) Electrochemical stripping analysis of nanogold label-induced silver deposition for ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of tumor markers. Anal Chim Acta 721:1–6
Ma EH, Wang P, Yang QS, Yu HX, Pei FB et al (2019) Electrochemical immunosensor based on MoS2 NFs/Au@AgPt YNCs as signal amplification label for sensitive detection of CEA. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111580
Jia YL, Li YY, Zhang S, Wang P, Liu Q et al (2020) Mulberry-like Au@PtPd porous nanorods composites as signal amplifiers for sensitive detection of CEA. Biosens Bioelectron 149
Cao LL, Xiao HL, Fang C, Zhao FJ, Chen ZC (2020) Electrochemical immunosensor based on binary nanoparticles decorated rGO-TEPA as magnetic capture and Au@PtNPs as probe for CEA detection. Microchim Acta 187(10):584
Tian XL, Cao PH, Sun D, Wang ZM, Dinga M et al (2020) Synthesis of CeBi0.4O3.7 nanofeather for ultrasensitive sandwich-like immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Appl Surf Sci 528:146956
Wang ZM, Tian XL, Sun D, Cao PH, Ding MK et al (2020) A new Bi2MoO6 nano-tremella-based electrochemical immunosensor for the sensitive detection of a carcinoembryonic antigen. RSC Adv 10(27):15870–15880
Bao CZ, Liu X, Shao XR, Ren X, Zhang Y et al (2020) Cardiac troponin I photoelectrochemical sensor: {Mo-368} as electrode donor for Bi2S3 and Au co-sensitized FeOOH composite. Biosens Bioelectron 157:112157
Liu Y, Zheng YL, Chen Z, Qin YL, Guo R (2019) High-Performance Integrated Enzyme Cascade Bioplatform Based on Protein-BiPt Nanochain@Graphene Oxide Hybrid Guided One-Pot Self-Assembly Strategy. Small 15(12):1804987
Zeng ZT, Fang SY, Tang D, Xiao R, Tang L et al (2019) Ultrasensitive sensor based on novel bismuth carbon nanomaterial for lead and cadmium determination in natural water, contaminated soil and human plasma. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 284:177–185
Wang XY, Chen Y, Mei LP, Wang AJ, Yuan PX et al (2020) Confining signal probe in porous PdPtCoNi@Pt-skin nanopolyhedra to construct a sandwich-type electrochemical immmunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of creatine kinase-MB. Sens. Actuators B Chem 315:128088
Liu J, Zhang J, Huang F, Deng Y, Li B et al (2020) X-ray and NIR light dual-triggered mesoporous upconversion nanophosphor/Bi heterojunction radiosensitizer for highly efficient tumor ablation. Acta Biomate 113:570–583
Liu J, Deng Y, Qin XJ, Li B, Zhang JP et al (2019) Ultrafast Synthesizing Bismuth Mesoporous Nanolitchi Radiosensitizer Loading High Dose DOX for CT-Guided Enhanced Chemoradiotherapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(46):42932–42942
Kouame BSR, Baranton S, Brault P, Canaff C, Chamorro-Coral W et al (2020) Insights on the unique electro-catalytic behavior of PtBi/C materials. Electrochim Acta 329:135161
Li FY, Feng JH, Gao ZQ, Shi L, Wu D et al (2019) Facile Synthesis of Cu2O@TiO2-PtCu Nanocomposites as a Signal Amplification Strategy for the Insulin Detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(9):8945–8953
Zhang Z, Sebe G, Wang XS, Tam KC (2018) Gold nanoparticles stabilized by poly(4-vinylpyridine) grafted cellulose nanocrystals as efficient and recyclable catalysts. Carbohydr Polym 182:61–68
Sun XB, Ye YK, He SD, Wu ZY, Yue JY et al (2019) A novel oriented antibody immobilization based voltammetric immunosensor for allergenic activity detection of lectin in kidney bean by using AuNPs-PEI-MWCNTs modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111607
Qin X, Liu J, Xu Y, Li B, Cheng J, Wu X, Zhang J, Liu Z, Ning R, Li Y, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Lu JJ (2020) Mesoporous Bi-containing radiosensitizer loading with DOX to repolarize tumor-associated macrophages and elicit immunogenic tumor cell death to inhibit tumor progression. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 12:31225–31234
Lee H, Sohn Y, Rhee CK (2020) Pt Deposits on Bi/Pt NP Catalyst for Formic Acid Oxidation: Catalytic Enhancement and Longer Lifetime. Langmuir 36(19):5359–5368
Song DD, Zheng J, Myung NV, Xu JL, Zhang M (2021) Sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for CEA detection using magnetic hollow Ni/C@SiO2 nanomatrix and boronic acid functionalized CPS@PANI@Au probe. Talanta 225: 122006
Khan MS, Ameer H, Chi YW (2021) Label-Free and Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescent Immunosensor Based on Novel Luminophores of Ce2Sn2O7 Nanocubes. Analytical Chemistry 93(7): 3618-3625
Song X et al (2022) Trimetallic nanoparticle-decorated MXene nanosheets for catalytic electrochemical detection of carcinoembryonic antigen via Exo III-aided dual recycling amplifications. Sensors Actuators B Chem 359:131617
Krishnan S, He XX, Zhao FJ, Zhang YQ, Liu SH et al (2020) Dual labeled mesoporous silica nanospheres based electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chim Acta 1133:119–127
Chen SY, Yang YX, Li WJ, Song YJ, Shi L et al (2020) A sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor using Ag@CeO2-Au as a lable for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchem J 159:105415
Jiang L, Chen PW, Zha L, Liu JY, Sun D et al (2022) Enhanced catalytic amplification of mesoporous bismuth-gold nano-electrocatalyst triggering efficient capture of tumor marker. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 220:112924
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (19ZR1434800), Shanghai Collaborative Innovation Center of Energy Therapy for Tumors, Clinical research project of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (201940078), and Scientific research program of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission (21140903200). The authors greatly appreciated this support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare in this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, R., Zhang, W., Liu, J. et al. Pt Nanodot Inlaid Mesoporous NaBiOF Nanoblackberry for Remarkable Signal Amplification Toward Biomarker Detection. Microchim Acta 190, 214 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05789-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05789-w