Abstract
Usually, carbon dots (CDs) display a relatively weak fluorescence quantum yield (QY). In order to obtain brighter CDs, phosphorus and chlorine co-doped CDs (P,Cl-CDs) were prepared via hydrothermal treatment of maltose in the presence of phosphoric and hydrochloric acids. The new CDs are highly monodispersed in water solution, have high fractions of P (14.4 atomic%) and Cl (8.9 atomic%), and exhibited yellow fluorescence with a QY of 15%. This is higher than that of monoatomic doped CDs (8.7 and 9.3% for P-CDs and Cl-CDs, respectively). The P,Cl-CDs are highly photostable, and fluorescence is strongly (statically) quenched by Fe(III). Fluorescence decreases with increasing concentration of Fe(III) in the range from 0.1–8.0 μmol⋅L-1, with a 60 nmol⋅L-1 detection limit. The doped CDs are shown to be a viable nanoprobe for the fluorometric determination of Fe(III) in spiked serum and water samples.

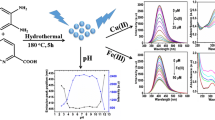
Schematic presentation of one-step synthesis of phosphorus and chlorine co-doped carbon dots with high photoluminescence for the detection of ferric ions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atchudan R, Edison T, Aseer KR, Perumal S, Karthik N, Lee YR (2018) Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe(III) ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens Bioelectron 99:303–311
Wang R, Wang X, Sun Y (2017) One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sens Actuat B-Chem 241:73–79
Chen TH, Tseng WL (2017) Self-assembly of monodisperse carbon dots into high-brightness nanoaggregates for cellular uptake imaging and iron(III) sensing. Anal Chem 89:11348–11356
Wang C, Hu T, Wen Z, Zhou J, Wang X, Wu Q, Wang C (2018) Concentration-dependent color tunability of nitrogen-doped carbon dots and their application for iron(III) detection and multicolor bioimaging. J Colloid Interface Sci 521:33–41
Li L, Ning X, Qian Y, Pu G, Wang Y, Zhang X, Wang H, Chen J, Shan D, Lu X (2018) Porphyrin nanosphere–graphene oxide composite for ehanced electrochemiluminescence and sensitive detection of Fe(III) in human serum. Sens Actuat B-Chem 257:331–339
Lunvongsa S, Oshima M, Motomizu S (2006) Determination of total and dissolved amount of iron in water samples using catalytic spectrophotometric flow injection analysis. Talanta 68:969–973
Andersen JE (2005) A novel method for the filterless preconcentration of iron. Analyst 130:85–90
Wang B, Hai J, Liu Z, Wang Q, Yang Z, Sun S (2010) Selective detection of iron(III) by rhodamine-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:4576–4579
Peng W, Yan L, Yan XP (2009) CdTe quantum dots (QDs) based kinetic discrimination of Fe2+ and Fe(III), and CdTe QDs-fenton hybrid system for sensitive photoluminescent detection of Fe2+. Anal Chem 81:6252–6257
Zhang T, Fan H, Liu G, Jiang J, Zhou J, Jin Q (2008) Different effects of Fe2+ and Fe(III) on conjugated polymer PPESO3: a novel platform for sensitive assays of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Chem Commun 42:5414–5416
Wang X, Sun G, Li N, Chen P (2016) Quantum dots derived from two-dimensional materials and their applications for catalysis and energy. Chem Soc Rev 45:2239–2262
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:362–381
Sun YQ, Wang XJ, Wang C, Tong DY, Wu Q, Jiang KL, Jiang YN, Wang CX, Yang MH (2018) Red emitting and highly stable carbon dots with dual response to pH values and ferric ions. Microchim Acta 185:83–91
Liu YN, Xue HY, Liu JH, Wang QZ, Wang L (2018) Carbon quantum dot-based fluorometric nitrite assay by exploiting the oxidation of iron(II) to iron(III). Microchim Acta 185:129–136
Wang FX, Hao QL, Zhang YH, Xu YJ, Lei W (2016) Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:273–279
Lin L, Rong M, Lu S, Song X, Zhong Y, Yan J, Wang Y, Chen X (2015) A facile synthesis of highly luminescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for the detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol in aqueous solution. Nanoscale 7:1872–1878
Kundu S, Yadav RM, Narayanan TN, Shelke MV, Vajtai R, Ajayan PM, Pillai VK (2015) Synthesis of N, F and S co-doped graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 7:11515–11519
Wu F, Yang M, Zhang H, Zhu S, Zhu X, Wang K (2018) Facile synthesis of sulfur-doped carbon quantum dots from vitamin B1 for highly selective detection of Fe(III) ion. Opt Mater 77:258–263
Zhang L, Zhang ZY, Liang RP, Li YH, Qiu JD (2014) Boron-doped graphene quantum dots for selective glucose sensing based on the "abnormal" aggregation-induced photoluminescence enhancement. Anal Chem 86:4423–4430
Qu D, Sun Z, Zheng M, Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang G, Zhao H, Liu X, Xie Z (2015) Three colors emission from S,N co-doped graphene quantum dots for visible light H2 production and bioimaging. Adv Opt Mater 3:360–367
Li Y, Li S, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu H, Liu X, Wang L, Liu X, Xue W, Ma N (2017) Electrochemical synthesis of phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dots for free radical scavenging. Phys Chem Chem Phys 19:11631–11638
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang Y, Routh P, Sk MA, Than A, Lin M, Zhang J, Chen J, Sun H, Chen P (2015) Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped graphene quantum dots: synthesis from adenosine triphosphate, optical properties, and cellular imaging. Nanoscale 7:8159–8165
Li X, Lau SP, Tang L, Ji R, Yang P (2013) Multicolour light emission from chlorine-doped graphene quantum dots. J Mater Chem C 1:7308–7313
Rao L, Tang Y, Li Z, Ding X, Liang G, Lu H, Yan C, Tang K, Yu B (2017) Efficient synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon dots by microreactor method and their application in Fe(III) ion detection. Mater Sci Eng C 81:213–223
Khan WU, Wang D, Zhang W, Tang Z, Ma X, Ding X, Du S, Wang Y (2017) High quantum yield green-emitting carbon dots for Fe(III) detection, biocompatible fluorescent ink and cellular imaging. Sci Rep 7:14866–14875
Shi B, Su Y, Zhang L, Huang M, Liu R, Zhao S (2016) Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbon nanodots as a novel fluorescent probe for highly sensitive detection of Fe(III) in human serum and living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:10717–10725
Han Y, Tang D, Yang Y, Li C, Kong W, Huang H, Liu Y, Kang Z (2015) Non-metal single/dual doped carbon quantum dots: a general flame synthetic method and electro-catalytic properties. Nanoscale 7:5955–5962
Tam TV, Choi WM (2018) One-pot synthesis of highly fluorescent amino-functionalized graphene quantum dots for effective detection of copper ions. Curr Appl Phys 18:1255–1260
Li L, Yu B, You T (2015) Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive detection of Hg (II) ions. Biosens Bioelectron 74:263–269
Qian ZS, Shan XY, Chai LJ, Chen JR, Feng H (2015) A fluorescent nanosensor based on graphene quantum dots-aptamer probe and graphene oxide platform for detection of lead (II) ion. Biosens Bioelectron 68:225–231
Qu KG, Wang JS, Ren JS, Qu XG (2013) Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem Eur J 19:7243–7249
Sachdev A, Gopinath P (2015) Green synthesis of multifunctional carbon dots from coriander leaves and their potential application as antioxidants, sensors and bioimaging agents. Analyst 140:4260–4269
Zhou M, Zhou ZL, Gong AH, Zhang Y, Li QJ (2015) Synthesis of highly photoluminescent carbon dots via citric acid and Tris for iron(III) ions sensors and bioimaging. Talanta 143:107–113
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21675062), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Fujian Province, China (2017 J05024, 2018D0019), and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University (NCETFJ, B16164).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 716 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Peng, J., Li, F. et al. Phosphorus and chlorine co-doped carbon dots with strong photoluminescence as a fluorescent probe for ferric ions. Microchim Acta 186, 32 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3140-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3140-8