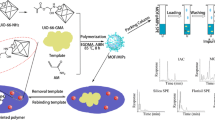
Abstract
A core consisting of nanoporous carbon (MNPC) and magnetized with Co3O4 was coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) by atom transfer radical precipitation polymerization. Ethyl 3-coumarincarboxylate was used as a pseudo-template to give a MIP that has a fairly specific recognition capability for aflatoxins. Batch rebinding studies were carried out to determine the specific adsorption equilibrium and specific recognition. Extraction is achieved in a single step by mixing and vortexing the sample extract with the Co-MNPC@MIP. The loaded nanosorbent was then magnetically separated and eluted with acetonitrile/water (6/4, v/v). The aflatoxins were then quantified by HPLC. Under optimal conditions, the detection limits for aflatoxins typically are 0.05–0.07 ng mL−1, recoveries from spiked corn are found to be 75.1 to 99.4%, and relative standard deviations range from 1.7 to 5.1 (n = 6).

Poly(methacrylic acid) was imprinted with the pseudo-template ethyl 3-coumarincarboxylate by atom transfer radical precipitation polymerization on the surface of cobalt-derived magnetic nanoporous carbon (Co-MNPC). This nanosorbent was used for the magnetic solid phase extraction of aflatoxins, followed by HPLC analysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eaton DL, Groopman, JD (2013) The toxicology of aflatoxins: human health, veterinary, and agricultural significance. Academic Press, Cambridge
Liu H, Luan Y, Lu A, Li B, Yang M, Wang J (2017) An oligosorbent-based aptamer affinity column for selective extraction of aflatoxin B2 prior to HPLC with fluorometric detection. Microchim Acta 185(1):71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2591-7
Jacobsen AM, Halling-Sørensen B, Ingerslev F, Hansen SH (2004) Simultaneous extraction of tetracycline, macrolide and sulfonamide antibiotics from agricultural soils using pressurised liquid extraction, followed by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1038(1):157–170
Lindsey ME, Meyer M, Thurman E (2001) Analysis of trace levels of sulfonamide and tetracycline antimicrobials in groundwater and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 73(19):4640–4646
Anastassiades M, Lehotay SJ, Štajnbaher D, Schenck FJ (2003) Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J AOAC Int 86(2):412–431
Chen M, Wang R, Zhu Y, Liu M, Zhu F, Xiao J, Chen X (2018) 4-Mercaptophenylboronic acid-modified spirally-curved mesoporous silica nanofibers coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry for determination of brassinosteroids in plants. Food Chem 263:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.129
Wang Y, Wang E, Wu Z, Li H, Zhu Z, Zhu X, Dong Y (2014) Synthesis of chitosan molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction of methandrostenolone. Carbohydr Polym 101(supplement C):517–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.078
Tamayo F, Turiel E, Martín-Esteban A (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for solid-phase extraction and solid-phase microextraction: recent developments and future trends. J Chromatogr A 1152(1):32–40
Chen L, Xu S, Li J (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev 40(5):2922–2942
Gale PA, Steed JW (2012) Supramolecular chemistry: from molecules to nanomaterials, vol 8. Wiley,Hoboken
Komiyama M, Takeuchi T, Mukawa T, Asanuma H (2003) Molecular imprinting: from fundamentals to applications, vol 148. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Zu B, Pan G, Guo X, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2009) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer microspheres via atom transfer radical precipitation polymerization. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 47(13):3257–3270. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.23389
Patten TE, Matyjaszewski K (1998) Atom transfer radical polymerization and the synthesis of polymeric materials. Adv Mater 10(12):901–915. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-4095(199808)10:12<901::AID-ADMA901>3.0.CO;2-B
Zhang M, He J, Shen Y, He W, Li Y, Zhao D, Zhang S (2018) Application of pseudo-template molecularly imprinted polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization to the solid-phase extraction of pyrethroids. Talanta 178(supplement C):1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.100
Xie X, Chen L, Pan X, Wang S (2015) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer strategy and its application in the Sudan dyes residue analysis. J Chromatogr A 1405(supplement C):32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.05.068
Zheng L, Zhao X-E, Ji W, Wang X, Tao Y, Sun J, Xu Y, Wang X, Zhu S, You J (2018) Core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers used rhodamine B hydroxyproline derivate as template combined with in situ derivatization for the specific measurement of L-hydroxyproline. J Chromatogr A 1532:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2017.11.053
Anirudhan TS, Christa J, Deepa JR (2017) Extraction of melamine from milk using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem 227:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.12.090
Liu G, Jiang Z, Cao K, Nair S, Cheng X, Zhao J, Gomaa H, Wu H, Pan F (2017) Pervaporation performance comparison of hybrid membranes filled with two-dimensional ZIF-L nanosheets and zero-dimensional ZIF-8 nanoparticles. J Membr Sci 523(supplement C):185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.09.064
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Li Z, Zang X, Wang Z (2014) Metal–organic framework derived magnetic Nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem 86(24):12199–12205
Tan L, He R, Chen K, Peng R, Huang C, Yang R, Tang Y (2016) Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry for determination of aflatoxins using dummy molecularly imprinted polymers deposited on silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(4):1469–1477
Low Z-X, Yao J, Liu Q, He M, Wang Z, Suresh AK, Bellare J, Wang H (2014) Crystal transformation in Zeolitic-Imidazolate framework. Cryst Growth Des 14(12):6589–6598. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg501502r
Sorribes-Soriano A, Esteve-Turrillas FA, Armenta S, Montoya A, Herrero-Martínez JM, de la Guardia M (2018) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective determination of cocaine by ion mobility spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1545:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.055
Yáñez-Sedeño P, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM (2017) Electrochemical sensors based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers: a review. Anal Chim Acta 960:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.01.003
Huang S, Xu J, Zheng J, Zhu F, Xie L, Ouyang G (2018) Synthesis and application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers in sample preparation. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:3991–4014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1013-y
Xie L, Guo J, Zhang Y, Hu Y, You Q, Shi S (2015) Novel molecular imprinted polymers over magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective and efficient determination of protocatechuic acid in Syzygium aromaticum. Food Chem 178:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.069
Ning F, Qiu T, Wang Q, Peng H, Li Y, Wu X, Zhang Z, Chen L, Xiong H (2017) Dummy-surface molecularly imprinted polymers on magnetic graphene oxide for rapid and selective quantification of acrylamide in heat-processed (including fried) foods. Food Chem 221:1797–1804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.101
Wang L, Zhu F, Chen M, Zhu Y, Xiao J, Yang H, Chen X (2019) Rapid and visual detection of aflatoxin B1 in foodstuffs using aptamer/G-quadruplex DNAzyme probe with low background noise. Food Chem 271:581–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.007
Zhou T, Ding J, He Z, Li J, Liang Z, Li C, Li Y, Chen Y, Ding L (2018) Preparation of magnetic superhydrophilic molecularly imprinted composite resin based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes to detect triazines in environmental water. Chem Eng J 334:2293–2302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.185
Liu X, Wang C, Wang Z, Wu Q, Wang Z (2015) Nanoporous carbon derived from a metal organic framework as a new kind of adsorbent for dispersive solid phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides. Microchim Acta 182(11):1903–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1530-8
Xing W, Zhuo S-P, Gao X-l (2009) α-Fe-incorporated nanoporous carbon with magnetic properties. Mater Lett 63(13):1177–1179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2009.02.023
Zhang X, Ji G, Liu W, Quan B, Liang X, Shang C, Cheng Y, Du Y (2015) Thermal conversion of an Fe3O4@metal-organic framework: a new method for an efficient Fe-co/nanoporous carbon microwave absorbing material. Nanoscale 7(30):12932–12942
Torad NL, Hu M, Ishihara S, Sukegawa H, Belik AA, Imura M, Ariga K, Sakka Y, Yamauchi Y (2014) Direct Synthesis of MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon with Magnetic Co Nanoparticles toward Efficient Water Treatment. Small 10(10):2096–2107. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201302910
Sellergren B (2000) Molecularly imprinted polymers: man-made mimics of antibodies and their application in analytical chemistry. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Xue S, Jiang H, Zhong Z, Low Z-X, Chen R, Xing W (2016) Palladium nanoparticles supported on a two-dimensional layered zeolitic imidazolate framework-L as an efficient size-selective catalyst. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 221:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.09.053
Nasir AM, Md Nordin NAH, Goh PS, Ismail AF (2018) Application of two-dimensional leaf-shaped zeolitic imidazolate framework (2D ZIF-L) as arsenite adsorbent: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism. J Mol Liq 250:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.12.005
Zhou K, Mousavi B, Luo Z, Phatanasri S, Chaemchuen S, Verpoort F (2016) Characterization and properties of Zn/co zeolitic imidazolate frameworks vs. ZIF-8 and ZIF-67. J Mater Chem A 5(3):952–957
Liu Q, Low Z-X, Feng Y, Leong S, Zhong Z, Yao J, Hapgood K, Wang H (2014) Direct conversion of two-dimensional ZIF-L film to porous ZnO nano-sheet film and its performance as photoanode in dye-sensitized solar cell. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 194:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.03.023
Liu S, Pan J, Zhu H, Pan G, Qiu F, Meng M, Yao J, Yuan D (2016) Graphene oxide based molecularly imprinted polymers with double recognition abilities: the combination of covalent boronic acid and traditional non-covalent monomers. Chem Eng J 290:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.061
Urraca JL, Huertas-Pérez JF, Cazorla GA, Gracia-Mora J, García-Campaña AM, Moreno-Bondi MC (2016) Development of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for selective extraction: determination of citrinin in rice samples by liquid chromatography with UV diode array detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(11):3033–3042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9348-8
Low Z-X, Razmjou A, Wang K, Gray S, Duke M, Wang H (2014) Effect of addition of two-dimensional ZIF-L nanoflakes on the properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane. J Membr Sci 460:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2014.02.026
Li X, Zhang W, Liu Y, Li R (2016) Palladium nanoparticles immobilized on magnetic porous carbon Derived from ZIF-67 as efficient catalysts for the Semihydrogenation of Phenylacetylene under extremely mild conditions. Chemcatchem 8(6):1111–1118
Wang Z, Beier RC, Shen J (2017) Immunoassays for the detection of macrocyclic lactones in food matrices – a review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 92:42–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.04.008
Gao B, Chen L, Li Y (2016) Preparation of surface imprinted material of single enantiomer of mandelic acid with a new surface imprinting technique and study on its chiral recognition and resolution properties. J Chromatogr A 1443:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.03.018
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully appreciate the financial support from the following research funds: National Natural Science Foundation of China (21575034, 51502079, 21577031, 21775140), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Henan Provincial Colleges and Universities in Henan University of Technology (2017RCJH10). We are especially indebted to Prof. Shi Bai from University of Delaware for helping to polish the language.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5043 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., He, J., Li, Y. et al. Solid-phase extraction of aflatoxins using a nanosorbent consisting of a magnetized nanoporous carbon core coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 185, 515 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3051-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3051-8