Abstract
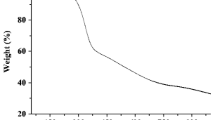
We are introducing nanoporous fructose (np-F) modified with dithizone as a new solid-phase for extraction of heavy metals ions including cadmium(II), copper(II), nickel(II) and lead(II). Effects of pH value, flow rates, type, concentration and volume of the eluent, breakthrough volume, and of other ions were studied. Under optimized conditions, the extraction efficiency is >97 %, and the limits of detection are 0.025, 0.15, 0.5 and 1.2 ng mL−1 for the ions of cadmium, copper, nickel, and lead, respectively, and the adsorption capacities for these ions are 101, 81, 74 and 178 mg g−1. The modified np-F sorbent was characterized by thermogravimetric analysis, differential thermal analysis, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, and nitrogen adsorption surface area (BET) measurements.

We are introducing nanoporous fructose (np-F) modified with dithizone as a new solid-phase for extraction of heavy metals ions including cadmium(II), copper(II), nickel(II) and lead(II). This SPE technique was successfully applied for separation, determination, and preconcentration of cadmium, copper, nickel and lead in biological, food and environmental water samples




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tabrizi HB (2007) Development of a cloud point extraction-spectrofluorimetric method for trace copper(II) determination in water samples and parenteral solutions. J Hazard Mater 139:260–264
Gama EM, Lima AS, Lemos VA (2006) Preconcentration system for cadmium and lead determination in environmental samples using polyurethane foam/Me-BTANC. J Hazard Mater 136:757–762
Maranho TA, Borges DLG, da Veiga MAMS, Curtius AJ (2005) Cloud point extraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in biological samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 60:667–672
Ferreira SLC, dos Santos WNL, Lemos VA (2001) On-line preconcentration system for nickel determination in food samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 445:145–151
Mayer MG, Wilson DN (1998) Health and safety—the downward trend in lead levels. J Power Sources 73:17–22
Duran C, Senturk HB, Elci L, Soylak M, Tufekci M (2009) Simultaneous preconcentration of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from environmental samples on Amberlite XAD-2000 column and determination by FAAS. J Hazard Mater 162:292–299
Komjarova I, Blust R (2006) Comparison of liquid–liquid extraction, solid-phase extraction and co-precipitation preconcentration methods for the determination of cadmium, copper, nickel, lead and zinc in seawater. Anal Chim Acta 576:221–228
Wei GT, Yang Z, Jung Chen C (2003) Room temperature ionic liquid as a novel medium for liquid/liquid extraction of metal ions. Anal Chim Acta 488:183–192
Matlock MM, Howerton BS, Atwood DA (2002) Chemical precipitation of lead from lead battery recycling plant wastewater. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:1579–1582
Matlock MM, Howerton BS, Atwood DA (2002) Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Res 36:4757–4764
Maliou E, Malamis M (1992) Lead and cadmium removal by ion exchange. Water Sci Technol 25:133–138
Akcin N, Koyuncu L, Akcin G (2011) Determination of zinc, nickel and cadmium in natural water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration with ion exchange and flotation techniques. Rev Anal Chem 30:65–71
Akieh MN, Lahtinen M, Väisänen A, Sillanpää M (2008) Preparation and characterization of sodium iron titanate ion exchanger and its application in heavy metal removal from waste waters. J Hazard Mater 152:640–647
Camel V (2003) Solid phase extraction of trace elements. Spectrochim Acta B 58:1177–1233
Hennion MC (1999) Solid-phase extraction: method development, sorbents, and coupling with liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 856:3–54
Ravelo-Pérez LM, Herrera-Herrera AV, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2010) Carbon nanotubes: solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1217:2618–2641
Hennion MC (2000) Graphitized carbons for solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 885:73–95
Vidal L, Riekkola ML, Canals A (2012) Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation: a review. Anal Chim Acta 715:19–41
Berrueta LA, Gallo B, Vicente F (1995) A review of solid phase extraction: basic principles and new developments. Chromatographia 40:474–483
Yang H, Xu R, Xue X, Li F, Liu G (2008) Hybrid surfactant templated mesoporous silica formed in ethanol and its application for heavy metal removal. J Hazard Mater 152:690–698
Ghaedi M, Montazerozohori M, Behfar M, Khodadoust S, Andikaey Z, Nejati Biareh M (2011) Chemically modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes as efficient material for construction of new zinc (II) ion selective carbon paste electrode. Sens Lett 9:1718–1725
Shawabkeh R, Rockstraw D, Bhada R (2002) Copper and strontium adsorption by a novel carbon material manufactured from pecan shells. Carbon 40:781–786
Kubo S, White RJ, Yoshizawa N, Antonietti M, Titirici M (2011) Ordered carbohydrate-derived porous carbons. Chem Mater 23:4882–4885
Zhou HY, Cheung RYH, Chan KM, Wong MH (1998) Metal concentrations in sediments and tilapia collected from inland waters of Hong Kong. Water Res 32:3331–3334
Wua X, Yang Y (2011) Heavy metal (Pb, Co, Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn and Zn) concentrations in harvest-size white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei tissues from aquaculture and wild source. J Food Compos Anal 24:62–65
Bagheri A, Behbahani M, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Taghizade M, Baghayi L, Salarian M (2012) Simultaneous separation and determination of trace amounts of Cd(II) and Cu(II) in environmental samples using novel diphenylcarbazide modified nanoporous silica. Talanta 89:455–461
Behbahani M, Salarian M, Amini MM, Sadeghi O, Bagheri A, Bagheri S (2012) Application of a new functionalized nanoporous silica for simultaneous trace separation and determination of Cd(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Pb(II) in food and agricultural products. Food Anal Methods. doi:10.1007/s12161-012-9545-9
Barnes K, Liang J, Worley SD, Lee J, Broughton RM, Huang TS (2007) Modification of silica gel, cellulose, and polyurethane with a sterically hindered N-Halamine moiety to produce antimicrobial activity. J Appl Polym Sci 105:2306–2613
ALOthman ZA, Habila M, Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2012) Solid phase extraction of Cd(II), Pb(II), Zn(II) and Ni(II) from food samples using multiwalled carbon nanotubes impregnated with 4-(2-thiazolylazo)resorcinol. Microchim Acta 177:397–403
Sohrabi MR, Matbouie Z, Asgharinezhad AA, Dehghani A (2013) Solid phase extraction of Cd(II) and Pb(II) using a magnetic metal-organic framework, and their determination by FAAS. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0952-4
Ayata S, Bozkurt SS, Ocakoglu K (2011) Separation and preconcentration of Pb(II) using ionic liquid-modified silica and its determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 84:212–215
Silva EL, Roldan PS, Giné MF (2009) Simultaneous preconcentration of copper, zinc, cadmium, and nickel in water samples by cloud point extraction using 4-(2-pyridylazo)-resorcinol and their determination by inductively coupled plasma optic emission spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 171:1133–1138
Ghaedi M, Ahmadi F, Shokrollahi A (2007) Simultaneous preconcentration and determination of copper, nickel, cobalt and lead ions content by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 142:272–278
Kumar M, Rathore DPS, Singh AK (2000) Amberlite XAD-2 functionalized with o-aminophenol: synthesis and applications as extractant for copper(II), cobalt(II), cadmium(II), nickel(II), zinc(II) and lead(II). Talanta 51:1187–1196
Nabid MR, Sedghi R, Bagheri A, Behbahani M, Taghizadeh M, Abdi Oskooie H, Heravi MM (2012) Preparation and application of poly(2-amino thiophenol)/MWCNTs nanocomposite for adsorption and separation of cadmium and lead ions via solid phase extraction. J Hazard Mater 203–204:93–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 171 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behbahani, M., Najafi, M., Amini, M.M. et al. Dithizone-modified nanoporous fructose as a novel sorbent for solid-phase extraction of ultra-trace levels of heavy metals. Microchim Acta 180, 911–920 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1013-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1013-8