Abstract
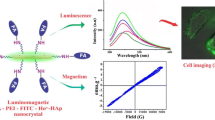
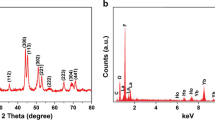
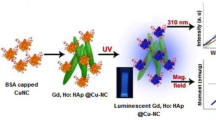
The authors report on upconversion nanocrystals (NCs) based on a fluoroapatite (FAp) support that was engineered to enable multimodal imaging by fluorescence imaging (FI), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and upconversion luminescence imaging. A fluorescein based fluorophore (FITC) was incorporated into the FAp nanocrystals and then doped with Yb(III) and Ho(III) by microwave-assisted solution combustion synthesis. The hexagonal phase nanocrystals (FITC-FAp:Yb/Ho) exhibit spindle like morphology with an average diameter and length of 15 nm and 196 nm, respectively. The doping concentration of the Yb (5 %) and Ho (0.6 %) was determined by ICP-MS. The nanocrystals exhibit upconversion luminescence when irradiated with NIR light of wavelength 980 nm. The emission spectrum consists of two bands centered at 542 nm (green emission) and 654 nm (red emission) corresponding to two transitions of Ho(III). The pump power dependence of upconversion luminescence intensity confirmed the 2-photon process. The presence of FITC in the nanocrystal imparts green fluorescence (peaking at 521 nm) by a conventional downconversion process. The presence of Ho(III) endows the NCs with paramagnetism. The magnetization is 21.063 emu∙g−1 at room temperature. The NCs exhibit a longitudinal relaxivity (r1) of 0.12 s−1∙mM−1, and a transverse relaxivity (r2) of 29 s−1∙mM−1, which makes the system suitable for developing T2 MRI contrast agents. The nanocrystals are surface aminized using polyethyleneimine (PEI) and covalently conjugated to folic acid (FA) in order to target the folate receptors that are overexpressed in many cancer cells. The FA-conjugated nanocrystals have been tested for their applicability in fluorescence imaging of HeLa cells. Their biocompatibility, upconversion and downconversion luminescence, and magnetism render these NCs potentially powerful nanoprobes for trimodal imaging.

Fluorescein-labeled fluorapatite nanocrystals codoped with Yb(III) and Ho(III) ions (FITC-FAp:Yb/Ho) have been prepared through microwave route. The up and downconversion luminescence, biocompatibility and magnetism are explored. The folic acid conjugated nanocrystals are promising candidates for trimodal imaging (up- and downconversion imaging and magnetic resonance imaging)









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee SY, Jeon SI, Jung S, Chung IJ, Ahn C-H (2014) Targeted multimodal imaging modalities. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 76:60–78
Jennings LE, Long NJ (2009) ‘two is better than one’-probes for dual modality molecular imaging. Chem Commun:3511–3524
Ashokan A, Menon D, Nair S, Koyakutty M (2010) A molecular receptor targeted, hydroxyapatite nanocrystals based multi-modal contrast agent. Biomaterials 31:2606–2616
Syamchand SS, Sony G (2015) Multifunctional hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for drug delivery and multimodal molecular imaging. Microchim Acta 182:1567–1589
Nikcevic I, Jokanovic V, Mitric M, Nedic Z, Makovec D, Uskokovic D (2004) Mechanochemical synthesis of nanostructured fluorapatite/fluorhydroxyapatite and carbonated fluorapatite/fluorhydroxyapatite. J Solid State Chem 177:2565–2574
Chen H, Sun K, Tang Z, Law RV, Mansfield JF, −Jakubowska AC, Clarkson, BH (2006) Synthesis of fluorapatite nanorods and nanowires by direct precipitation from solution. Cryst Growth Des 6: 1504–1508
Hui J, Wang X (2011) Luminescent, colloidal, F-substituted, hydroxyapatite nanocrystals. Chem Eur J 17:6926–6930
Fathi MH, Zahrani EM (2009) Mechanochemical alloying synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of nanocrystalline fluoridated hydroxyapatite. J Crystal Growth 311:1392–1403
Eslami H, Hashjin MS, Tahriri M (2009) The comparison of powder characteristics and physicochemical, mechanical and biological properties between nanostructure ceramics of hydroxyapatite and fluoridated hydroxyapatite. Mater Sci Eng C 29:1387–1398
Zeng H, Li X, Xie F, Teng L, Chen H (2014) Dextran-coated fluorapatite nanorods doped with lanthanides in labelling and directing osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Mater Chem 2:3609–3617
Hui J, Zhang X, Zhang Z, Wang S, Tao L, Wei Y, Wang X (2012) Fluoridated hap: ln3+ (Ln = Eu or Tb) nanaoparticles for cell-imaging. Nanoscale 4:6967–6970
Cheng L, Yang K, Li Y, Zeng X, Shao M, Lee S-T, Liu Z (2012) Multifunctional nanoparticles for upconversion luminescence/MR multimodal imaging and magnetically targeted photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 33:2215–2222
Mader HS, Kele P, Saleh SM, Wolfbeis OS (2010) Upconverting luminescent nanoparticles for use in bioconjugation and bioimaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol 14:582–596
DaCosta MV, Doughan S, Han Y, Krull UJ (2014) Lanthanide upconversion nanoparticles and applications in bioassays and bioimaging: a review. Anal Chim Acta 832:1–33
Sun L-D, Wang Y-F, Yan C-H (2014) Paradigms and challenges for Bioapplication of rare earth upconversion luminescent nanoparticles: small size and tunable emission/excitation spectra. Acc Chem Res 47:1001–1009
Chen C, Li C, Shi Z (2016) Current advances in lanthanide-doped upconversion nanostructures for detection and Bioapplication. Adv Sci 1600029:1–26
Boyer J-C, Cuccia LA, Capobianco JA (2007) Synthesis of colloidal Upconverting NaYF4: Er3+/Yb3+ and Tm3+/Yb3+ monodisperse nanocrystals. Nano Lett 7:847–852
Zhou J, Liu Q, Feng W, Sun Y, Li F (2015) Upconversion LuminescentMaterials: advances and applications. Chem Rev 115:395–465
Lecuna CR, Rodriguez RM, Valiente R (2011) Origin of the high upconversion green luminescence efficiency in β-NaYF4:2%Er3+, 2 % Yb3+. Chem Mater 23:3442–3448
Naccache R, Yu Q, Capobianco JA (2015) The fluoride host: nucleation, growth, and upconversion of lanthanide-doped nanoparticles. Adv Opt Mater 3:482–509
Haase M, Schafer H (2011) Upconverting Naoparticles. Angew Chem Int Edn 50:5808–5829
Hu X, Zhu J, Li X, Zhang X, Meng Q, Yuan L, Zhang J, Fu X, Duan X, Chen H, Ao Y (2015) Dextran-coated fluorapatite crystals doped with Yb3+/Ho3+ for labelling and tracking chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 52:441–451
Li X, Zhu J, Man Z, Ao Y, Chen H (2014) Investigation on the structure and upconversion fluorescence of Yb3+/Ho3+ co-doped fluorapatite crystals for potential biomedical applications. Sci Rep 4(4446):1–7
Nicolay K, Strijkers G, Grull H (2013)Gd- Containing nanoparticles as MRI contrast agents In: Merbach A et al (ed) The chemistry of contrast agents in medical magnetic resonance imaging, 2nd edn, Wiley, UK, pp 449–483
Das GK, Johnson NJJ, Cramen J, Blasiak B, Latta P, Tomanek B, vanVeggel FCJM (2012) NaDyF4 nanoparticles as T2 contrast agents for ultrahigh field magnetic resonance imaging. J Phys Chem Lett 3:524–529
Imhof A, Megens M, Engelberts JJ, deLang DTN, Sprik R, Vos WL (1999) Spectroscopy of fluorescein (FITC) dyed colloidal silica spheres. J Phys Chem B103:1408–1415
Nabiyouni M, Zhou H, Luchini TJF, Bhaduri SB (2014) Formation of nanostructured fluorapatite via microwave assisted solution synthesis. Mater Sci Eng C 37:363–368
Montazeri N, Jahandideh R, Biazer E (2011) Synthesis of fluorapatite- hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and toxicity investigations. Int J Nanomed 6:197–201
Liu S, Yin Y, Chen H (2013) PEO-assisted precipitation of human enamel-like fluorapatite films for tooth whitening. Cryst Eng Comm 15:5853–5859
Escudero A, Calvo ME, Fernandez SR, de laFuente JM, Ocana M (2013) Microwave –assisted synthesis of biocompatible europium-doped calcium hydroxyapatite and Fluoroapatie luminescent nanospindles functionalized with poly(acrylic acid). Langmuir 29:1985–1994
Yu X, Liang S, Sun Z, Duan Y, Qin Y, Duan L, Xia H, Zhao P, Li D (2014) Microstructure and upconversion luminescence in Ho3+ and Yb3+ co-doped ZnO nanocrystalline powders. Opt Commun 313:90–93
Norek M, Peters JA (2011) MRI contrast agents based on dysprosium or holmium. Progress in NMR 59:64–82
Voung QL, Doorslaer SV, Bridot J-L, Argante C, Alejandro G, Hermann R, Disch S, Mattea C, Stapf S, Gossuin Y (2012) Paramagnetic nanoparticles as potential MRI contrast agents: characterization, NMR relaxation, simulations and theory. Magn Reson Mater Phy 25:467–478
Kattel K, Park JY, Xu W, Kim HG, Lee EJ, Bony BA, Heo WC, Lee JJ, Jin S, Baeck JS, Chang Y, Kim TJ, Bae JE, Chae KS, Lee GH (2011) A facile synthesis, in vitro and in vivo MR studies of D-glucuronic acid-coated ultra small Ln2O3 (Ln = Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, and Er) nanoparticles as a new potential MRI contrast agent. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:3325–3334
Ma J, Huang P, He M, Pan L, Zhou Z, Feng L, Gao G, Cui D, Ohys J (2012) Folic acid-conjugated LaF3:Yb,Tm@SiO2 nanoprobes for targeting dual-modality imaging of upconversion luminescence and X-ray computed tomography. Chem B 116:14062–14070
Wolfbeis OS (2015) An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bioimaging. Chem Soc Rev 44:4743–4768
Chen M, Yin M (2014) Design and development of fluorescent nanostructures for bioimaging. Prog Polym Sci 39:365–395
Ai J, Xu Y, Li D, Liu Z, Wang E (2012) Folic acid as delivery vehicles: targeting folate conjugated fluorescent nanoparticles to tumour imaging. Talanta 101:32–37
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Director, National Centre for Ultrafast Process (NCUP, University of Madras), Director, CSIR-NIIST (Thiruvananthapuram), Head, SAIF-IIT Madras, Director, IISER (Thiruvanathapuram), Director, SAIF-STIC-CUSAT (Kochi) and the Head, Department of Chemistry, University of Kerala (Kariavattom Campus), Thiruvananthapuram, for the sophisticated characterization techniques provided for the work. S.S. S would like to acknowledge University Grant Commission (UGC) New Delhi, for providing financial assistance through Teacher Fellowship under Faculty Improvement programme (FIP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 571 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Syamchand, S.S., Sony, G. Fluorescein-labeled fluoroapatite nanocrystals codoped with Yb(III) and Ho(III) for trimodal (downconversion, upconversion and magnetic resonance) imaging of cancer cells. Microchim Acta 183, 3209–3219 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1970-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1970-9