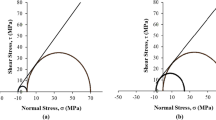
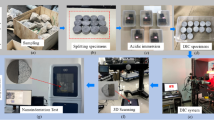
Abstract
Studies investigating the effect of high temperatures on physical and strength properties of natural rocks face the problem of sample heterogeneity even if the samples are prepared from the same block. The general approach available in the literature involves using different groups of samples for each temperature level during heat treatment and testing. In this study, a different approach where entire heat treatment and testing is conducted on the same samples was introduced. Disc-shaped samples were prepared from three volcanic rocks, and six groups containing five samples were created. One group from each rock type were treated at temperatures of 200, 350, 500, and 680 °C in successive steps. Two non-destructive tests (NDT), Leeb hardness, and P-wave velocity measurements, were conducted on the samples after each heat treatment step. After the last heat treatment step, ultimate tensile strengths of the samples were determined through Brazilian tests. Five groups from each rock type were tested according to the general approach. Results indicate that the suggested approach better represents the thermal damage inflicted on the samples because irrelevant and inconsistent data caused by sample heterogeneity is not present. Evaluation of thermal treatment coefficients, scanning electron microscope images, and X-ray diffractometers indicated that the heating–cooling cycles applied during the suggested approach does not cause significant exhaustion on the samples. An estimation model was established to estimate the thermal damage inflicted on the samples using NDT. Tensile strength of the samples for a desired temperature can also be predicted by the suggested estimation model.
Highlights
-
Heterogeneous physical and strength properties of rocks prevent examining their response to high temperatures properly.
-
A new methodology where same group of samples are used at each temperature step in heat treatment and testing is proposed.
-
Suggested methodology better represent the thermal damage inflicted on the samples than the general methodology available in the literature.
-
Thermal treatment coefficients, SEM images, and XRD analyses indicate samples do not suffer fatigue because of the suggested methodology.
-
An estimation model is proposed to accurately predict the tensile strength of the samples for a desired temperature using non-destructive tests.















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
02 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03142-w
References
Anon OH (1979) Classification of rocks and soils for engineering geological mapping: Part 1—rock and soil materials. Bull Int Assoc Eng Geol 19:364–371
Aoki H, Matsukura Y (2008) Estimating the unconfined compressive strength of intact rocks from Equotip hardness. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-007-0116-z
Arslan M, Temizel I, Abdioğlu E, Kolaylı H, Yücel C, Boztuğ D, Şen C (2013) 40 Ar–39 Ar dating, whole-rock and Sr–Nd–Pb isotope geochemistry of post-collisional Eocene volcanic rocks in the southern part of the Eastern Pontides (NE Turkey): implications for magma evolution in extension-induced origin. Contrib Mineral Petrol 166:113–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-013-0868-3
Asiri Y, Corkum A, Naggar HE (2016) Leeb hardness test for UCS estimation of sandstone. 69th GeoVancouver Conference, Vancouver, Canada
Aydin F, Karsli O, Chen B (2008) Petrogenesis of the Neogene alkaline volcanics with implications for post-collisional lithospheric thinning of the Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Lithos 104:249–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.010
Beck K, Janvier-Badosa S, Brunetaud X, Török Á, Al-Mukhtar M (2016) Non-destructive diagnosis by colorimetry of building stone subjected to high temperatures. Eur J Environ Civ Eng 20:643–655. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2015.1035804
Broch E, Franklin JA (1972) The point-load strength test. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 9:669–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(72)90030-7
Brotóns V, Tomás R, Ivorra S, Alarcón JC (2013) Temperature influence on the physical and mechanical properties of a porous rock: San Julian’s calcarenite. Eng Geol 167:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.012
Browning J, Meredith P, Gudmundsson A (2016) Cooling-dominated cracking in thermally stressed volcanic rocks. Geophys Res Lett 43:8417–8425. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070532
Chaki S, Takarli M, Agbodjan WP (2008) Influence of thermal damage on physical properties of a granite rock: porosity, permeability and ultrasonic wave evolutions. Constr Build Mater 22:1456–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.04.002
Chen S, Yang C, Wang G (2017) Evolution of thermal damage and permeability of Beishan granite. Appl Therm Eng 110:1533–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.075
Corkum AG, Asiri Y, El Naggar H, Kinakin D (2018) The Leeb hardness test for rock: an updated methodology and UCS correlation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51:665–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1372-2
Crosby ZK, Gullett PM, Akers SA, Graham SS (2018) Characterization of the mechanical behavior of Salem limestone containing thermally-induced microcracks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 101:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.002
Desarnaud J, Kiriyama K, Bicer Simsir B, Wilhelm K, Viles H (2019) A laboratory study of Equotip surface hardness measurements on a range of sandstones: what influences the values and what do they mean? Earth Surf Process Landforms 44:1419–1429. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.4584
Dong Z, Sun Q, Ye J, Zhang W (2020) Changes in color and roughness of red sandstone at high temperatures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1959–1966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01678-w
Ersoy H, Acar S (2016) Influences of petrographic and textural properties on the strength of very strong granitic rocks. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6277-y
Ersoy H, Yalçinalp B, Arslan M, Babacan AE, Çetiner G (2016) Geological and geomechanical properties of the carbonate rocks at the eastern Black Sea Region (NE Turkey). J African Earth Sci 123:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.07.026
Ersoy H, Kolaylı H, Karahan M, Harputlu H, Sünnetci MO (2019a) Effect of thermal damage on mineralogical and strength properties of basic volcanic rocks exposed to high temperatures. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:1515–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1208-z
Ersoy H, Karahan M, Babacan AE, Sünnetci MO (2019b) A new approach to the effect of sample dimensions and measurement techniques on ultrasonic wave velocity. Eng Geol 251:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.02.011
Ersoy H, Karahan M, Kolaylı H, Sünnetci MO (2021a) Influence of mineralogical and micro-structural changes on the physical and strength properties of post-thermal-treatment clayey rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:679–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02282-1
Ersoy H, Atalar C, Sünnetci MO, Kolaylı H, Karahan M, Fırat Ersoy A (2021b) Assessment of damage on geo-mechanical and micro-structural properties of weak calcareous rocks exposed to fires using thermal treatment coefficient. Eng Geo 284:106046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106046
EN 1991-1-2, 2002. Eurocode 1: Actions on structures—Part 1-2: General actions—Actions on structures exposed to fire. British Standards
Eyuboglu Y, Santosh M, Dudas FO, Akaryalı E, Chung SL, Akdağ K, Bektaş O (2013) The nature of transition from adakitic to non-adakitic magmatism in a slab window setting: a synthesis from the eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. Geosci Front 4:353–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2012.10.001
Fortin J, Stanchits S, Vinciguerra S, Guéguen Y (2011) Influence of thermal and mechanical cracks on permeability and elastic wave velocities in a basalt from Mt. Etna volcano subjected to elevated pressure. Tectonophysics 503:60–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2010.09.028
Garrido ME, Petnga FB, Martínez-Ibáñez V, Serón JB, Hidalgo-Signes C, Tomás R (2021) Predicting the uniaxial compressive strength of a limestone exposed to high temperatures by point load and Leeb rebound hardness testing. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02647-0
Garrido ME, M-Ibáñez V, Signes CH, Tomás R (2021) Using non-destructive testing to assess static elastic modulus of a limestone exposed to high temperatures. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing
Ge Z, Sun Q (2018) Acoustic emission (AE) characteristics of granite after heating and cooling cycles. Eng Fract Mech 200:418–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.08.011
González-Gómez WS, Quintana P, May-Pat A, Avilés F, May-Crespo J, Alvarado-Gil JJ (2015) Thermal effects on the physical properties of limestones from the Yucatan Peninsula. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 75:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.12.010
Griffiths L, Heap MJ, Baud P, Schmittbuhl J (2017) Quantification of microcrack characteristics and implications for stiffness and strength of granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 100:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.10.013
Guler S, Türkmenoğlu ZF, Varol OO (2021) Thermal shock and freeze-thaw resistance of different types of carbonate rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 137:104545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104545
Güven İH (1993) 1: 25000 Scale Geology and Compilation of the Eastern Pontides. General Directorate of Mineral Research and Exploration of Turkey (MTA), Ankara [unpublished]
Hale PA, Shakoor A (2003) A laboratory investigation of the effects of cyclic heating and cooling, wetting and drying, and freezing and thawing on the compressive strength of selected sandstones. Environ Eng Geosci 9:117–130. https://doi.org/10.2113/9.2.117
Heap MJ, Violay M, Wadsworth FB, Vasseur J (2017) From rock to magma and back again: the evolution of temperature and deformation mechanism in conduit margin zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 463:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.01.021
Heap M, Kushnir A, Griffiths L et al (2018) Fire resistance of the Mt. Epomeo Green Tuff, a widely-used building stone on Ischia Island (Italy). Volcanica 1:33–48. https://doi.org/10.30909/vol.01.01.3348
Heap MJ, Kushnir AR, Vasseur J et al (2020) The thermal properties of porous andesite. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 398:106901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2020.106901
Hueckel T, Peano A, Pellegrini R (1994) A constitutive law for thermo-plastic behaviour of rocks: an analogy with clays. Surv Geophys 15:643–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690178
Kawanishi T, Hirata T, Yashiro T, Kawai K (2019) A simple method to evaluate the depth of concrete degradation by fire. J Adv Concr Technol 17:639–647. https://doi.org/10.3151/jact.17.639
Kawasaki S, Tanimoto C, Koizumi K, Ishikawa M (2002) An attempt to estimate mechanical properties of rocks using the equotip hardness tester. J Japan Soc Eng Geol 43:244–248. https://doi.org/10.5110/jjseg.43.24410.5110/jjseg.43.244
Kendrick JE, Smith R, Sammonds P, Meredith PG, Dainty M, Pallister JS (2013) The influence of thermal and cyclic stressing on the strength of rocks from Mount St. Helens. Washington Bull Volcanol 75:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-013-0728-z
Kiliç Ö (2006) The influence of high temperatures on limestone P-wave velocity and Schmidt hammer strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43:980–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.12.013
Kunze GW (1965) Pretreatment for mineralogical analysis. In: Black CA (Eds) Methods of Soil Analysis, Part I: Physical and Mineralogical Properties Including Statistics of Measurement and Sampling. Am Soc Agron, Madison
Kurt CH (2010) Dolomit cevherinin kalsinasyon karakteristiklerinin belirlenmesi. Cukurova University, Institute of Natural and Applied Sciences
Leeb D (1979) New dynamic method for hardness testing of metallic materials Rev de. Metal 15:57–63
Li D, Wong LNY (2013) The brazilian disc test for rock mechanics applications: review and new insights. Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:269–287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0257-7
Li Z, Fortin J, Nicolas A, Deldicque D, Guéguen Y (2019) Physical and mechanical properties of thermally cracked andesite under pressure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:3509–3529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01785-w
Li Q, Yin T, Li X, Zhang S (2020) Effects of rapid cooling treatment on heated sandstone: a comparison between water and liquid nitrogen cooling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:313–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01571-6
Liu Z, Yao Q, Kong B, Yin J (2020) Macro-micro mechanical properties of building sandstone under different thermal damage conditions and thermal stability evaluation using acoustic emission technology. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118485
Mahmutoglu Y (1998) Mechanical behaviour of cyclically heated fine grained rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 31:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s006030050017
Mao XB, Zhang LY, Li TZ, Liu HS (2009) Properties of failure mode and thermal damage for limestone at high temperature. Min Sci Technol 19:290–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1674-5264(09)60054-5
Martínez-Ibáñez V, Garrido ME, Signes, CH, Tomás R (2020) Indirect evaluation of strength for limestones subjected to high temperatures. ISRM International Symposium-EUROCK 2020. OnePetro, Trondheim, Norway, pp 1–9.
Martínez-Ibáñez V, Garrido ME, Signes CH, Tomás R (2021) Micro and macro-structural effects of high temperatures in Prada limestone: key factors for future fire-intervention protocols in Tres Ponts Tunnel (Spain). Constr Build Mater 286:122960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122960
Meng QB, Wang CK, Liu JF, Zhang MW, Lu MM, Wu Y (2020) Physical and micro-structural characteristics of limestone after high temperature exposure. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1259–1274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01620-0
Mutlutürk M, Altindag R, Türk G (2004) A decay function model for the integrity loss of rock when subjected to recurrent cycles of freezing-thawing and heating-cooling. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00095-9
Nigay PM, Cutard T, Nzihou A (2017) The impact of heat treatment on the microstructure of a clay ceramic and its thermal and mechanical properties. Ceram Int 43:1747–1754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.10.084
Ozguven A, Ozcelik Y (2014) Effects of high temperature on physico-mechanical properties of Turkish natural building stones. Eng Geol 183:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.10.006
Rong G, Peng J, Cai M, Yao M, Zhou C, Sha S (2018) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of bedrocks in geothermal fields. Appl Therm Eng 141:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.05.126
Różański A, Różańska A, Sobótka M, Pachnicz M, Bukowska M (2021) Identification of changes in mechanical properties of sandstone subjected to high temperature: meso-and micro-scale testing and analysis. Arch Civ Mech Eng 21:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00187-6
Schaefer LN, Kendrick JE, Oommen T, Lavallée Y, Chigna G (2015) Geomechanical rock properties of a basaltic volcano. Front Earth Sci 3:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2015.00029
Sengun N (2014) Influence of thermal damage on the physical and mechanical properties of carbonate rocks. Arab J Geosci 7:5543–5551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1177-x
Shen Y, Hou X, Yuan J, Xu Z, Hao J, Gu L, Liu Z (2020) Thermal deterioration of high-temperature granite after cooling shock: multiple-identification and damage mechanism. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:5385–5398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01888-7
Tomás R, Cano M, Pulgarín LF, Brotons V, Benavente D, Miranda T, Vasconcelos G (2021) Thermal effect of high temperatures on the physical and mechanical properties of a granite used in UNESCO World Heritage sites in North Portugal. J Build Eng 43:102823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102823
Torok A, Hajpál M (2005) Effect of temperature changes on the mineralogy and physical properties of sandstones: a laboratory study. Int J Restoration Buildings Monuments 11:211
Ugur I, Sengun N, Demirdag S, Altindag R (2014) Analysis of the alterations in porosity features of some natural stones due to thermal effect. Ultrasonics 54:1332–1336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2014.01.013
Ulusay R (2014) The ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007–2014. Springer
Uygun E (2018) Geological and tectonic characteristics of Atasu Dam Lake area (Trabzon/Macka). Dissertation, Karadeniz Technical University
Verwaal W, Mulder A (1993) Estimating rock strength with the equotip hardness tester. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 30:659–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(93)91226-9
Violay M, Heap MJ, Acosta M, Madonna C (2017) Porosity evolution at the brittle-ductile transition in the continental crust: Implications for deep hydro-geothermal circulation. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08108-5
Wang P, Xu JY, Liu S (2015) Ultrasonic method to evaluate the residual properties of thermally damaged sandstone based on time-frequency analysis. Nondestruct Test Eval 30:74–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/10589759.2014.1002838
Wang P, Xu J, Liu S, Wang H (2016) Dynamic mechanical properties and deterioration of red-sandstone subjected to repeated thermal shocks. Eng Geol 212:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.07.015
Wang X, Huang L, Zhang J (2019) A rheological model of sandstones considering response to thermal treatment. Adv Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2143748
Wei S, Yang Y, Su C, Cardosh SR, Wang H (2019) Experimental study of the effect of high temperature on the mechanical properties of coarse sandstone. Appl Sci 9:2424. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9122424
Wu G, Wang Y, Swift G, Chen J (2013) Laboratory Investigation of the Effects of Temperature on the Mechanical Properties of Sandstone. Geotech Geol Eng 31:809–816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-013-9614-x
Yalcinalp B, Ogretmen Aydin Z, Ersoy H, Seren A (2018) Investigation of geological, geotechnical and geophysical properties of Kiratli (Bayburt, NE Turkey) travertine. Carbonates Evaporites 33:421–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-017-0344-7
Yang G, Liu X, Huang X (2004) Ultrasonic non-destructive test of stresses in rock under high temperatures. Key Eng Mater 274:883–888. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.274-276.883
Yang J, Fu LY, Zhang W, Wang Z (2019) Mechanical property and thermal damage factor of limestone at high temperature. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 117:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.012
Yavuz H (2011) Effect of freeze-thaw and thermal shock weathering on the physical and mechanical properties of an andesite stone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0302-2
Yavuz H, Altindag R, Sarac S, Ugur I, Sengun N (2006) Estimating the index properties of deteriorated carbonate rocks due to freeze-thaw and thermal shock weathering. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 43:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.12.004
Yavuz H, Demirdag S, Caran S (2010) Thermal effect on the physical properties of carbonate rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.09.014
Yilmaz NG (2013) The influence of testing procedures on uniaxial compressive strength prediction of carbonate rocks from Equotip hardness tester (EHT) and proposal of a new testing methodology: Hybrid dynamic hardness (HDH). Rock Mech Rock Eng 46:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0261-y
Zhang L (2016) Engineering properties of rocks. Butterworth-Heinemann
Zhang L, Mao X, Lu A (2009) Experimental study on the mechanical properties of rocks at high temperature. Sci China Ser E Technol Sci 52:641–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0063-y
Zhao H, Yin G, Chen L (2009) Experimental study on effect of temperature on sandstone damage. Chinese J Rock Mech Eng 28:2784–2788
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sunnetci, M.O., Ersoy, H. A New Perspective Based on Overcoming Sample Heterogeneity for the Estimation of Thermal Damage Inflicted on Volcanic Rocks Using Non-destructive Tests. Rock Mech Rock Eng 56, 35–56 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03065-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-03065-6