Abstract
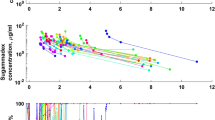
Sugammadex is an innovative reversal agent for neuromuscular blockade (NMB) induced by rocuronium. Although there is a case that re-paralysis is necessary after sugammadex administration, limited reports can be found on the sugammadex dosage for reversal from profound paralysis after induction and immediate re-paralysis following such reversal in detail. We experienced a case in which NMB reversal was required in a short period after paralysis for induction due to the discovery of anisocoria. We successfully re-induced general anesthesia with tracheal intubation soon after. To examine the validity of the dosing, we performed a pharmacometric analysis. A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model was developed for the patient based on a published pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model for rocuronium and sugammadex. The developed model appropriately describes the train of four ratio observed. In this case, the dose of approximately 8 mg/kg sugammadex but not the conventional dose of 16 mg/kg would be enough for immediate reversal after induction. For the re-paralysis 30 min after NMB reversal, not 1.4 mg/kg but 2.2 mg/kg rocuronium was an adequate dose. Taking individual differences including given dose and time intervals in consideration, NMB monitoring should be used to determine the necessary dose of rocuronium and sugammadex in such situations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srivastava A, Hunter JM. Reversal of neuromuscular block. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103:115–29.
Booij LHDJ. Cyclodextrins and the emergence of sugammadex. Anesthesia. 2009;64:31–7.
Dubois PE, Mulier JP. A review of the interest of sugammadex for deep neuromuscular blockade management in Belgium. Acta Anaesth Belg. 2013;64:49–60.
Askin T, Unver S, Oguz D, Kutay K. Case report: Neuromuscular block induced by rocuronium following sugammadex administration. J Clin Anesth. 2017;37:166–7.
Lee H-J, Kim KS, Kim TY, Lee JH, Jeong M. The use of 3 sugammadex out of 5 reversal of during recovery of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in a patient with post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage -a case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;67:43–7.
Pühringer FK, Rex C, Sielenkämper AW, Claudius C, Larsen PB, Prins ME. Reversal of profound, high-dose rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex at two different time points: an international, multicenter, randomized, dose-finding, safety assessor-blinded, phase II trial. Anesthesiology. 2008;109:188–97.
Iwasaki H, Sasakawa T, Takahoko K, Takagi S, Nakatsuka H, Suzuki T, Iwasaki H. A case series of re-establishment of neuromuscular block with rocuronium after sugammadex reversal. J Anesth. 2016;30:534–7.
de Boer HD, Driessen JJ, Marcus MA, Kerkkamp H, Heeringa M, Klimek M. Reversal of rocuronium-induced (1.2 mg/kg) profound neuromuscular block by sugammadex: a multicenter, dose-finding and safety study. Anesthesiology. 2007;107:239–44.
Cammu G, De Kam PH, Demeyer I, Decoopman M, Peeters PAM, Smeets JMW, Foubert L. Safety and tolerability of single intravenous doses of sugammadex administered simultaneously with rocuronium or vecuronium in healthy volunteers. Br J Anaesth. 2008;100:373–9.
Kleijn HJ, Zollinger DP, van den Heuvel MW, Kersbusch T. Population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis for sugammadex-mediated reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;72:415–33.
Masui K, Ishigaki S, Tomita A, Otake H. Rocuronium pharmacodynamic models for published five pharmacokinetic models: age and sex are covariates in pharmacodynamic models. J Anesth. 2018;32:709–16.
Kopman AF. Sugammadex: A revolutionary approach to neuromuscular antagonism. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:631–3.
Kim YH. Repeat dosing of rocuronium-sugammadex: unpredictable. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;67:1–3.
Cammu G, de Kam PJ, De Graeve K, van den Heuevel M, Suy K, Morias K, Foubert L, Grobara P, Peeters P. Repeat dosing of rocuronium 1.2 mg kg-1 after reversal of neuromuscular block by sugammadex 4.0 mg kg-1 in anaesthetized healthy volunteers: a modelling-based pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 2010;105:487–92.
Acknowledgements
Support for this study was solely provided by departmental and institutional funding of Department of Anesthesiology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. A part of this case report has been presented at the 26th annual meeting of Japanese Society of Intravenous Anesthesia (JSIVA), Tokyo, 2019, and received JSIVA prize for the best presentation. Kenichi Masui is an Editor of the Journal of Anesthesia, and an associate editorial board member of the British Journal of Anaesthesia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Analyzed and interpreted the data, and drafted and revised the manuscript: YK, KM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Support for this study was solely provided by departmental and institutional funding of Department of Anesthesiology, Showa University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. The authors have no other conflict of interest for this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kashima, Y., Masui, K. Individual pharmacometric analysis for sugammadex reversal and re-administration of neuromuscular blockade. J Anesth 34, 786–789 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-020-02824-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-020-02824-5