Abstract
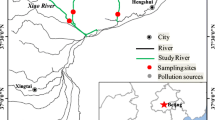
To assess the status and risk of metal pollution in landscape water body replenished by wastewater treatment plant effluent, the distribution of metals in sediments from three regions [regulation pond (RP), wetland lake (WL), and main lake (ML)] of Harbor Lake, Tianjin, China, was characterized. Higher levels of all metals (except Cr and Pb) were observed in RP sediments. As, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were mainly bound to organic matter and sulfide (F3) and residual fractions (F4), while the exchangeable and carbonate fraction (F1) and Fe/Mn oxide fraction (F2) were the dominant forms for Cd. Additionally, finding showed that the overall risk of sediments in aquatic systems was affected by both metal toxicity and metal fractionation. Thus, according to a modified risk assessment code (RAC), the potential adverse effect of metals in sediments was medium (although As, Cd, Ni, and Zn had high mobility risks based on the RAC), decreasing in the order RP > WL > ML.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekteshi L, Lazo P, Qarri F, Stafilov T (2015) Application of the normalization process in the survey of atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in Albania through moss biomonitoring. Ecol Indic 56:50–59
Chen R, Ao D, Ji J, Wang XC, Li Y-Y, Huang Y, Xue T, Guo H, Wang N, Zhang L (2017) Insight into the risk of replenishing urban landscape ponds with reclaimed wastewater. J Hazard Mater 324:573–582
Ciarkowska K (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution risks and enzyme activity of meadow soils in urban area under tourism load: a case study from Zakopane (Poland). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13709–13718
Clark EV, Odhiambo BK, Ricker MC (2014) Comparative analysis of metal concentrations and sediment accumulation rates in two Virginian Reservoirs, USA: Lakes Moomaw and Pelham. Water Air Soil Poll 225:1860
Guo W, Huo SL, Xi BD, Zhang JT, Wu FC (2015) Heavy metal contamination in sediments from typical lakes in the five geographic regions of China: distribution, bioavailability, and risk. Ecol Eng 81:243–255
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah -Al- Mamun M, Islam MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol Indic 48:282–291
Khan S, Ahmad I, Shah MT, Rehman S, Khaliq A (2009) Use of constructed wetland for the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J Environ Manage 90:3451–3457
Kim KW, Myung JH, Ahn JS, Chon HT (1998) Heavy metal contamination in dusts and stream sediments in the Taejon area, Korea. J Geochem Explor 64:409–419
Liang GN, Zhang B, Lin M, Wu SM, Hou H, Zhang J, Qian GR, Huang X, Zhou JZ (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal mobilization in creek sediment: Influence of RAC values and ambient environmental factors. Sci Total Environ 607:1339–1347
Liu HL, Li L, Yin CQ, Shan BQ (2008) Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Moshui Lake. J Environ Sci 20:390–397
Luo MB, Li JQ, Cao WP, Wang ML (2008) Study of heavy metal speciation in branch sediments of Poyang Lake. J Environ Sci 20:161–166
Malvandi H (2017) Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 117:547–553
Nemati K, Abu Bakar NK, Sobhanzadeh E, Abas MR (2009) A modification of the BCR sequential extraction procedure to investigate the potential mobility of copper and zinc in shrimp aquaculture sludge. Microchem J 92:165–169
Pardo R, Barrado E, Castrillejo Y, Velasco MA, Vega M (1993) Study of the contents and speciation of heavy metals in river sediments by factor analysis. Anal Lett 26:1719–1739
Ranjbar Jafarabadi A, Riyahi Bakhtiari A, Spanò N, Cappello T (2018) First report of geochemical fractionation distribution, bioavailability and risk assessment of potentially toxic inorganic elements in sediments of coral reef Islands of the Persian Gulf, Iran. Mar Pollut Bull 137:185–197
Saeedi M, Jamshidi-Zanjani A (2015) Development of a new aggregative index to assess potential effect of metals pollution in aquatic sediments. Ecol Indic 58:235–243
Singh KP, Mohan D, Singh VK, Malik A (2005) Studies on distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in Gomti river sediments—a tributary of the Ganges, India. J Hydrol 312:14–27
Tang WZ, Zhao Y, Wang C, Shan BQ, Cui JG (2013) Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe Basin in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 98:317–323
Tessier A, Campbell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Vosoogh A, Saeedi M, Lak R (2017) Metal fractionation and pollution risk assessment of different sediment sizes in three major southwestern rivers of Caspian Sea. Environ Earth Sci 76:292
Wu QH, Zhou HC, Tam NFY, Tian Y, Tan Y, Zhou S, Li Q, Chen YH, Leung JYS (2016) Contamination, toxicity and speciation of heavy metals in an industrialized urban river: implications for the dispersal of heavy metals. Mar Pollut Bull 104:153–161
Xu L, Wang TY, Wang JH, Lu AX (2017) Occurrence, speciation and transportation of heavy metals in 9 coastal rivers from watershed of Laizhou Bay, China. Chemosphere 173:61–68
Yang XF, Xiong BX, Yang MS (2010) Relationships among heavy metals and organic matter in sediment cores from lake Nanhu, an Urban lake in Wuhan, China. J Freshwat Ecol 25:243–249
Yang ZP, Lu WX, Long YQ, Bao XH, Yang QC (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J Geochem Explor 108:27–38
Yang J, Chen L, Liu L-Z, Shi W-L, Meng X-Z (2014) Comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in lake sediment from public parks in Shanghai. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 102:129–135
Ye H, Zang S, Xiao H, Zhang L (2015) Speciation and ecological risk of heavy metals and metalloid in the sediments of Zhalong Wetland in China. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:115–124
Zhang C, Shan BQ, Tang WZ, Dong LX, Zhang WQ, Pei YS (2017a) Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 139:263–271
Zhang GL, Bai JH, Xiao R, Zhao QQ, Jia J, Cui BS, Liu XH (2017b) Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 184:278–288
Zhang YF, Han YW, Yang JX, Zhu LY, Zhong WJ (2017c) Toxicities and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake, China, based on sediment quality guidelines. J Environ Sci 62:31–38
Zhang Y, Su Y, Liu Z, Kong L, Yu J, Jin M (2018) Aliphatic hydrocarbon biomarkers as indicators of organic matter source and composition in surface sediments from shallow lakes along the lower Yangtze River, Eastern China. Org Geochem 122:29–40
Zhao L, Xu Y, Hou H, Shangguan Y, Li F (2014) Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Sci Total Environ 468–469:654–662
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Tianjin Research Program of Applied Science and Advanced Technology (Grant No. 15JCZDJC41000), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51808431), and National Major Project of China (Grant No. 2012ZX07308-001-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, N., Wang, X.C., Liu, H. et al. Speciation, Distribution and Risk Assessment of Metals in Sediments from a Water Body Replenished by Effluent from a Wastewater Treatment Plant. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102, 525–530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02562-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02562-9