Abstract
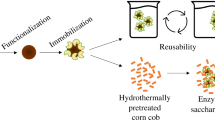
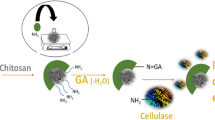
In the present study, Trichoderma reesei cellulase was covalently immobilized on chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles using glutaraldehyde as a coupling agent. The average diameter of magnetic nanoparticles before and after enzyme immobilization was about 8 and 10 nm, respectively. The immobilized enzyme retained about 37 % of its initial activity, and also showed better thermal and storage stability than free enzyme. Immobilized cellulase retained about 80 % of its activity after 15 cycles of carboxymethylcellulose hydrolysis and was easily separated with the application of an external magnetic field. However, in this reaction, K m was increased eight times. The immobilized enzyme was able to hydrolyze lignocellulosic material from Agave atrovirens leaves with yield close to the amount detected with free enzyme and it was re-used in vegetal material conversion up to four cycles with 50 % of activity decrease. This provides an opportunity to reduce the enzyme consumption during lignocellulosic material saccharification for bioethanol production.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li C, Yoshimoto M, Fukunaga K, Nakao K (2007) Characterization and immobilization of liposome-bound cellulase for hydrolysis of insoluble cellulose. Bioresour Technol 98:1366–1372
Ungurean M, Paul C, Peter F (2013) Cellulase immobilized by sol–gel entrapment for efficient hydrolysis of cellulose. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 36:1327–1338
Bhat MK (2000) Cellulases and related enzymes in biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 18:355–383
Gokhale AA, Lee I (2012) Cellulase immobilized nanostructured supports for efficient saccharification of cellulosic substrates. Top Catal 55:1231–1246. doi:10.1007/s11244-012-9891-2
Sánchez-Ramírez J, Iliná A, Segura-Ceniceros EP, Aguilar CN, Medina-Morales MA, Martínez-Hernández JL (2014) Influencia de pretratamientos en la bioconversión enzimática de fibras de pencas de Agave. Rev Fac Nac Agron 67(2):915–916
Khoshnevisan K, Bordbar AK, Zare D, Davoodi D, Noruzi M, Barkhi M, Tabatabaei M (2011) Immobilization of cellulase enzyme on superparamagnetic nanoparticles and determination of its activity and stability. Chem Eng J 171(2):669–673
Cheng C, Chang KC (2013) Development of immobilized cellulase through functionalized gold nano-particles for glucose production by continuous hydrolysis of waste bamboo chopsticks. Enzym Microb Technol 53:444–451
Valenzuela R, Castro JF, Parra C, Baeza J, Durán N, Freer J (2012) β-Glucosidase immobilisation on synthetic superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles and their application in saccharification of wheat straw and Eucalyptus globulus pulps. J Exp Nanosci. doi:10.1080/17458080.2011.651167
Weiss N, Börjesson J, Pedersen SL, Meyer SA (2013) Enzymatic lignocellulose hydrolysis: improved cellulase productivity by insoluble solids recycling. Biotechnol Biofuels. doi:10.1186/1754-6834-6-5
Spahn C, Minteer SD (2008) Enzyme immobilization in biotechnology. Recent Patents Eng 2(3):195–200
Datta S, Christena LR, Rajaram YRS (2013) Enzyme immobilization: an overview on techniques and support materials. 3 Biotech 3(1):1–9. doi:10.1007/s13205-012-0071-7
Gregorio-Jáuregui KM, Rivera-Salinas JE, Saade-Caballero H, López-Campos RG, Martínez-Hernández JL, Ilina A (2012) In: Avalos F (ed) Química Hoy: tópicos selectos de investigación, UA de C, Coahuila, México
Afsahi B, Kazemi A, Kheirolomoom A, Nejati S (2007) Immobilization of cellulase enzyme on non-porous ultrafine silica particles. Sci Iran 14(4):379–383
Dinçer A, Telefoncu A (2007) Improving the stability of cellulase by immobilization on modified polyvinyl alcohol coated chitosan beads. J Mol Catal B Enzym 45(1–2):10–14
Daoud FBO, Kaddour S, Sadoun T (2010) Adsorption of cellulase Aspergillus niger on a commercial activated carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Colloids Surf B 75:93–99
Das S, Berke-Schlessel D, Hai-Feng J, McDonough J, Wei Y (2011) Enzimatic hydrolysis of biomass with recyclable use of cellobiase enzyme immobilized in sol–gel routed mesoporous silica. J Mol Catal B Enzym 70:49–54
Abd RM, Nour AH (2012) Optimisation of immobilized cellulose onto carbon nanotubes using response surface methodology. Int J Phys Sci 7(5):841–849
Sánchez-Ramírez J, Martínez-Hernández JL, Segura-Ceniceros EP, Contreras- Esquivel JC, Medina-Morales MA, Aguilar CN, Iliná A (2014) Inmovilización de enzimas lignocelulolíticas en nanopartículas magnéticas. Quim Nova 37(3):504–512
Franzreb M, Siemann-Herzberg M, Hobley TJ, Thomas ORT (2006) Protein purification using magnetic adsorbent particles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(5):505–516
Gubin SP, Koksharov Y, Khomutov GB (2005) Magnetic nanoparticles: preparation, structure and properties. Russ Chem Rev 74(6):489–520
Gregorio-Jáuregui KM, Rivera-Salinas JE, Saade-Caballero H, López-Campos RG, Martínez-Hernández JL, Ilina A (2012) Las nanopartículas magnéticas y sus múltiples aplicaciones. In: Coahuila UAD (ed) Química Hoy, tópicos selectos de investigación. Coahuila, México
Mozafari MR, Khosravi-Darani K, Borazan GG, Cui J, Pardakhty A, Yurdugul S (2008) Encapsulation of food ingredients using nanoliposome technology. Int J Food Prop 11(4):833–844
Kim J, Grate JW, Wang P (2008) Nanobiocatalysis and its potential applications. Trends Biotechnol 26:639–646
Xie T, Wang A, Huang L, Li H, Chen Z, Wang Q, Yin X (2009) Recent advances in the support and technology used in enzyme immobilization. Afr J Biotechnol 8(19):4724–4733
Bornscheuer UT (2003) Immobilizing enzymes: how to create more suitable biocatalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 42(29):3336–3337
Lu A, Salabas EL, Schuth F (2007) Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(8):1222–1244
Liu X, Lei L, Li Y, Zhu H, Cui Y, Hu H (2011) Preparation of carriers based on magnetic nanoparticles grafted polymer and immobilization for lipase. Biochem Eng J 56(3):142–149
Zhao F, Zhang B, Feng L (2012) Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater Lett 68:112–114
Netto CGC, Toma HE, Andrade LH (2013) Superparamagnetic nanoparticles as versatile carriers and supporting materials for enzymes. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85:71–92
Gao JH, Gu HW, Xu B (2009) Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles: design, synthesis, and biomedical applications. Acc Chem Res 42(8):1097–1107
Chang MY, Juang RS (2007) Use of chitosan-clay composite as immobilization support for improved activity and stability of β-glucosidase. Biochem Eng J 35:93–98
Belessi V, Zboril R, Tucek J, Mashlan M, Tzitzios V, Petridis D (2008) Ferrofluids from magnetic-chitosan hybrids. Chem Mater 20(10):3298–3305
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. In: Wood TM, Kellogg ST (eds) Methods in enzymology, vol 160. Academic Press Inc, London, pp 87–112
Rodrigues DS, Mendes AA, Adriano WS, Gonçalves LRB, Giordano RLC (2008) Multipoint covalent immobilization of microbial lipase on chitosan and agarose activated by different methods. J Mol Catal B Enzym 51:100–109
Liao H, Chen D, Yuan L, Zheng M, Zhu Y, Liua X (2010) Immobilized cellulase by polyvinyl alcohol/Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticle to degrade microcrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 82(3):600–604
Jordan J, Kumar CSS, Theegala C (2011) Preparation and characterization of cellulase-bound magnetite nanoparticles. J Mol Catal B Enzym 68(2):139–146
Jordan J, Theegala C (2014) Probing the limitations for recycling cellulase enzymes immobilized on iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Biomass Convers Biorefin 4(1):25–33. doi:10.1007/s13399-013-0089-z
Xu J, Huo S, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Xu H, Guo Y, Liang C, Zhuang X (2011) Characterization of direct cellulase immobilization with superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Biocatal Biotransform 29(2–3):71–76
Gregorio-Jauregui KM, Pineda MG, Rivera-Salinas JE, Hurtado G, Saade H, Martinez JL, Ilyina A, López RG (2012) One-step method for preparation of magnetic nanoparticles coated with chitosan. J Nanomater 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/813958
Osuna Y, Gregorio-Jauregui KM, Gaona LG, De la Garza RIM, Ilina A, Barriga CED, Saade H, Lopez RG (2012) Chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles with low chitosan content prepared in one-step. J Nanomater 2012. doi:10.1155/2012/327562
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Kaiser E, Colescott RL, Bossinger CD, Cook PI (1970) Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal Biochem 34(2):595–598
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31(3):426–428
Ghose TK (1987) Measurement of cellulose activities. Pure Appl Chem 59(2):257–268
Camassola M, Dillon A (2012) Cellulase determination: modifications to make the filter paper assay easy, fast, practical and efficient. J Anal Bioanal Tech 1(S1). doi:10.4172/scientificreports.125
Vattem DA, Shetty K (2003) Ellagic acid production and phenolic antioxidant activity in cranberry pomace (Vaccinium macrocarpon) mediated by Lentinus edodes using a solid state system. Process Biochem 39:367–379
Li A, Antizar-Ladislao B, Khraisheh M (2007) Bioconversion of municipal solid waste to glucose for bio-ethanol production. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 30(3):189–196. doi:10.1007/s00449-007-0114-3
Gregorio-Jauregui K, Carrizalez-Alvarez S, Rivera-Salinas J, Saade H, Martinez J, López R, Segura E, Ilyina A (2014) Extraction and immobilization of SA-α-2,6-Gal receptors on magnetic nanoparticles to study receptor stability and inter action with sambucus nigra lectin. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172(8):3721–3735
Kuo C-H, Liu Y-C, Chang C-MJ, Chen J-H, Chang C, Shieh C-J (2012) Optimum conditions for lipase immobilization on chitosan-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 87:2538–2545
Pariona N, Camacho-Aguilar KI, Ramos-González R, Martinez AI, Herrera-Trejo M, Baggio-Saitovitch E (2016) Magnetic and structural properties of ferrihydrite/hematite nanocomposites. J Magn Magn Mater 406:221–227. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.01.001
Li B, Jia D, Zhou Y, Hu Q, Cai W (2006) In situ hybridization to chitosan/magnetite nanocomposite induced by the magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 306(2):223–227. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.250
G-y Li, Y-r Jiang, K-l Huang, Ding P, Chen J (2008) Preparation and properties of magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 466(1–2):451–456. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2007.11.100
Arroyo M (1998) Inmovilización de enzimas. Fundamentos, métodos y aplicaciones. Ars Pharm 39(2):23–39
Hu J, Li S (2006) Propierties of immobilized pepsin on modified PMMA microspheres. Biotechnol J 1:75–77
Sohn OJ, Kim CK, Rhee JI (2008) Immobilization of glucose oxidase and lactate dehydrogenase onto magnetic nanoparticles for bioprocess monitoring system. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 13:716–723. doi:10.1007/s12257-008-0096-2
Khan MJ, Husain Q, Azam A (2012) Immobilization of porcine pancreatic α-amylase on magnetic Fe2O3 nanoparticles: applications to the hydrolysis of starch. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17:377–384
Magri ML, Miranda MV, Cascone O (2005) Immobilization of soybean seed coat peroxidase on polyaniline: synthesis optimization and catalytic properties. Biocatal Biotransform 23:339–346
Alahakoon T, Koh WJ, Chong CWX, Lim LTW (2012) Immobilization of cellulases on amine and aldehyde functionalized Fe2O3 magnetic nanoparticles. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 42(3):234–248. doi:10.1080/10826068.2011.602800
Liu J, Cao X (2014) Biodegradation of cellulose by β-glucosidase and cellulase immobilized on a pH-responsive copolymer. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 19:829–837. doi:10.1007/s12257-013-0716-3
Alftrén J, Hobley T (2013) Covalent immobilization of β-glucosidase on magnetic particles for lignocellulose hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:2076–2087. doi:10.1007/s12010-013-0122-5
Lupoi SJ, Smith AE (2011) Evaluation of nanoparticle-immobilized cellulase for improved ethanol yield in simultaneous saccharification and fermentation reactions. Biotechnol Bioeng 108(12):2835–2843
Varavinit S, Chaokasem N, Shobsngob S (2002) Immobilization of a thermostable alpha-amylase. Sci Asia 28(3):247–251
Alftrén J, Hobley TJ (2014) Immobilization of cellulases on magnetic particles to enable enzyme recycling during hydrolysis of lignocellulose. PhD Thesis. National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark. www.biosustain.dtu.dk/…2014/Phd-afhandling_Johan_Alftrén.as. Accessed 21 April 2016
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by Grant (PDCPN2013-01) No. 213844 (CONACYT). We thank Mexican Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT) for Masters Scholarship and for the financial support under the program “Cátedras-CONACYT, 2015”, Grant No. 729.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Ramírez, J., Martínez-Hernández, J.L., Segura-Ceniceros, P. et al. Cellulases immobilization on chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles: application for Agave Atrovirens lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40, 9–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1670-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1670-1