Abstract
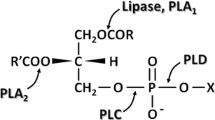
DHA/EPA-rich phosphatidylcholine (PC) was successfully synthesized by immobilized phospholipase A1 (PLA1)-catalyzed transesterification of PC and DHA/EPA-rich ethyl esters in a solvent-free system. Effects of reaction temperature, water addition and substrate mass ratio on the incorporation of DHA/EPA were evaluated using response surface methods (RSM). Water addition had most significant effect on the incorporation. Reaction temperature and substrate mass ratio, however, had no significant effect on the incorporation. The maximal incorporation was 19.09 % (24 h) under the following conditions: temperature 55.7 °C, water addition 1.1 wt % and substrate mass ratio (ethyl esters/PC) 6.8:1. Furthermore, effects of water addition (from 0 to 1.25 wt %) on DHA/EPA incorporation and the composition of products were further investigated. The immobilized PLA1 was more active when water addition was above 0.5 wt %. By monitoring the reaction processes with different water addition, a possible reaction scheme was proposed for transesterification of PC with DHA/EPA-rich ethyl esters. In summary, PC and sn2-lysophosphatidylocholine (LPC) were predominant in the mixtures at early stages of reaction, whereas sn1-LPC and glycerophosphocholine (GPC) predominant at later stages. The vacuum employed after 24 h significantly increased the incorporation of DHA/EPA and the composition of PC, and the highest incorporation (30.31 %) of DHA/EPA was obtained at 72 h and the yield of PC was 47.2 %.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty K, Paul RP (2009) Selective enrichment of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with C18–C20 acyl chain length from sardine oil using Pseudomonas fluorescens MTCC 2421 lipase. Food Chem 114:142–150
Larsson SC, Kumlin M, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Wolk A (2003) Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention of cancer: a review of potential mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr 79:935–945
Ward OP, Singh A (2005) Omega-3/6 fatty acids: alternative sources of production. Process Biochem 40:3627–3652
Galli C, Sirtori CR, Mosconi C, Medini L, Gianfranceschi G, Vaccarino V, Scolastico C (1992) Prolonged retention of doubly labeled phosphatidylcholine in human plasma and erythrocytes after oral administration. Lipids 27:1005–1012
Li X, Chen JF, Yang B, Li DM, Wang YH, Wang WF (2014) Production of structured Phosphatidylcholine with high content of DHA/EPA by immobilized phospholipase A1-catalyzed transesterification. Int J Mol Sci 15:15244–15258
Marsaoui N, Laplante S, Raies A, Naghmouchi K (2013) Incorporation of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids into soybean lecithin: effect of amines and divalent cations on transesterification by lipases. World J Microb Biot 29:2233–2238
Marsaoui N, Naghmouchi K, Baah J, Raies A, Laplante S (2015) Incorporation of ethyl esters of EPA and DHA in soybean lecithin using Rhizomucor miehei Lipase: effect of additives and solvent-free conditions. Appl Biochem Biotech 176:938–946
Kim IH, García HS, Hill Jr CG (2007) Phospholipase A1-catalyzed synthesis of phospholipids enriched in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid residues. Enzym Microb Technol 40:1130–1135
García HS, Kim I, López-Hernández A, Hill Jr CG (2008) Enrichment of lecithin with n-3 fatty acids by acidolysis using immobilized phospholipase A1. Grasas Aceites 59:368–374
Kim IH, García HS, Hill Jr CG (2010) Synthesis of structured phosphatidylcholine containing n-3 PUFA residues via acidolysis mediated by immobilized phospholipase A1. J Am Oil Chem Soc 87:1293–1299
Zhao TT, No DS, Kim BH, Garcia HS, Kim Y, Kim IH (2014) Immobilized phospholipase A1-catalyzed modification of phosphatidylcholine with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid. Food Chem 157:132–140
Vikbjerg AF, Mu HL, Xu XB (2007) Synthesis of structured phospholipids by immobilized phospholipase A2 catalyzed acidolysis. J Biotechnol 128:545–554
Peng LF, Xu XB, Mu HL, Hoy CE, Adler-Nissen J (2002) Production of structured phospholipids by lipase-catalyzed acidolysis: optimization using response surface methodology. Enzym Microb Technol 31:523–532
Xi X, Feng XM, Shi NR, Ma XX, Lin H, Han YQ (2016) Immobilized phospholipase A1-catalyzed acidolysis of phosphatidylcholine from Antarctica krill (Euphausia superba) for docosahexaenoic acid enrichment under supercritical conditions. J Mol Catal B-Enzym 126:46–55
Awano S, Miyamoto K, Hosokawa M, Mankura M, Takahashi K (2006) Production of docosahexaenoic acid bounded phospholipids via phospholipase A2 mediated bioconversion. Fisheries Sci 72:909–911
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram 342 quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Wang YH, Mai QY, Qin XL, Yang B, Wang ZL, Chen HT (2010) Establishment of an evaluation model for human milk fat substitutes. J Agric Food Chem 58:642–649
Zheng PY, Xu Y, Wang WF, Qin XL, Ning ZX, Wang YH, Yang B (2014) Production of diacylglycerol-mixture of regioisomers with high purity by two-step enzymatic reactions combined with molecular distillation. J Am Oil Chem Soc 91:251–259
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program, 2014AA093514, 2014AA093601) and Science and Technology Planning project of Guangdong province (2013B090200015, 2014CX01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Qin, X., Wang, W. et al. Synthesis of DHA/EPA-rich phosphatidylcholine by immobilized phospholipase A1: effect of water addition and vacuum condition. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 39, 1305–1314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1609-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1609-6