Abstract
Main conclusion
ZmCBL8-1 enhances salt stress tolerance in maize by improving the antioxidant system to neutralize ROS homeostasis and inducing Na+/H+ antiporter gene expressions of leaves.
Abstract
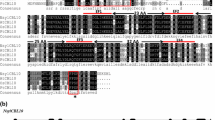
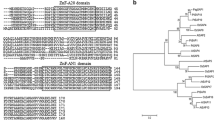
Calcineurin B-like proteins (CBLs) as plant-specific calcium sensors have been explored for their roles in the regulation of abiotic stress tolerance. Further, the functional variations in ZmCBL8, encoding a component of the salt overly sensitive pathway, conferred the salt stress tolerance in maize. ZmCBL8-1 is a transcript of ZmCBL8 found in maize, but its function in the salt stress response is still unclear. The present study aimed to characterize the protein ZmCBL8-1 that was determined to be composed of 194 amino acids (aa) with three conserved EF hands responsible for binding Ca2+. However, a 20-aa fragment was found to be missing from its C-terminus relative to another transcript of ZmCBL8. Results indicated that it harbored a dual-lipid modification motif MGCXXS at its N-terminus and was located on the cell membrane. The accumulation of ZmCBL8-1 transcripts was high in the roots but relatively lower in the leaves of maize under normal condition. In contrast, its expression was significantly decreased in the roots, while increased in the leaves under NaCl treatment. The overexpression of ZmCBL8-1 resulted in higher salt stress resistance of transgenic Arabidopsis in a Ca2+-dependent manner relative to that of the wild type (WT). In ZmCBL8-1-overexpressing plants exposed to NaCl, the contents of malondialdehyde and hydrogen peroxide were decreased in comparison with those in the WT, and the expression of key genes involved in the antioxidant defense system and Na+/H+ antiporter were upregulated. These results suggested that ZmCBL8-1 played a positive role in the response of leaves to salt stress by inducing the expression of Na+/H+ antiporter genes and enhancing the antioxidant system to neutralize the accumulation of reactive oxygen species. These observations further indicate that ZmCBL8-1 confers salt stress tolerance, suggesting that transcriptional regulation of the ZmCBL8 gene is important for salt tolerance.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
Abbreviations
- CBL:
-
Calcineurin B-like protein
- CIPK:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- NHX:
-
Na+/H+ antiporter
- SOS:
-
Salt overly sensitive
References
Batistič O, Kudla J (2009) Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(6):985–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.10.006
Batistic O, Sorek N, Schültke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2008) Dual fatty acylmodification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20(5):1346–1362. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058123
Belkhodja R, Morales F, Abadia A, Gomez-Aparisi J, Abadia J (1994) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a possible tool for salinity tolerance screening in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Physiol 104(2):667–673. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.2.667
Chen X, Huang Q, Zhang F, Wang B, Wang J, Zheng J (2014) ZmCIPK21, a maize CBL-interacting kinase, enhances salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int J Mol Sci 15(8):14819–14834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814819
Chen GQ, Ren L, Zhang J, Reed BM, Zhang D, Shen XH (2015) Cryopreservation affects ROS-induced oxidative stress and antioxidant response in Arabidopsis seedlings. Cryobiology 70(1):38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryobiol.2014.11.004
Chen X, Ding Y, Yang Y, Song C, Wang B, Yang S, Guo Y, Gong Z (2021) Protein kinases in plant responses to drought, salt, and cold stress. J Integr Plant Biol 63(1):53–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13061
Day IS, Reddy VS, Shad Ali G, Reddy AS (2002) Analysis of EF-hand-containing proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 3(10):research0056. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-10-research0056
Deng X, Zhou S, Hu W, Feng J, Zhang F, Chen L, Huang C, Luo Q, He Y, Yang G, He G (2013) Ectopic expression of wheat TaCIPK14, encoding a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, confers salinity and cold tolerance in tobacco. Plant Physiol 149(3):367–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12046
Drerup MM, Schlucking K, Hashimoto K, Manishankar P, Steinhorst L, Kuchitsu K, Kudla J (2013) The calcineurin B-like calcium sensors CBL1 and CBL9 together with their interacting protein kinase CIPK26 regulate the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase RBOHF. Mol Plant 6(2):559–569. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst009
Du W, Lin H, Chen S, Wu Y, Zhang J, Fuglsang AT, Palmgren MG, Wu W, Guo Y (2011) Phosphorylation of SOS3-like calcium-binding proteins by their interacting SOS2-like protein kinases is a common regulatory mechanism in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156(4):2235–2243. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.173377
Foyer CH, Noctor G (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17(7):1866–1875. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.033589
Gao C, Lu S, Zhou R, Wang Z, Li Y, Fang H, Wang B, Chen M, Cao Y (2022) The OsCBL8-OsCIPK17 module regulates seedling growth and confers resistance to heat and drought in rice. Int J Mol Sci 23(20):12451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012451
Halfter U, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3735–3740. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.7.3735
Han JP, Köster P, Drerup MM, Scholz M, Li S, Edel KH, Hashimoto K, Kuchitsu K, Hippler M, Kudla J (2019) Fine-tuning of RBOHF activity is achieved by differential phosphorylation and Ca2+ binding. New Phytol 221(4):1935–1949. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15543
Hanin M, Ebel C, Ngom M, Laplaze L, Masmoudi K (2016) New insights on plant salt tolerance mechanisms and their potential use for breeding. Front Plant Sci 7:1787. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01787
Harper JF, Harmon A (2005) Plants, symbiosis and parasites: a calcium signalling connection. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(7):555–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1679
He Y, Fu J, Yu C, Wang X, Jiang Q, Hong J, Lu K, Xue G, Yan C, James A, Xu L, Chen J, Jiang D (2015) Increasing cyclic electron flow is related to Na+ sequestration into vacuoles for salt tolerance in soybean. J Exp Bot 66(21):6877–6889. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv392
Hu DG, Ma QJ, Sun CH, Sun MH, You CX, Hao YJ (2016) Overexpression of MdSOS2L1, a CIPK protein kinase, increases the antioxidant metabolites to enhance salt tolerance in apple and tomato. Physiol Plant 156(2):201–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12354
Huang SL, Chen M, Zhao YJ, Wen XW, Guo ZF, Lu SY (2020) CBL4-CIPK5 pathway confers salt but not drought and chilling tolerance by regulating on homeostasis. Environ Exp Bot 179:104230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2020.104230
Jia MX, Jiang XR, Xu J, Di W, Shi Y, Liu Y (2018) CAT and MDH improve the germination and alleviate the oxidative stress of cryopreserved Paeonia and Magnolia pollen. Acta Physiol Plant 40(2):37–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-018-2612-0
Khedia J, Agarwal P, Agarwal PK (2018) AlNAC4 transcription factor from halophyte Aeluropus lagopoides mitigates oxidative stress by maintaining ROS homeostasis in transgenic tobacco. Front Plant Sci 9:1522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01522
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schultke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 52(3):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03249.x
Kleist TJ, Spencley AL, Luan S (2014) Comparative phylogenomics of the CBL-CIPK calcium-decoding network in the moss Physcomitrella, Arabidopsis, and other green lineages. Front Plant Sci 14(5):187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00187
Kolukisaoglu U, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 134(1):43–58. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.033068
Kudla J, Xu Q, Harter K, Gruissem W, Luan S (1999) Genes for calcineurin B-like proteins in Arabidopsis are differentially regulated by stress signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(8):4718–4723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.8.4718
Kurusu T, Hamada H, Koyano T, Kuchitsu K (2012) Intracellular localization and physiological function of a rice Ca2+-permeable channel OsTPC1. Plant Signal Behav 7(11):1428–1430. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.22086
Lee MH, Cho EJ, Wi SG, Bae H, Kim JE, Lee CJY, S, Kim JH, Chung BY, (2013) Divergences in morphological changes and antioxidant responses in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice seedlings after salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 70:325–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy
Li H, Wang XH, Li Q, Xu P, Liu ZN, Xu M, Cui XY (2022) GmCIPK21, a CBL-interacting protein kinase confers salt tolerance in soybean (Glycine max. L). Plant Physiol Bioch 184:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.05.027
Liu J, Ishitani M, Halfter U, Kim CS, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana SOS2 gene encodes a protein kinase that is required for salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(7):3730–3734. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.7.3730
Liu JF, Yang WJ, Jiang ZP, Guo QS, Jin JQ, Xue L (2011) Effects of shading on photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in leaves of the endangered plant Thuja sutchuenensis. Acta Ecol Sin 31(20):5999–6004. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1011.2011.00110
Lu L, Chen XY, Wang PK, Lu Y, Zhang JB, Yang XY, Cheng TL, Shi JS, Chen JH (2021) CIPK11: a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase from Nitraria tangutorum, confers tolerance to salt and drought in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol 21(1):123. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-02878-x
Luan S (2009) The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci 14(1):37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants
Luan S, Kudla J, Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Yalovsky S, Gruissem W (2002) Calmodulins and calcineurin B-like proteins: calcium sensors for specific signal response coupling in plants. Plant Cell 14:S389-400. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.001115
Luo Q, Wei Q, Wang R, Zhang Y, Zhang F, He Y, Zhou S, Feng J, Yang G, He G (2017) BdCIPK31, a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, regulates plant response to drought and salt stress. Front Plant Sci 8:1184. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01184
Ma QJ, Sun MH, Kang H, Lu J, You CX, Hao YJ (2019) A CIPK protein kinase targets sucrose transporter MdSUT2.2 at Ser254 for phosphorylation to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ 42(3):918–930. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13349
Manishankar P, Wang N, Köster P, Alatar AA, Kudla J (2018) Calcium signaling during salt stress and in the regulation of ion homeostasis. J Exp Bot 10:1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery201
Maxwell K, Johnson GN (2000) Chlorophyll fluorescence - a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51(345):659–668. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.345.659
Mohanta TK, Mohanta N, Mohanta YK, Parida P, Bae H (2015) Genome-wide identification of Calcineurin B-Like (CBL) gene family of plants reveals novel conserved motifs and evolutionary aspects in calcium signaling events. BMC Plant Biol 6(15):189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0543-0
Mohanta TK, Yadav D, Khan AL, Hashem A, Abd Allah EF, Al-Harrasi A (2019) Molecular players of EF-hand containing calcium signaling event in plants. Int J Mol Sci 20(6):1476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061476
Moller IM, Jensen PE, Hansson A (2007) Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:459–481. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103946
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Pandey GK, Kanwar P, Singh A, Steinhorst L, Pandey A, Yadav AK, Tokas I, Sanyal SK, Kim BG, Lee SC, Cheong YH, Kudla J, Luan S (2015) Calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase CIPK21 regulates osmotic and salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169(1):780–792. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00623
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):8436–8441. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122224699
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I, Zhang Y, Cao W, Yang Y, Shang M, Chen S, Pardo JM, Guo Y (2007) SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19(4):1415–1431. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.042291
Saito S, Uozumi N (2020) Calcium-regulated phosphorylation systems controlling uptake and balance of plant nutrients. Front Plant Sci 11:44. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00044
Sánchez-Barrena MJ, Martínez-Ripoll M, Albert A (2013) Structural biology of a major signaling network that regulates plant abiotic stress: the CBL-CIPK mediated pathway. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):5734–5749. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14035734
Sanyal SK, Pandey A, Pandey GK (2015) The CBL-CIPK signaling module in plants: a mechanistic perspective. Physiol Plant 155(2):89–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12344
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(12):6896–6901. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.120170197
Singh DP, Sarkar RK (2014) Distinction and characterisation of salinity tolerant and sensitive rice cultivars as probed by the chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics and growth parameters. Funct Plant Biol 41(7):727–736. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP13229
Su Y, Guo A, Huang Y, Wang Y, Hua J (2020) GhCIPK6a increases salt tolerance in transgenic upland cotton by involving in ROS scavenging and MAPK signaling pathways. BMC Plant Biol 20(1):421. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02548-4
Tang RJ, Yang Y, Yang L, Liu H, Wang CT, Yu MM, Gao XS, Zhang HX (2014) Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell Environ 37(3):573–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12178
Tang RJ, Wang C, Li K, Luan S (2020) The CBL-CIPK calcium signaling network: Unified paradigm from 20 years of discoveries. Trends Plant Sci 25(6):604–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.01.009
Tsai YC, Chen KC, Cheng TS, Lee C, Lin SH, Tung CW (2019) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis in diverse rice varieties reveals the positive correlation between the seedlings salt tolerance and photosynthetic efficiency. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):403. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1983-8
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL-CIPK Ca2+ decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184(3):517–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02938.x
Yamane K, Kawasaki M, Taniguchi M, Miyake H (2008) Correlation between chloroplast ultrastructure and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in the leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown under salinity. Plant Prod Sci 11(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.11.139
Yang Y, Guo Y (2018) Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol 217(2):523–539. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14920
Yang Q, Chen ZZ, Zhou XF, Yin HB, Li X, Xin XF, Hong XH, Zhu JK, Gong Z (2009) Over-expressing of SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive) genes increases salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 2(1):22–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssn058
Yang Y, Zhang C, Tang RJ, Xu HX, Lan WZ, Zhao FG, Luan S (2019) Calcineurin B-like proteins CBL4 and CBL10 mediate two independent salt tolerance pathways in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 20(10):2421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102421
Yang H, Zhao YL, Chen N, Liu YP, Yang SY, Du HW, Wang W, Wu JY, Tai FJ, Chen F, Hu XL (2021) A new adenylyl cyclase, putative disease-resistance RPP13-like protein 3, participates in abscisic acid-mediated resistance to heat stress in maize. J Exp Bot 72(2):283–301. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa431
Yin X, Xia Y, Xie Q, Cao Y, Wang Z, Hao G, Song J, Zhou Y, Jiang X (2020) The protein kinase complex CBL10-CIPK8-SOS1 functions in Arabidopsis to regulate salt tolerance. J Exp Bot 71(6):1801–1814. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz549
Yoo SD, Cho YH, Sheen J (2007) Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat Protoc 2(7):1565–1572. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.199
Zhang L, Ma H, Chen T, Pen J, Yu S, Zhao X (2014) Morphological and physiological responses of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plants to salinity. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112807. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112807
Zhang F, Li L, Jiao Z, Chen Y, Liu H, Chen X, Fu J, Wang G, Zheng J (2016) Characterization of the calcineurin B-Like (CBL) gene family in maize and functional analysis of ZmCBL9 under abscisic acid and abiotic stress treatments. Plant Sci 253:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.09.011
Zhang YM, Linghu JJ, Wang D, Liu X, Yu AL, Li FT, Zhao JF, Zhao TY (2017) Foxtail millet CBL4 (SiCBL4) interacts with SiCIPK24, modulates plant salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol Rep 35(6):634–646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1051-1
Zhang CM, Shi SL, Liu Z, Yang F, Yin GL (2019) Drought tolerance in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) varieties is associated with enhanced antioxidative protection and declined lipid peroxidation. J Plant Physiol 232:226–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2018.10.023
Zhao JF, Sun ZF, Zheng J, Guo XY, Dong ZG, Huai JL, Gou MY, He JG, Jin YS, Wang JH, Wang GY (2009) Cloning and characterization of a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from maize. Plant Mol Biol 69(6):661–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9445-y
Zhou X, Li J, Wang Y, Liang X, Zhang M, Lu M, Guo Y, Qin F, Jiang C (2022) The classical SOS pathway confers natural variation of salt tolerance in maize. New Phytol 236(2):479–494. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.18278
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, China (222300420461 and 162300410154), the Special Innovation Project of Henan Agricultural University, China (KJCX2020C02), and the Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province, China (221RTSTHN0230). The authors would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing and Dr. Tao Li of Henan Agricultural University for providing vector pYFP for subcellular localization assay.
Funding
Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province, 222300420461, Fuju Tai, 162300410154, Rui He, Special Innovation Project of Henan Agricultural University, KJCX2020C02, Fuju Tai, Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province, 221RTSTHN0230, Xiuli Hu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RW and PC conducted experiments and prepared parts of the manuscript. MH took part in some of the experiments. WW analyzed data and XH provided technical support. RH analyzed data and contributed to prepare and revise the manuscript. FT conceived and designed the research, analyzed the results, and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Chen, P., Han, M. et al. Calcineurin B-like protein ZmCBL8-1 promotes salt stress resistance in Arabidopsis. Planta 259, 49 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04330-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-024-04330-4