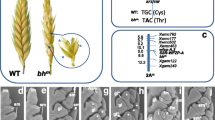
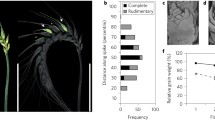
Abstract
Main conclusion
The triggers of genetic instability in barley homeotic double mutants are tweaky spike -type mutations associated with an auxin imbalance in separate spike phytomeres.
Barley homeotic tweaky spike;Hooded (tw;Hd) double mutants are characterized by an inherited instability of spike and flower development, which is absent in the single parental constituents. The aim of the present study was to show that the trigger of genetic instability in the double mutants is the tw mutations, which are associated with an auxin imbalance in the developing spikes. Their pleiotropic effects on genes related to spike/flower development may cause the genetic instability of double mutants. The study of four double-mutant groups composed of different mutant alleles showed that the instability arose only if the mutant allele tw was a constituent of the double mutants. Application of auxin inhibitors and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) demonstrated the relationship of the instability of the double mutants and the phenotype of the tw mutants to auxin imbalance. 2,4-D induced phenocopies of the tw mutation in wild-type plants and rescued the phenotypes of three allelic tw mutants. The differential display (dd-PCR) method allowed the identification of several putative candidate genes in tw that may be responsible for the initiation of instability in the double mutants by pleiotropic variations of their expression in the tw mutant associated with auxin imbalance in the developing spikes. The results of the present study linked the genetic instability of homeotic double mutants with an auxin imbalance caused by one of the constituents (tw). The genetic instability of the double mutants in relation to auxin imbalance was studied for the first time. A matrocliny on instability expression was also observed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BKn3 :
-
Barley Knox3 gene
- H :
-
Hooded/Kap1 mutant
- Hd :
-
Hooded-type mutant/mutation
- HFCA:
-
9-Hydroxyfluorene-9-carboxylic acid
- lax :
-
laxatum mutant/mutation
- Lh :
-
Lemma hooded mutant
- PCIB:
-
p-Chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid
- tw :
-
tweaky spike mutant
- twmk :
-
tweaky and missing kernels mutant
- twN18 :
-
tweaky N18 mutant
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Abebe T, Wise RP, Skadsen RW (2009) Comparative transcriptional profiling established the awn as the major photosynthetic organ of the barley spike while the lemma and the palea primarily protect the seed. Plant Genome 2:247–259. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome.2009.07.0019
Alexander DL, Mellor EA, Langdale JA (2005) CORKSCREW1 defines a novel mechanism of domain specification in the maize shoot. Plant Physiol 138:1396–1408. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.063909
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W et al (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Andres F, Romera-Branchat M, Martínez-Gallegos R et al (2015) Floral induction in Arabidopsis by FLOWERING LOCUS T requires direct repression of BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes by homeodomain protein PENNYWISE. Plant Physiol 169:2187–2199. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00960
Babb S, Muehlbauer G (2003) Genetic and morphological characterization of the barley uniculm2 (cul2) mutant. Theor Appl Genet 106:846–857. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1104-0
Badr A, Müller K, Schäfer-Pregl R et al (2000) On the origin and domestication history of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Mol Biol Evol 17:499–510
Badra A, Klinck HR (1981) The influence of inter-plant competition on the morphological development of spikes of non-tillering barley (Hordeum vulgare L. emend. Lam.). Can J Plant Sci 61:829–835. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps81-125
Benbouza H, Jacquemin J-M, Baudoin J-P, Mergeai G (2006) Optimization of a reliable, fast, cheap and sensitive silver staining method to detect SSR markers in polyacrylamide gels. Biotechnol Agron Soc Environ 10:77–81
Bieliūnienė A, Švėgždienė D, Rančelis V (2003) A peculiar structure of the flower in the homeotic barley mutant tweaky spike. Biologija 49:25–28
Bonnett OT (1938) Hood and supernumerary spike development in barley. J Agric Res 57:371–377
Boyko A, Kovalchuk I (2011) Genome instability and epigenetic modification—heritable responses to environmental stress? Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:260–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2011.03.003
Chen Y, Lowenfeld R, Cullis CA (2009) An environmentally induced adaptive (?) insertion event in flax. Int J Genet Mol Biol 1:38–47
Chiou T-J, Lin S-I (2011) Signaling network in sensing phosphate availability in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:185–206. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103849
Chu C-G, Tan CT, Yu G-T et al (2011) A novel retrotransposon inserted in the dominant Vrn-B1 allele confers spring growth habit in tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum L.). G3 Genes Genomes Genet 1:637–645. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.111.001131
Cockram J, Mackay IJ, O’Sullivan DM (2007) The role of double-stranded break repair in the creation of phenotypic diversity at cereal VRN1 loci. Genetics 177:2535–2539. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.074765
del Pozo JC, Manzano C (2014) Auxin and the ubiquitin pathway. Two players–one target: the cell cycle in action. J Exp Bot 65:2617–2632. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert363
Derscheid LA (1952) Physiological and morphological responses of barley to 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Plant Physiol 27:121–134
Dreni L, Pilatone A, Yun D et al (2011) Functional analysis of all AGAMOUS subfamily members in rice reveals their roles in reproductive organ identity determination and meristem determinacy. Plant Cell 23:2850–2863. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.087007
Durrant A (2009) Inherited changes induced by the environment. In: http://sidthomas.net/wp/. http://sidthomas.net/pdf/03%202009%20Durrant%20Book_pdf.pdf. Accessed 20 Oct 2016
Eyer L, Vain T, Pařízková B et al (2016) 2,4-D and IAA amino acid conjugates show distinct metabolism in Arabidopsis. PLoS One 11:e0159269. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159269
Fawcett JA, Innan H (2016) High similarity between distantly related species of a plant SINE family is consistent with a scenario of vertical transmission without horizontal transfers. Mol Biol Evol 33:2593–2604. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw130
Forster BP, Franckowiak JD, Lundqvist U et al (2007) The barley phytomer. Ann Bot 100:725–733. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm183
Gallavotti A, Yang Y, Schmidt RJ, Jackson D (2008) The relationship between auxin transport and maize branching. Plant Physiol 147:1913–1923. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.121541
Ghareeb H, Becker A, Iven T et al (2011) Sporisorium reilianum infection changes inflorescence and branching architectures of maize. Plant Physiol 156:2037–2052. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.179499
Gilbert GA, Knight JD, Vance CP, Allan DL (2000) Proteoid root development of phosphorus deficient lupin is mimicked by auxin and phosphonate. Ann Bot 85:921–928. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbo.2000.1133
Hay A, Tsiantis M (2010) KNOX genes: versatile regulators of plant development and diversity. Dev Camb Engl 137:3153–3165. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.030049
Hussien A, Tavakol E, Horner DS et al (2014) Genetics of tillering in rice and barley. Plant Genome 7:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.10.0032
Jensen J, Jørgensen JH (1975) The barley chromosome 5 linkage map. Hereditas 80:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1975.tb01494.x
Jost M, Taketa S, Mascher M et al (2016) A homolog of Blade-On-Petiole 1 and 2 (BOP1/2) controls internode length and homeotic changes of the barley inflorescence. Plant Physiol 171:1113–1127. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00124
Kapazoglou A, Drosou V, Argiriou A, Tsaftaris AS (2013) The study of a barley epigenetic regulator, HvDME, in seed development and under drought. BMC Plant Biol 13:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-172
Kim SY, Lee J, Eshed-Williams L et al (2012) EMF1 and PRC2 cooperate to repress key regulators of Arabidopsis development. PLoS Genet 8:e1002512. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002512
Kirby EJM (1973) Effect of temperature on ear abnormalities in uniculm barley. J Exp Bot 24:935–945. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/24.5.935
Komatsuda T (2014) The genetics of inflorescence architecture in Hordeum. J Syst Evol 52:779–782. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12121
Kumar S, Singh AK (2010) A review on herbicide 2,4-D damage reports in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J Chem Pharm Res 2:118–124
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Kusaba S, Kano-Murakami Y, Matsuoka M et al (1998) Alteration of hormone levels in transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the rice homeobox gene OSH1. Plant Physiol 116:471–476
Laurie DA, Pratchett N, Allen RL, Hantke SS (1996) RFLP mapping of the barley homeotic mutant lax-a. Theor Appl Genet 93:81–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225730
Li X, Yu X, Wang N et al (2007) Genetic and epigenetic instabilities induced by tissue culture in wild barley (Hordeum brevisubulatum (Trin.) Link). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 90:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-007-9224-5
Li H, Liang W, Yin C et al (2011) Genetic interaction of OsMADS3, DROOPING LEAF, and OsMADS13 in specifying rice floral organ identities and meristem determinacy. Plant Physiol 156:263–274
Lin L, Tian S, Kaeppler S et al (2014) Conserved transcriptional regulatory programs underlying rice and barley germination. PLoS One 9:e87261. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087261
Loubser JW, Cairns ALP (1989) Abnormalities of the growth point and ear of barley caused by 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid. South Afr J Plant Soil 6:103–107. https://doi.org/10.1080/02571862.1989.10634491
Luxová M, Lux A (1964) Character of morphoses caused in the barley (Hordeum distichum L.) spike by 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxycetil acid (MCPA). Biol Plant 6:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931007
McSteen P (2009) Hormonal regulation of branching in grasses. Plant Physiol 149:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.129056
Miura K, Lee J, Gong Q et al (2011) SIZ1 regulation of phosphate starvation-induced root architecture remodeling involves the control of auxin accumulation. Plant Physiol 155:1000–1012. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.165191
Müller KJ, Romano N, Gerstner O et al (1995) The barley Hooded mutation caused by a duplication in a homeobox gene intron. Nature 374:727–730. https://doi.org/10.1038/374727a0
Oka M, Miyamoto K, Okada K, Ueda J (1999) Auxin polar transport and flower formation in Arabidopsis thaliana transformed with indoleacetamide hydrolase (iaaH) gene. Plant Cell Physiol 40:231–237
Oshino T, Miura S, Kikuchi S et al (2011) Auxin depletion in barley plants under high-temperature conditions represses DNA proliferation in organelles and nuclei via transcriptional alterations. Plant Cell Environ 34:284–290. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02242.x
Paque S, Weijers D (2016) Q&A: auxin: the plant molecule that influences almost anything. BMC Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12915-016-0291-0
Piacentini L, Fanti L, Specchia V et al (2014) Transposons, environmental changes, and heritable induced phenotypic variability. Chromosoma 123:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-014-0464-y
Poursarebani N, Seidensticker T, Koppolu R et al (2015) The genetic basis of composite spike form in barley and “Miracle-Wheat”. Genetics 201:155–165. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.115.176628
Qianqian L, Xiaoli J, Fengli H et al (2015) Comparison of dynamic changes of endogenous plant hormones and hormone-related gene expression between near isogenic lines with normal spike and branched spike wheat. J Agric Sci 7:203–214. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v7n7p203
Rančelis V, Vaitkūnienė V, Žilinskaitė S (1994) Intragenic recombination and appearance of genotypic mosaics in the tw locus of barley. Biologija 3:21–30
Reid DA, Wiebe GA (1968) Barley: origin, botany, culture, winterhardiness, genetics, utilization, pests, 338th edn. Agricultural Research Service U.S. Department of agriculture
Richardson AE, Rebocho AB, Coen ES (2016) Ectopic KNOX expression affects plant development by altering tissue cell polarity and identity. Plant Cell 28:2079–2096. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00284
Roig C, Pozzi C, Santi L et al (2004) Genetics of barley Hooded suppression. Genetics 167:439–448. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.167.1.439
Rossini L, Okagaki R, Druka A, Muehlbauer GJ (2014) Shoot and inflorescence architecture. In: Kumlehn J, Stein N (eds) Biotechnological approaches to barley improvement. Springer, Berlin, pp 55–80
Scanlon MJ, Henderson DC, Bernstein B (2002) SEMAPHORE1 functions during the regulation of ancestrally duplicated knox genes and polar auxin transport in maize. Development 129:2663–2673
Scofield S, Murray JAH (2006) KNOX gene function in plant stem cell niches. Plant Mol Biol 60:929–946. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-4478-y
Siuksta R, Vaitkuniene V, Rancelis V et al (2012) Barley homeotic mutants and their hybrids for ornamental purposes. Acta Hortic. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2012.953.47
Šiukšta R, Vaitkūnienė V, Kaselytė G et al (2015) Inherited phenotype instability of inflorescence and floral organ development in homeotic barley double mutants and its specific modification by auxin inhibitors and 2,4-D. Ann Bot 115:651–663. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu263
Trevaskis B (2010) The central role of the VERNALIZATION1 gene in the vernalization response of cereals. Funct Plant Biol 37:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP10056
Trevaskis B, Tadege M, Hemming MN et al (2007) Short Vegetative Phase-like MADS-box genes inhibit floral meristem identity in barley. Plant Physiol 143:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.090860
Vahamidis P, Karamanos A, Economou G, Fasseas C (2014) A new scale for the assessment of wheat spike morphogenesis. Ann Appl Biol 164:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12097
Vaitkūnienė V, Varnaitė A, Rančelis V (2004a) Interaction of tweaky spike and laxatum mutations in F1 hybrids. Biologija 50:10–15
Vaitkūnienė V, Varnaitė A, Rančelis V (2004b) Interaction of barley mutants Hooded and tweaky spike in F1 hybrids. Biologija 50:13–20
Wei W, Zhang Y-Q, Tao J-J et al (2015) The Alfin-like homeodomain finger protein AL5 suppresses multiple negative factors to confer abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 81:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12773
Woerlen N, Allam G, Popescu A et al (2017) Repression of BLADE-ON-PETIOLE genes by KNOX homeodomain protein BREVIPEDICELLUS is essential for differentiation of secondary xylem in Arabidopsis root. Planta 245:1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2663-2
Woodward EJ, Marshall C (1989) Effects of plant growth regulators on tiller bud outgrowth in uniculm cereals. Ann Appl Biol 114:597–608. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1989.tb03375.x
Yan D, Zhang X, Zhang L et al (2015) CURVED CHIMERIC PALEA 1 encoding an EMF1-like protein maintains epigenetic repression of OsMADS58 in rice palea development. Plant J 82:12–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12784
Yang C-H, Chen L-J, Sung ZR (1995) Genetic regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis: role of the EMF genes. Dev Biol 169:421–435. https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1995.1158
Yasui Y, Nasuda S, Matsuoka Y, Kawahara T (2001) The Au family, a novel short interspersed element (SINE) from Aegilops umbellulata. Theor Appl Genet 102:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051668
Youssef HM, Koppolu R, Rutten T et al (2014) Genetic mapping of the labile (lab) gene: a recessive locus causing irregular spikelet fertility in labile-barley (Hordeum vulgare convar. labile). Theor Appl Genet 127:1123–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2284-0
Yuo T, Yamashita Y, Kanamori H et al (2012) A SHORT INTERNODES (SHI) family transcription factor gene regulates awn elongation and pistil morphology in barley. J Exp Bot 63:5223–5232. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers182
Zadoks JC, Chang TT, Konzak CF (1974) A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3180.1974.tb01084.x
Zheng M, Wang Y, Wang Y et al (2015) DEFORMED FLORAL ORGAN1 (DFO1) regulates floral organ identity by epigenetically repressing the expression of OsMADS58 in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 206:1476–1490. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13318
Acknowledgements
Our work was funded by Ph.D. student Grant DOK-13396 (Lietuvos Mokslo Taryba) from Research Council of Lithuania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šiukšta, R., Vaitkūnienė, V. & Rančelis, V. Is auxin involved in the induction of genetic instability in barley homeotic double mutants?. Planta 247, 483–498 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2802-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2802-9