Abstract
Background
The aim was to examine the validity of a triaxial accelerometer (ACCTRI) and a simplified physical activity record (sPAR) in estimating total energy expenditure (TEE) and physical activity level (PAL) in older adults with the doubly labeled water (DLW) method.
Methods
A total of 44 Japanese elderly individuals (64–96 years), of which 28 were community-dwelling healthy adults with or without sporting habits (S or NS group) and 16 were care home residents with frailty (F group), were included in the study. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) was measured by indirect calorimetry, TEE was obtained by the DLW method, and PAL was calculated as TEE/BMR. Daily step count was monitored by a pedometer (Lifecorder). The 24-h average metabolic equivalent was assessed by ACCTRI and sPAR.
Results
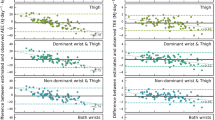
The TEEDLW in men was 2704 ± 353, 2308 ± 442, and 1795 ± 338 kcal d−1, and that in women was 2260 ± 208, 1922 ± 285, and 1421 ± 274 kcal d−1 for the S, NS, and F groups, respectively. ACCTRI and sPAR systematically underestimated actual TEE (− 14.2 ± 11.6 and − 15.3 ± 12.3% for ACCTRI and sPAR, respectively). After diet-induced thermogenesis was taken into account for ACCTRI and sPAR, TEEDLW was significantly correlated with TEEACCTRI (R2 = 0.714) and TEEsPAR (R2 = 0.668). PALDLW was also significantly correlated with PALACCTRI (R2 = 0.438) and PALsPAR (R2 = 0.402).
Conclusions
Age, living conditions, frailty, and sporting habits contribute to TEE and PAL in the elderly population. ACCTRI and sPAR underestimated TEE and PAL, and adequate corrections are required. The corrected ACCTRI and sPAR are both useful tools to estimate TEE and PAL.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACCTRI:
-
Triaxial accelerometer
- AEE:
-
Physical activity energy expenditure
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- DIT:
-
Diet-induced thermogenesis
- DLW:
-
Doubly labeled water
- EER:
-
Estimated energy requirement
- F group:
-
Care home residents
- FFM:
-
Fat-free mass
- FM:
-
Fat mass
- IAEA:
-
International Atomic Energy Agency
- mBMR:
-
Measured basal metabolic rate
- MET:
-
Metabolic equivalent
- Nd:
-
2H dilution spaces
- No:
-
18O dilution spaces
- NS group:
-
Community-dwelling healthy adults without sporting habits
- PAL:
-
Physical activity level
- pBMR:
-
Predicted basal metabolic rate
- rCO2 :
-
Rate of carbon dioxide production
- RDA:
-
Recommended dietary allowance
- RER:
-
Estimated 24-h respiratory exchange ratio
- S group:
-
Community-dwelling healthy adults with sporting habits
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- sPAR:
-
Simplified physical activity record
- TBW:
-
Total body water
- TEE:
-
Total energy expenditure
- VO2 :
-
Oxygen uptake
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
- Wt:
-
Body weight
References
Abdullah A, Peeters A, de Courten M, Stoelwinder J (2010) The magnitude of association between overweight and obesity and the risk of diabetes: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 89(3):309–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.04.012
Ando T, Usui C, Ohkawara K, Miyake R, Miyashita M, Park J, Ezaki O, Higuchi M, Tanaka S (2013) Effects of intermittent physical activity on fat utilization over a whole day. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45(7):1410–1418. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182885e4b
Aoyagi Y, Park H, Watanabe E, Park S, Shephard RJ (2009) Habitual physical activity and physical fitness in older Japanese adults: the Nakanojo Study. Gerontology 55(5):523–531. https://doi.org/10.1159/000236326
Blanc S, Schoeller DA, Bauer D, Danielson ME, Tylavsky F, Simonsick EM, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Everhart JE (2004) Energy requirements in the eighth decade of life. Am J Clin Nutr 79(2):303–310
Broadwin J, Goodman-Gruen D, Slymen D (2001) Ability of fat and fat-free mass percentages to predict functional disability in older men and women. J Am Geriatr Soc 49(12):1641–1645
Cao ZB, Oh T, Miyatake N, Tsushita K, Higuchi M, Tabata I (2014) Steps per day required for meeting physical activity guidelines in Japanese adults. J Phys Act Health 11(7):1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1123/jpah.2012-0333
Chen KY, Muniyappa R, Abel BS, Mullins KP, Staker P, Brychta RJ, Zhao X, Ring M, Psota TL, Cone RD, Panaro BL, Gottesdiener KM, Van der Ploeg LH, Reitman ML, Skarulis MC (2015) RM-493, a melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) agonist, increases resting energy expenditure in obese individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(4):1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-4024
Cooper JA, Watras AC, Adams AK, Schoeller DA (2009) Effects of dietary fatty acid composition on 24-h energy expenditure and chronic disease risk factors in men. Am J Clin Nutr 89(5):1350–1356. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.27419
Cooper JA, Manini TM, Paton CM, Yamada Y, Everhart JE, Cummings S, Mackey DC, Newman AB, Glynn NW, Tylavsky F, Harris T, Schoeller DA (2013) Longitudinal change in energy expenditure and effects on energy requirements of the elderly. Nutr J 12:73. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-12-73
Crouter SE, Schneider PL, Karabulut M, Bassett DR Jr (2003) Validity of 10 electronic pedometers for measuring steps, distance, and energy cost. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1455–1460. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000078932.61440.a2
Davison KK, Ford ES, Cogswell ME, Dietz WH (2002) Percentage of body fat and body mass index are associated with mobility limitations in people aged 70 and older from NHANES III. J Am Geriatr Soc 50(11):1802–1809
Gando Y, Yamamoto K, Murakami H, Ohmori Y, Kawakami R, Sanada K, Higuchi M, Tabata I, Miyachi M (2010) Longer time spent in light physical activity is associated with reduced arterial stiffness in older adults. Hypertension 56(3):540–546. https://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.110.156331
Hara T, Matsumura Y, Yamamoto M, Kitado T, Nakao H, Nakao H, Suzuki T, Yoshikawa T, Fujimoto S (2006) The relationship between body weight reduction and intensity of daily physical activities assessed with 3-dimension accelerometer. Jpn J Phys Fit Sports Med 55(4):385–391
Harris AM, Lanningham-Foster LM, McCrady SK, Levine JA (2007) Nonexercise movement in elderly compared with young people. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 292(4):E1207–E1212. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00509.2006
Hatamoto Y, Yamada Y, Sagayama H, Higaki Y, Kiyonaga A, Tanaka H (2014) The relationship between running velocity and the energy cost of turning during running. PLoS One 9(1):e81850. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081850
Hatamoto Y, Yamada Y, Higaki Y, Tanaka H (2016) A novel approach for measuring energy expenditure of a single sit-to-stand movement. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(5):997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3355-5
Health Promotion and Nutrition Division-Health Service Bureau, Ministry of Health and Welfare (1995) Recommended dietary allowances for the Japanese, 4th revision. Dai-ichi Shuppan, Tokyo
Ikeda N, Takimoto H, Imai S, Miyachi M, Nishi N (2015) Data resource profile: the Japan National Health and Nutrition Survey (NHNS). Int J Epidemiol 44(6):1842–1849. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv152
Ikeda N, Nishi N, Noda H, Noda M (2017) Trends in prevalence and management of diabetes and related vascular risks in Japanese adults: Japan National Health and Nutrition Surveys 2003–2012. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 127:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.011
Inoue S, Ohya Y, Odagiri Y, Takamiya T, Suijo K, Kamada M, Okada S, Tudor-Locke C, Shimomitsu T (2011) Sociodemographic determinants of pedometer-determined physical activity among Japanese adults. Am J Prevent Med 40(5):566–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2010.12.023
International Atomic Energy Agency (2009) IAEA human health series no. 3. Vienna International Centre, Vienna, pp 37–40
International Atomic Energy Agency (2010) IAEA human health series no. 12. Vienna International Centre, Vienna, pp 9–11
Isabel TD, Correia M, Waitzberg DL (2003) The impact of malnutrition on morbidity, mortality, length of hospital stay and costs evaluated through a multivariate model analysis. Clin Nutr 22(3):235–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-5614(02)00215-7
Ishikawa-Takata K, Tabata I, Sasaki S, Rafamantanantsoa HH, Okazaki H, Okubo H, Tanaka S, Yamamoto S, Shirota T, Uchida K, Murata M (2007) Physical activity level in healthy free-living Japanese estimated by doubly labelled water method and International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Eur J Clin Nutr 62(7):885–891
Itoi A, Yamada Y, Nakae S, Kimura M (2015) Decline in objective physical activity over a 10-year period in a Japanese elementary school. J Physiol Anthropol 34:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40101-015-0078-y
Kaiser M, Bandinelli S, Lunenfeld B (2010) Frailty and the role of nutrition in older people. A review of the current literature. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parmensis 81(Suppl 1):37–45
Kodama S, Fujihara K, Ishiguro H, Horikawa C, Ohara N, Yachi Y, Tanaka S, Shimano H, Kato K, Hanyu O, Sone H (2017) Unstable bodyweight and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. J Diabetes Investig 8(4):501–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12623
Koebnick C, Wagner K, Thielecke F, Moeseneder J, Hoehne A, Franke A, Meyer H, Garcia AL, Trippo U, Zunft HJF (2005) Validation of a simplified physical activity record by doubly labeled water technique. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 29(3):302–309
Kumahara H, Schutz Y, Ayabe M, Yoshioka M, Yoshitake Y, Shindo M, Ishii K, Tanaka H (2004) The use of uniaxial accelerometry for the assessment of physical-activity-related energy expenditure: a validation study against whole-body indirect calorimetry. Br J Nutr 91(2):235–243. https://doi.org/10.1079/bjn20031033
Matsumura Y, Yamamoto M, Kitado T, Nakamura H, Kidera K, Fujimoto S (2008) High-accuracy physical activity monitor utilizing three-axis accelerometer. Natl Tech Rep 56(2):60–66
Melanson EL (2017) The effect of exercise on non-exercise physical activity and sedentary behavior in adults. Obes Rev Off J Int Assoc Study Obes 18(Suppl 1):40–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12507
Meng XL, Rosenthal R, Rubin DB (1992) Comparing correlated correlation-coefficients. Psychol Bull 111(1):172–175
Mian OS, Thom JM, Ardigo LP, Narici MV, Minetti AE (2006) Metabolic cost, mechanical work, and efficiency during walking in young and older men. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 186(2):127–139
Miles-Chan JL, Fares EJ, Berkachy R, Jacquet P, Isacco L, Schutz Y, Montani JP, Dulloo AG (2017) Standing economy: does the heterogeneity in the energy cost of posture maintenance reside in differential patterns of spontaneous weight-shifting? Eur J Appl Physiol 117(4):795–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3563-7
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Japan (2014) Estimated energy requirement. In: Hishida A, Sasaki S (eds) Dietary reference intakes for Japanese, 2015. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Tokyo, pp 59–87
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Japan (2017) Japan National Health and Nutrition Surveys 2016
Murakami H, Iemitsu M, Sanada K, Gando Y, Ohmori Y, Kawakami R, Sasaki S, Tabata I, Miyachi M (2011) Associations among objectively measured physical activity, fasting plasma homocysteine concentration, and MTHFR C677T genotype. Eur J Appl Physiol 111(12):2997–3005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-1926-z
Murakami H, Kawakami R, Nakae S, Nakata Y, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tanaka S, Miyachi M (2016) Accuracy of wearable devices for estimating total energy expenditure: comparison with metabolic chamber and doubly labeled water method. JAMA Intern Med 176(5):702–703. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.0152
Namba H, Yamaguchi Y, Yamada Y, Tokushima S, Hatamoto Y, Sagayama H, Kimura M, Higaki Y, Tanaka H (2012) Validation of web-based physical activity measurement systems using doubly labeled water. J Med Internet Res 14(5):e123
Nanri H, Yamada Y, Yoshida T, Okabe Y, Nozawa Y, Itoi A, Yoshimura E, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi M, Yokoyama K, Ishikawa-Takata K, Koyabashi H, Kimura M, Group K-KS (2018) Sex difference in the association between protein intake and frailty: assessed using the Kihon Checklist Indexes among the elderly. JAMDA (in Press)
Ohkawara K, Tanaka S, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tabata I (2008) Twenty-four-hour analysis of elevated energy expenditure after physical activity in a metabolic chamber: models of daily total energy expenditure. Am J Clin Nutr 87(5):1268–1276. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/87.5.1268
Ohkawara K, Oshima Y, Hikihara Y, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tabata I, Tanaka S (2011) Real-time estimation of daily physical activity intensity by a triaxial accelerometer and a gravity-removal classification algorithm. Br J Nutr 105(11):1681–1691. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114510005441
Ortega JD, Farley CT (2007) Individual limb work does not explain the greater metabolic cost of walking in elderly adults. J Appl Physiol 102(6):2266–2273
Oshima Y, Kawaguchi K, Tanaka S, Ohkawara K, Hikihara Y, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tabata I (2010) Classifying household and locomotive activities using a triaxial accelerometer. Gait Posture 31(3):370–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.01.005
Park J, Ishikawa-Takata K, Tanaka S, Bessyo K, Tanaka S, Kimura T (2017) Accuracy of estimating step counts and intensity using accelerometers in older people with or without assistive devices. J Aging Phys Act 25(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1123/japa.2015-0201
Plasqui G, Westerterp KR (2007) Physical activity assessment with accelerometers: an evaluation against doubly labeled water. Obesity 15(10):2371–2379
Plasqui G, Bonomi AG, Westerterp KR (2013) Daily physical activity assessment with accelerometers: new insights and validation studies. Obes Rev Off J Int Assoc Study Obes 14(6):451–462. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12021
Pontzer H (2015) Constrained total energy expenditure and the evolutionary biology of energy balance. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 43(3):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1249/jes.0000000000000048
Pontzer H, Durazo-Arvizu R, Dugas LR, Plange-Rhule J, Bovet P, Forrester TE, Lambert EV, Cooper RS, Schoeller DA, Luke A (2016) Constrained total energy expenditure and metabolic adaptation to physical activity in adult humans. Curr Biol CB 26(3):410–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.046
Racette SB, Schoeller DA, Luke AH, Shay K, Hnilicka J, Kushner RF (1994) Relative dilution spaces of 2H- and 18O-labeled water in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 267(4):E585–E590
Rosenberg IH (1989) Summary comments. Am J Clin Nutr 50(5):1231–1233
Sagayama H, Yoshimura E, Yamada Y, Ichikawa M, Ebine N, Higaki Y, Kiyonaga A, Tanaka H (2014) Effects of rapid weight loss and regain on body composition and energy expenditure. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39(1):21–27. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2013-0096
Sagayama H, Yamada Y, Racine NM, Shriver TC, Schoeller DA (2016) Dilution space ratio of 2H and 18O of doubly labeled water method in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985) 120(11):1349–1354. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.01037.2015
Schneider PL, Crouter S, Bassett DR (2004) Pedometer measures of free-living physical activity: comparison of 13 models. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(2):331–335. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000113486.60548.e9
Schoeller DA, Westerterp M (2017) Advances in the assessment of dietary intake. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Schoeller DA, Ravussin E, Schutz Y, Acheson KJ, Baertschi P, Jequier E (1986) Energy expenditure by doubly labeled water: validation in humans and proposed calculation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 250(5):R823–R830
Sevits KJ, Melanson EL, Swibas T, Binns SE, Klochak AL, Lonac MC, Peltonen GL, Scalzo RL, Schweder MM, Smith AM, Wood LM, Melby CL, Bell C (2013) Total daily energy expenditure is increased following a single bout of sprint interval training. Physiol Rep 1(5):e00131. https://doi.org/10.1002/phy2.131
Shephard RJ, Park H, Park S, Aoyagi Y (2013) Objectively measured physical activity and progressive loss of lean tissue in older Japanese adults: longitudinal data from the Nakanojo study. J Am Geriatr Soc 61(11):1887–1893. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.12505
Shephard RJ, Park H, Park S, Aoyagi Y (2017) Objective longitudinal measures of physical activity and bone health in older Japanese: the Nakanojo Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 65(4):800–807. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14553
Speakman JR, Westerterp KR (2010) Associations between energy demands, physical activity, and body composition in adult humans between 18 and 96 y of age. Am J Clin Nutr 92(4):826–834. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2009.28540
Usui C, Ando T, Ohkawara K, Miyake R, Oshima Y, Hibi M, Oishi S, Tokuyama K, Tanaka S (2015) Validity and reproducibility of a novel method for time-course evaluation of diet-induced thermogenesis in a respiratory chamber. Physiol Rep. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12410
Weir JB (1949) New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J Physiol 109(1–2):1–9
Westerterp KR (2013) Physical activity and physical activity induced energy expenditure in humans: measurement, determinants, and effects. Front Physiol 4:90. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00090
Westerterp KR (2018) Exercise, energy expenditure and energy balance, as measured with doubly labelled water. Proc Nutr Soc 77(1):4–10. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0029665117001148
Westerterp KR, Brouns F, Saris WH, ten Hoor F (1988) Comparison of doubly labeled water with respirometry at low- and high-activity levels. J Appl Physiol (1985) 65(1):53–56. https://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1988.65.1.53
Wong WW, Clarke LL (2012) A hydrogen gas-water equilibration method produces accurate and precise stable hydrogen isotope ratio measurements in nutrition studies. J Nutr 142(11):2057–2062. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.167957
Wong WW, Clarke LL (2015) Accuracy of delta(18)O isotope ratio measurements on the same sample by continuous-flow isotope-ratio mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrometry RCM 29(23):2252–2256. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.7390
World Health Organization (2017) ANNEX B Tables of health statistics by country, WHO region and globally. In: World Health Statistics 2017: monitoring health for the SDGs, pp 85–102
Yamada Y, Masuo Y, Yokoyama K, Hashii Y, Ando S, Okayama Y, Morimoto T, Kimura M, Oda S (2009a) Proximal electrode placement improves the estimation of body composition in obese and lean elderly during segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur J Appl Physiol 107(2):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1106-6
Yamada Y, Yokoyama K, Noriyasu R, Osaki T, Adachi T, Itoi A, Naito Y, Morimoto T, Kimura M, Oda S (2009b) Light-intensity activities are important for estimating physical activity energy expenditure using uniaxial and triaxial accelerometers. Eur J Appl Physiol 105(1):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-008-0883-7
Yamada Y, Colman RJ, Kemnitz JW, Baum ST, Anderson RM, Weindruch R, Schoeller DA (2013a) Long-term calorie restriction decreases metabolic cost of movement and prevents decrease of physical activity during aging in rhesus monkeys. Exp Gerontol 48(11):1226–1235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2013.08.002
Yamada Y, Noriyasu R, Yokoyama K, Osaki T, Adachi T, Itoi A, Morimoto T, Oda S, Kimura M (2013b) Association between lifestyle and physical activity level in the elderly: a study using doubly labeled water and simplified physical activity record. Eur J Appl Physiol 113(10):2461–2471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2682-z
Yamada Y, Yokoyama K, Noriyasu R, Osaki T, Adachi T, Itoi A, Naito Y, Morimoto T, Kimura M, Oda S (2016) Erratum to: Calculation of total energy expenditure in publications on physical activity energy by Yamada et al. in 2009 and 2013. Eur J Appl Physiol 116(6):1279–1280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3376-0
Yamada Y, Nanri H, Watanabe Y, Yoshida T, Yokoyama K, Itoi A, Date H, Yamaguchi M, Miyake M, Yamagata E, Tamiya H, Nishimura M, Fujibayashi M, Ebine N, Yoshida M, Kikutani T, Yoshimura E, Ishikawa-Takata K, Yamada M, Nakaya T, Yoshinaka Y, Fujiwara Y, Arai H, Kimura M (2017) Prevalence of frailty assessed by Fried and Kihon Checklist Indexes in a prospective cohort study: design and demographics of the Kyoto-Kameoka longitudinal study. J Am Med Dir Assoc 18(8):733.e737–733.e715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.02.022
Yamada Y, Kemnitz JW, Weindruch R, Anderson RM, Schoeller DA, Colman RJ (2018) Caloric restriction and healthy life span: frail phenotype of nonhuman primates in the Wisconsin national primate research center caloric restriction study. J Gerontol Ser A 73(3):273–278. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glw225
Yamaguchi M, Yoshida T, Yamada Y, Watanabe Y, Nanri H, Yokoyama K, Date H, Miyake M, Itoi A, Yamagata E, Masumoto T, Okayama Y, Yoshinaka Y, Kimura M (2018) Sociodemographic and physical predictors of non-participation in community based physical checkup among older neighbors: a case-control study from the Kyoto–Kameoka Longitudinal Study, Japan. BMC Public Health 18(1):568. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5426-5
Acknowledgements
The current research is supported by Grants of JSPS KAKENHI for MK (24240091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY, KY, and MK conceived and designed the experiments; YY, YA, KY, AI, TA, and MK performed the experiments; YY analyzed the data and wrote the draft. All of the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Klaas R. Westerterp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, Y., Hashii-Arishima, Y., Yokoyama, K. et al. Validity of a triaxial accelerometer and simplified physical activity record in older adults aged 64–96 years: a doubly labeled water study. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 2133–2146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3944-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3944-6