Abstract
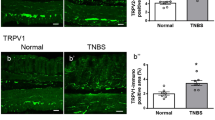
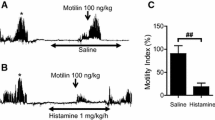
Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) plays a role in esophageal function. However, the distribution of TRPV1 nerve fibers in the esophagus is currently not well understood. In the present study, we investigated the distribution of TRPV1 and neurotransmitters released from TRPV1 nerve fibers in the mouse lower esophagus. Furthermore, we investigated changes in the presence of TRPV1 in the mouse model of esophagitis. Numerous TRPV1-immunoreactive nerve fibers were seen in both the submucosal layer and myenteric plexus of the lower esophagus and colocalized with calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). TRPV1 colocalized with substance P in axons in the submucosal layer and myenteric plexus. TRPV1 colocalized with neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the myenteric plexus. We observed some colocalization of CGRP with the vesicular acetylcholine (ACh) transporter, packaging of ACh into synaptic vesicles after its synthesis in terminal cytoplasm, in the submucosal layer and myenteric plexus. In the esophagitis model, the number of the TRPV1 nerve fibers did not change, but their immunoreactive intensity increased compared with sham-operated mice. Inhibitory effect of exogenous capsaicin on electrically stimulated twitch contraction significantly increased in esophagitis model compared with the effect in sham-operated mice. Overall, these results suggest that TRPV1 nerve fibers projecting to both the submucosal and muscle layer of the esophagus are extrinsic spinal and vagal afferent neurons. Furthermore, TRPV1 nerve fibers contain CGRP, substance P, nitric oxide, and ACh. Therefore, acid influx-mediated TRPV1 activation may play a role in regulating esophageal relaxation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiba Y, Mizumori M, Kuo M, Ham M, Guth PH, Engel E, Kaunitz JD (2008) CO2 chemosensing in rat oesophagus. Gut 57:1654–1664
Banerjee B, Medda BK, Lazarova Z, Bansal N, Shaker R, Sengupta JN (2007) Effect of reflux-induced inflammation on transient receptor potential vanilloid one (TRPV1) expression in primary sensory neurons innervating the oesophagus of rats. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:681–691
Bhat YM, Bielefeldt K (2006) Capsaicin receptor (TRPV1) and non-erosive reflux disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepato 18:263–270
Bielefeldt K, Davis BM (2008) Differential effects of ASIC3 and TRPV1 deletion on gastroesophageal sensation in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G130–G138
Boudaka A, Wörl J, Shiina T, Neuhuber WL, Kobayashi H, Shimizu Y, Takewaki T (2007a) Involvement of TRPV1-dependent and -independent components in the regulation of vagally induced contractions in the mouse esophagus. Eur J Pharmacol 556:157–165
Boudaka A, Wörl J, Shiina T, Saito S, Atoji Y, Kobayashi H, Shimizu Y, Takewaki T (2007b) Key role of mucosal primary afferents in mediating the inhibitory influence of capsaicin on vagally mediated contractions in the mouse esophagus. J Vet Med Sci 69:365–372
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389:816–824
Cheng L, de la Monte S, Ma J, Hong J, Tong M, Cao W, Behar J, Biancani P, Harnett KM (2009) HCl-activated neural and epithelial vanilloid receptors (TRPV1) in cat esophageal mucosa. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G135–G143
Furness JB (2000) Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:87–96
Harrington AM, Brierley SM, Isaacs NJ, Young RL, Ashley Blackshaw L (2013) Identifying spinal sensory pathways activated by noxious esophageal acid. Neurogastroenterol Motil 25:e660–e668
Horling L, Bunnett NW, Messlinger K, Neuhuber WL, Raab M (2014) Localization of receptors for calcitonin-gene-related peptide to intraganglionic laminar endings of the mouse esophagus: peripheral interaction between vagal and spinal afferents? Histochem Cell Biol 141:321–335
Kishimoto E1, Naito Y, Handa O, Okada H, Mizushima K, Hirai Y, Nakabe N, Uchiyama K, Ishikawa T, Takagi T, Yagi N, Kokura S, Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T (2011) Oxidative stress-induced posttranslational modification of TRPV1 expressed in esophageal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301:G230–238
Ma J, Altomare A, Guarino M, Cicala M, Rieder F, Fiocchi C, Li D, Cao W, Behar J, Biancani P, Harnett KM (2012) HCl-induced and ATP-dependent upregulation of TRPV1 receptor expression and cytokine production by human esophageal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 303:G635–G645
Matsumoto K, Kurosawa E, Terui H, Hosoya T, Tashima K, Murayama T, Priestley JV, Horie S (2009) Localization of TRPV1 and contractile effect of capsaicin in mouse large intestine: high abundance and sensitivity in rectum and distal colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G348–G360
Matsumoto K, Hosoya T, Tashima K, Namiki T, Murayama T, Horie S (2011) Distribution of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channel-expressing nerve fibers in mouse rectal and colonic enteric nervous system: relationship to peptidergic and nitrergic neurons 172:518–534
Matsumoto K, Lo MW, Hosoya T, Tashima K, Takayama H, Murayama T, Horie S (2012) Experimental colitis alters expression of 5-HT receptors and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 leading to visceral hypersensitivity in mice. Lab Invest 92:769–782
Matthews PJ, Aziz Q, Facer P, Davis JB, Thompson DG, Anand P (2004) Increased capsaicin receptor TRPV1 nerve fibres in the inflamed human oesophagus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16:897–902
Miwa H, Kondo T, Oshima T, Fukui H, Tomita T, Watari J (2010) Esophageal sensation and esophageal hypersensitivity—overview from bench to bedside. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:353–362
Omura N, Kashiwagi H, Chen G, Suzuki Y, Yano F, Aoki T (1999) Establishment of surgically induced chronic acid reflux esophagitis in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 34:948–953
Peles S, Medda BK, Zhang Z, Banerjee B, Lehmann A, Shaker R, Sengupta JN (2009) Differential effects of transient receptor vanilloid one (TRPV1) antagonists in acid-induced excitation of esophageal vagal afferent fibers of rats. Neuroscience 161:515–525
Qin C, Farber JP, Foreman RD (2008) Intraesophageal chemicals enhance responsiveness of upper thoracic spinal neurons to mechanical stimulation of esophagus in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 294:G708–G716
Raab M, Neuhuber WL (2004) Intraganglionic laminar endings and their relationships with neuronal and glial structures of myenteric ganglia in the esophagus of rat and mouse. Histochem Cell Biol 122:445–459
Russo D, Clavenzani P, Sorteni C, Bo Minelli L, Botti M, Gazza F, Panu R, Ragionieri L, Chiocchetti R (2013) Neurochemical features of boar lumbosacral dorsal root ganglion neurons and characterization of sensory neurons innervating the urinary bladder trigone. J Comp Neurol. 521:342–366
Sang Q, Young HM (1997) Development of nicotinic receptor clusters and innervation accompanying the change in muscle phenotype in the mouse esophagus. J Comp Neurol 386:119–136
Shieh KR, Yi CH, Liu TT, Tseng HL, Ho HC, Hsieh HT, Chen CL (2010) Evidence for neurotrophic factors associating with TRPV1 gene expression in the inflamed human esophagus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22:971–977
Shiina T, Shimizu Y, Boudaka A, Wörl J, Takewaki T (2006) Tachykinins are involved in local reflex modulation of vagally mediated striated muscle contractions in the rat esophagus via tachykinin NK1 receptors. Neuroscience 139:495–503
Sivarao DV, Mashimo HL, Thatte HS, Goyal RK (2001) Lower esophageal sphincter is achalasic in nNOS(-/-) and hypotensive in W/W(v) mutant mice. Gastroenterology 121:34–42
Surdenikova L, Ru F, Nassenstein C, Tatar M, Kollarik M (2012) The neural crest- and placodes-derived afferent innervation of the mouse esophagus. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24:e517–e525
Wörl J, Dütsch F, Neuhuber WL (2002) Development of neuromuscular junctions in the mouse esophagus: focus on establishment and reduction of enteric co-innervation. Anat Embryol (Berl) 205:141–152
Yoshida N, Kuroda M, Suzuki T, Kamada K, Uchiyama K, Handa O, Takagi T, Yoshikawa T, Kuramoto H (2013) Role of nociceptors/neuropeptides in the pathogenesis of visceral hypersensitivity of nonerosive reflux disease. Dig Dis Sci 58:2237–2243
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, and by Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, Tokyo, JAPAN.
Conflict of interest
Syunji Horie received a research grant for the present study from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. The other authors have no competing interests and have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, K., Hosoya, T., Ishikawa, E. et al. Distribution of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1-expressing nerve fibers in mouse esophagus. Histochem Cell Biol 142, 635–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1246-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-014-1246-6