Abstract
Dipping product of natural rubber (NR) latex has superior comprehensive properties superior to those made from synthetic latex. Compared with synthetic latex, the component characteristics of NR show the existence of non-rubber components (NRC). In this paper, NRC, mainly proteins and phospholipids, are separately removed by enzyme treatment to study their effect on the film formation behavior of natural rubber latex. The changes of NR latex particles are in situ visualize by using freeze-drying SEM technology and AFM during the film formation process. The results demonstrate that contact, deformation, and coalescence of latex particles occur more readily after the removal of proteins and phospholipids. It shows that removing NRC can quicken NR film formation. However, the mechanical properties of the NR film decrease in the absence of NRC. Based on the research, a film formation mechanism for NR latex is proposed, which can provide a more insightful understanding toward the structure-property relationship of NR film.

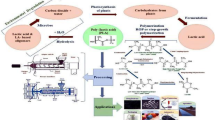
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang CR, Yang M, Yu J, Hu SN, Huang HS (2016) The rubber tree genome reveals new insights into rubber production and species adaptation. Nat Plants 2:16073–16082
Wegst UGK, Bai H, Saiz E, Tomsia AP, Ritchie RO (2015) Bioinspired structural materials. Nat Mater 14:23–36
Liu H, Huang GS, Wei LY, Zeng J, Fu X, Huang C, Wu JR (2019) Inhomogeneous natural network promoting strain-induced crystallization: a mesoscale model of natural rubber. Chinese J Polym Sci 37:1142–1151
Tanaka Y (2001) Structural characterization of natural polyisoprenes: solve the mystery of natural rubber based on structural study. Rubber Chem Tech 74:355–375
Li DF, Li SH, Cui DM, Zhang XQ (2010) β-Diketiminato rare-earth metal complexes. Structures, catalysis, and active species for highlycis-1,4-selective polymerization of isoprene. Organometallics 29:2186–2193
Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J, Tanaka Y (2009) Green strength of natural rubber: the origin of the stress-strain behavior of natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 111:2127–2133
Joanicot M, Wong K, Maquet J, Chevalier Y, Cabane B (1990) Ordering of latex particles during film formation. Colloid Polym Sci 81:175–183
Juhue JLD (1995) Film formation from dispersion of core-shell latex particles. Macromolecules 28:1306–1308
Chevalier Y, Pichot C, Graillat C, Joanicot M, Cabane B (1992) Film formation with latex particles. Colloid Polym Sci 270:806–821
Sakdapipanich JT, Nawamawat K, Kawahara S (2002) Characterization of the large and small rubber particles in fresh Hevea latex. Rubber Chem Technol 75:179–185
Manus S, Adun N, Sirirat K, Chakrit S, Jitladda S, Shigeyuki T (2018) Viscoelastic and mechanical properties of large- and small-particle natural rubber before and after vulcanization. Polym Test 70:127–134
Sriring M, Nimpaiboon A, Kumarn S, Takahara A, Sakdapipanich J (2019) Enhancing viscoelastic and mechanical performances of natural rubber through variation of large and small rubber particle combinations. Polym Test 81:106225
Xiang Q, Xia KC, Dai LJ, Kang GJ, Li Y, Nie ZY, Duan CF, Zeng RH (2012) Proteome analysis of the large and the small rubber particles of Hevea brasiliensis using 2D-DIGE. Plant Physiol Bioch 60:207–213
Oouchi M, Ukawa J, Ishii Y, Maeda H (2019) Structural analysis of the terminal groups in commercial hevea natural rubber by 2D-NMR with DOSY filters and multiple-wet methods using ultrahigh-field NMR. Biomacromolecules 20:1394–1400
Tanaka Y, Tarachiwin L (2009) Recent advances in structural characterization of natural rubber. Rubber Chem Technol 82:283–314
Kosugi K, Kawahara S (2015) Natural rubber with nanomatrix of non-rubber components observed by focused ion beam-scanning electron microscopy. Colloid Polym Sci 293:135–141
Huang C, Huang G, Li S, Luo M, Liu H, Fu X, Qu W, Xie Z, Wu J (2018) Research on architectur and composition of natural network in natural rubber. Polymer 154:90–100
Chaikumpollert O, Yamamoto Y, Suchiva K, Kawahara S (2012) Protein-free natural rubber. Colloid Polym Sci 290:331–338
Sansatsadeeku J, Sakdapipanich J, Rojruthai P (2011) Characterization of associated proteins and phospholipids in natural rubber latex. J Biosci Bioeng 111:628–634
Chaikumpollert O, Yamamoto Y, Suchiva K, Nghia PT, Kawahara S (2012) Preparation and characterization of protein-free natural rubber. Polym Advan Technol 23:825–828
Wu J, Qu W, Huang G, Wang S, Liu H (2017) Super-resolution fluorescence imaging of spatial organization of proteins and lipids in natural rubber. Biomacromolecules 18:1705–1712
Nawamawat K, Sakdapipanich JT, Ho CC, Ma Y, Song J, Vancso JG (2011) Surface nanostructure of Hevea brasiliensis natural rubber latex particles. Colloid Surface A 390:157–166
Rochette CN, Crassous JJ, Drechsler M, Gaboriaud F, Eloy M, B-d G, Duval JFL (2013) Shell structure of natural rubber particles: evidence of chemical stratification by electrokinetics and Cryo-TEM. Langmuir 29:14655–14665
Toki S, Che J, Rong L, Hsiao BS, Amnuaypornsri S, Nimpaiboon A, Sakdapipanich J (2013) Entanglements and networks to strain-induced crystallization and stress-strain relations in natural rubber and synthetic polyisoprene at various temperatures. Macromolecules 46:5238–5248
Tarachiwin L, Sakdapipanich J, Ute K, Kitayama T, Bamba T, E-i F, Kobayashi A, Tanaka Y (2005) Structural characterization of α-terminal group of natural rubber. 1. Decomposition of branch-points by lipase and phosphatase treatments. Biomacromolecules 6:1851–1857
Karino T, Ikeda Y, Yasuda Y, Kohjiya S, Shibayama M (2007) Nonuniformity in natural rubber as revealed by small-angle neutron scattering, small-angle X-ray scattering, and atomic force microscopy. Biomacromolecules 8:693–699
Toki S, Burger C, Hsiao BS, Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J, Tanaka Y (2008) Multi-scaled microstructures in natural rubber characterized by synchrotron X-ray scattering and optical microscopy. J Polym Sci Polym Phys 46:2456–2464
Liu J, Wu S, Tang Z, Lin T, Guo B, Huang G (2015) New evidence disclosed for networking in natural rubber by dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Soft Matter 11:2290–2299
Kawahara S, Kakubo T, Sakdapipanich JT, Isono Y, Tanaka Y (2000) Characterization of fatty acids linked to natural rubber-role of linked fatty acids on crystallization of the rubber. Polymer 41:7483–7488
Xie ZT, Luo MC, Huang C, Wei LY, Liu YH, Fu XM (2018) Effects of graphene oxide on the strain-induced crystallization and mechanical properties of natural rubber crosslinked by different vulcanization systems. Polymer 151:279–286
Chen LJ, Gou XH, Luo YF, Jia ZX, Bai J, Chen YJ, Jia DM (2018) Effect of novel supported vulcanizing agent on the interfacial interaction and strain-induced crystallization properties of natural rubber nanocomposites. Polymer 148:390–399
Zhou Y, Kosugi K, Yamamoto Y, Kawahara S (2016) Effect of nonrubber components on the mechanical properties of natural rubber. Polym Advan Technol 28:159–165
Chaikumpollert O, Yamamoto Y, Suchiva K, Kawahara S (2012) Mechanical properties and cross-linking structure of cross-linked natural rubber. Polym J 44:772–777
Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J, Toki S, Hsiao BS, Ichikawa N, Tanaka Y (2008) Strain-induced crystallization of natural rubber: effect of proteins and phospholipids. Rubber Chem Technol 81:753–766
Pipattananukul N, Ariyawiriyanan W, Kawahara S (2014) Thermal behavior of vulcanized deproteinzed natural rubber nano-composites. Energy Procedia 56:634–640
Lee JTY, Chow KL (2012) SEM sample preparation for cells on 3D scaffolds by freeze-drying and HMDS. Scanning 34:12–25
Ivan'Kova EM, Dobrovolskaya IP, Popryadukhin PV, Kryukov A, Yudin VE, Morganti P (2016) In-situ cryo-SEM investigation of porous structure formation of chitosan sponges. Polym Test 52:41–45
Bogner A, Thollet G, Basset D, Jouneau P-H, Gauthier C (2005) Wet STEM: a new development in environmental SEM for imaging nano-objects included in a liquid phase. Ultramicroscopy 104:290–301
Pralhad T, Rajendrakumar K (2004) Study of freeze-dried quercetin-cyclodextrin binary systems by DSC, FT-IR, X-ray diffraction and SEM analysis. J Pharmaceut Biomed 34:333–339
Kim C, Beuve JS, Guilbert S, Bonfils F (2009) Study of chain branching in natural rubber using size-exclusion chromatography coupled with a multi-angle light scattering detector (SEC-MALS). Eur Polym J 45:2249–2259
Tarachiwin L, Sakdapipanich J, Ute K, Kitayama T, Tanaka Y (2005) Structural characterization of α-terminal group of natural rubber. 2. Decomposition of branch-points by phospholipase and chemical treatments. Biomacromolecules 6:1858–1863
Sakdapipanich JT (2007) Structural characterization of natural rubber based on recent evidence from selective enzymatic treatments. J Biosci Bioeng 103:287–292
Luo M-C, Zeng J, Fu X, Huang G, Wu J (2016) Toughening diene elastomers by strong hydrogen bond interactions. Polymer 106:21–28
Wei Y-C, Liu G-X, Zhang H-F, Zhao F, Luo M-C, Liao S (2019) Non-rubber components tuning mechanical properties of natural rubber from vulcanization kinetics. Polymer 183:121911–121917
Wei Y-C, Liu G-X, Zhang L, Xu W-Z, Liao S, Luo M-C (2020) Mimicking mechanical robustness of natural rubber based on sacrificial network constructed by phospholipids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:14468–14475
Yu W-W, Xu W-Z, Xia J-H, Wei Y-C, Liao S, Luo M-C (2020) Toughening natural rubber by the innate sacrificial network. Polymer 194:122419–122425
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDC06010100), the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201403066), and the Major Science and Technology Plan Projects of Hainan Province (No. ZDKJ2016020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, YC., Xia, JH., Zhang, L. et al. Influence of non-rubber components on film formation behavior of natural rubber latex. Colloid Polym Sci 298, 1263–1271 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04703-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04703-7