Abstract
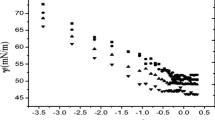
Two series of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-polylactide-b-poly(ε-caprolactone) (MPEG-PLA-PCL) triblock copolymers with similar end-blocks (MPEG and PCL) lengths but varying mid-block (PLA) lengths were prepared by ring-opening polymerization (ROP) method and characterized by 1H NMR and GPC. The influence of mid-block length of these obtained copolymers on their surface activity, aggregation behavior, and emulsifying properties was investigated. When short PLA chain was inserted into the MPEG-PCL diblock copolymers, the formed triblock copolymers offer the advantage over the corresponding diblock copolymers. They allow higher solubility, faster interfacial adsorption, tighter micelle molecular packing, slightly larger micelle size, and higher emulsifying volume. When PLA chain was long, however, the triblock copolymers exhibited different properties due to the hydrophobicity of the chain. PLA chain length does not significantly affect the equilibrium surface tension. The findings based on this study not only demonstrate the important role of an inserted block with intermediate hydrophobicity on the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of block copolymers but also emphasize the impact of the chain length on these properties.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tadros TF (2005) Applied surfactants: principles and applications. Wiley-VCH, Germany
Kimmins S, Cameron NR (2011) Functional porous polymers by emulsion templating: recent advances. Adv Funct Mater 21:211–225
Rossier-Miranda FJ, Schroën CGPH, Boom RM (2009) Colloidosomes: versatile microcapsules in perspective. Colloid Surface A 343:43–49
Binks BP (2002) Particles as surfactants—similarities and differences. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7:21–41
Melle S, Lask M, Fuller GG (2005) Pickering emulsions with controllable stability. Langmuir 21:2158–2162
Abend S, Bonnke N, Gutschner U, Lagaly G (1998) Stabilization of emulsions by heterocoagulation of clay minerals and layered double hydroxides. Colloid Polym Sci 276:730–737
Ikem VO, Menner A, Bismarck A (2008) High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by functionalized silica particles. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:8277–8279
Zou S, Yang Y, Liu H, Wang C (2013) Synergistic stabilization and tunable structures of Pickering high internal phase emulsions by nanoparticles and surfactants. Colloid Surface A 436:1–9
Schrade A, Landfester K, Ziener U (2013) Pickering-type stabilized nanoparticles by heterophase polymerization. Chem Soc Rev 42:6823–6839
Binks BP, Rodrigues JA (2005) Inversion of emulsions stabilized solely by ionizable nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:441–444
Akartuna I, Tervoort E, Wong JCH, Studart AR, Gauckler LJ (2009) Macroporous polymers from particle-stabilized emulsions. Polymer 50:3645–3651
Fujii S, Cai Y, Weaver JVM, Armes SP (2005) Syntheses of shell cross-linked micelles using acidic ABC triblock copolymers and their application as pH-responsive particulate emulsifiers. J Am Chem Soc 127:7304–7305
Hu M, McClements DJ, Decker EA (2003) Lipid oxidation in corn oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by casein, whey protein isolate, and soy protein isolate. J Agric Food Chem 51:1696–1700
Brugger B, Richtering W (2008) Emulsions stabilized by stimuli-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-co-methacrylic acid polymers: microgels versus low molecular weight polymers. Langmuir 24:7769–7777
Li Z, Ming T, Wang J, Ngai T (2009) High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by microgel particles. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:8490–8493
Brugger B, Rosen BA, Richtering W (2008) Microgels as stimuli-responsive stabilizers for emulsions. Langmuir 24:12202–12208
Liu S, Armes SP (2001) Recent advances in the synthesis of polymeric surfactants. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 6:249–256
Li L, Yang J, Zhou J (2013) Linear-, cyclic-, and multiblock amphiphilic polyelectrolytes as surfactants in emulsion polymerization: role of topological structure. Macromolecules 46:2808–2817
Raduan NH, Horozov TS, Georgiou TK (2010) “Comb-like” non-ionic polymeric macrosurfactants. Soft Matter 6:2321–2329
Zhulina EB, Borisov OV (2013) Effect of block copolymer architecture on morphology of self-assembled aggregates in solution. ACS Macro Lett 2:292–295
Riess G, Labbe C (2004) Block copolymers in emulsion and dispersion polymerization. Macromol Rapid Commun 25:401–435
Durand A, Marie E (2009) Macromolecular surfactants for miniemulsion polymerization. Adv Colloid Interfac 150:90–105
Denkova AG, Mendes E, Coppens MO (2010) Non-equilibrium dynamics of block copolymer micelles in solution: recent insights and open questions. Soft Matter 6:2351–2357
Nicolai T, Colombani O, Chassenieux C (2010) Dynamic polymeric micelles versus frozen nanoparticles formed by block copolymers. Soft Matter 6:3111–3118
Garnier S, Laschewsky A (2006) New amphiphilic diblock copolymers: surfactant properties and solubilization in their micelles. Langmuir 22:4044–4053
Matsuoka H, Chen H, Matsumoto K (2012) Molecular weight dependence of non-surface activity for ionic amphiphilic diblock copolymers. Soft Matter 8:9140–9146
van Stam J, Creutz S, De Schryver FC, Jérôme R (2000) Tuning of the exchange dynamics of unimers between block copolymer micelles with temperature, cosolvents, and cosurfactants. Macromolecules 33:6388–6395
Lejeune E, Drechsler M, Jestin J, Müller AHE, Chassenieux C, Colombani O (2010) Amphiphilic diblock copolymers with a moderately hydrophobic block: toward dynamic micelles. Macromolecules 43:2667–2671
Jacquin M, Muller P, Cottet H, Théodoly O (2010) Self-assembly of charged amphiphilic diblock copolymers with insoluble blocks of decreasing hydrophobicity: from kinetically frozen colloids to macrosurfactants. Langmuir 26:18681–18693
Salager JL, Antón RE, Sabatini DA, Harwell JH, Acosta EJ, Tolosa LI (2005) Enhancing solubilization in microemulsions—state of the art and current trends. J Surfactants Deterg 8:3–21
Phan TT, Attaphong C, Sabatini DA (2011) Effect of extended surfactant structure on interfacial tension and microemulsion formation with triglycerides. J Am Oil Chem Soc 88:1223–1228
Xie HQ, Xie D, Chen XY, Guo JS (2005) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of two-component amphiphilic polyoxyethylene-containing multiblock copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci 95:1295–1301
Scorzza C, Godé P, Goethals G, Martin P, Miñana-Pérez M, Salager JL, Usubillaga A, Villa P (2002) Another new family of “extended” glucidoamphiphiles. Synthesis and surfactant properties for different sugar head groups and spacer arm lengths. J Surfactants Deterg 5:337–343
Seo YS, Kim MW, Ou-Yang HD (2013) Effects of second solvents on the interaction of polymeric micelles in aqueous solution. J Chem Biol Interfaces 1:58–63
Lou A, Pethica BA (1997) Adsorption of hexane at the water/vapor interface. Langmuir 13:4933–4934
Fainerman VB, Mucic N, Pradines V, Aksenenko EV, Miller R (2013) Adsorption of alkyltrimethylammonium bromides at water/alkane interfaces: competitive adsorption of alkanes and surfactants. Langmuir 29:13783–13789
Buckton G, Machiste EO (1997) Differences between dynamic and equilibrium surface tension of poly(oxyethylene)-poly(oxypropylene)-poly(oxyethylene) block copolymer surfactants (poloxamers P407, P237, and P338) in aqueous solution. J Pharm Sci 86:163–166
Eastoe J, Dalton JS (2000) Dynamic surface tension and adsorption mechanisms of surfactants at the air-water interface. Adv Colloid Interfac 85:103–144
Mucic N, Javadi A, Kovalchuk NM, Aksenenko EV, Miller R (2011) Dynamics of interfacial layers-experimental feasibilities of adsorption kinetics and dilational rheology. Adv Colloid Interfac 168:167–178
Lin LH, Chou YS (2010) Surface activity and emulsification properties of hydrophobically modified dextrins. Colloid Surface A 364:55–60
Lin LH, Wang CC, Chen KM, Lin PC (2013) Synthesis and physicochemical properties of silicon-based gemini surfactants. Colloid Surface A 436:881–889
Perelstein OE, Ivanov VA, Möller M, Potemkin II (2010) Designed AB copolymers as efficient stabilizers of colloidal particles. Macromolecules 43:5442–5449
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support for this work from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (20973036, 21303013), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (13ZR1450900), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (12D10521, 14D110510).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, X., Zhang, W., Zong, Q. et al. Physicochemical and emulsifying properties of “extended” triblock copolymers. Colloid Polym Sci 293, 369–379 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3420-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-014-3420-8