Abstract
Introduction
For the past two decades, microsatellite instability (MSI) has been reported as a robust clinical biomarker associated with survival advantage attributed to its immunogenicity. However, MSI is also associated with high-risk adverse pathological features (poorly differentiated, mucinous, signet cell, higher grade) and exhibits a double-edged sword phenomenon. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the rate of dissemination and the prognosis of early and advanced stage colorectal cancer based on MSI status.
Methods
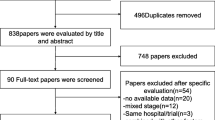
A systematic literature search of original studies was performed on Ovid searching MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, American College of Physicians ACP Journal Club, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects DARE, Clinical Trials databases from inception of database to June 2019. Colorectal cancer, microsatellite instability, genomic instability and DNA mismatch repair were used as key words or MeSH terms. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) reporting guideline was followed. Data were pooled using a random-effects model with odds ratio (OR) as the effect size. Statistical analysis was performed using RevMan ver 5.3 Cochrane Collaboration.
Results
From 5288 studies, 136 met the inclusion criteria (n = 92,035; MSI-H 11,746 (13%)). Overall, MSI-H was associated with improved OS (OR, 0.81; 95% CI 0.73–0.90), DFS (OR, 0.73; 95% CI 0.66–0.81) and DSS (OR, 0.69; 95% CI 0.52–0.90). Importantly, MSI-H had a protective effect against dissemination with a significantly lower rate of lymph node and distant metastases. By stage, the protective effect of MSI-H in terms of OS and DFS was observed clearly in stage II and stage III. Survival in stage I CRC was excellent irrespective of MSI status. In stage IV CRC, without immunotherapy, MSI-H was not associated with any survival benefit.
Conclusions
MSI-H CRC was associated with an overall survival benefit with a lower rate of dissemination. Survival benefit was clearly evident in both stage II and III CRC, but MSI-H was neither a robust prognostic marker in stage I nor stage IV CRC without immunotherapy.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popat S, Hubner R, Houlston RS (2005) Systematic review of microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 23(3):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.01.086
Guastadisegni C, Colafranceschi M, Ottini L, Dogliotti E (2010) Microsatellite instability as a marker of prognosis and response to therapy: a meta-analysis of colorectal cancer survival data. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 46(15):2788–2798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2010.05.009
Michael-Robinson JM, Biemer-Huttmann A, Purdie DM, Walsh MD, Simms LA, Biden KG, Young JP, Leggett BA, Jass JR, Radford-Smith GL (2001) Tumour infiltrating lymphocytes and apoptosis are independent features in colorectal cancer stratified according to microsatellite instability status. Gut 48(3):360–366
Kim JH, Kang GH (2014) Molecular and prognostic heterogeneity of microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 20(15):4230–4243. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4230
Greenson JK, Bonner JD, Ben-Yzhak O, Cohen HI, Miselevich I, Resnick MB, Trougouboff P, Tomsho LD, Kim E, Low M, Almog R, Rennert G, Gruber SB (2003) Phenotype of microsatellite unstable colorectal carcinomas: well-differentiated and focally mucinous tumors and the absence of dirty necrosis correlate with microsatellite instability. Am J Surg Pathol 27(5):563–570
Smyrk TC, Watson P, Kaul K, Lynch HT (2001) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are a marker for microsatellite instability in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 91(12):2417–2422
Tougeron D, Fauquembergue E, Rouquette A, Le Pessot F, Sesboue R, Laurent M, Berthet P, Mauillon J, Di Fiore F, Sabourin JC, Michel P, Tosi M, Frebourg T, Latouche JB (2009) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancers with microsatellite instability are correlated with the number and spectrum of frameshift mutations. Mod Pathol 22(9):1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2009.80
Pages F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo F, Costes A, Molidor R, Mlecnik B, Kirilovsky A, Nilsson M, Damotte D, Meatchi T, Bruneval P, Cugnenc PH, Trajanoski Z, Fridman WH, Galon J (2005) Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 353(25):2654–2666. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa051424
Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Berger A, Bindea G, Meatchi T, Bruneval P, Trajanoski Z, Fridman WH, Pages F, Galon J (2011) Histopathologic-based prognostic factors of colorectal cancers are associated with the state of the local immune reaction. J Clin Oncol 29(6):610–618. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.30.5425
Ling A, Edin S, Wikberg ML, Oberg A, Palmqvist R (2014) The intratumoural subsite and relation of CD8(+) and FOXP3(+) T lymphocytes in colorectal cancer provide important prognostic clues. Br J Cancer 110(10):2551–2559. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.161
Svennevig JL, Lunde OC, Holter J, Bjorgsvik D (1984) Lymphoid infiltration and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Cancer 49(3):375–377
Jass JR (1986) Lymphocytic infiltration and survival in rectal cancer. J Clin Pathol 39(6):585–589
Shunyakov L, Ryan CK, Sahasrabudhe DM, Khorana AA (2004) The influence of host response on colorectal cancer prognosis. Clin Colorectal Cancer 4(1):38–45
Dahlin AM, Henriksson ML, Van Guelpen B, Stenling R, Oberg A, Rutegard J, Palmqvist R (2011) Colorectal cancer prognosis depends on T-cell infiltration and molecular characteristics of the tumor. Mod Pathol 24(5):671–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2010.234
Chiba T, Ohtani H, Mizoi T, Naito Y, Sato E, Nagura H, Ohuchi A, Ohuchi K, Shiiba K, Kurokawa Y, Satomi S (2004) Intraepithelial CD8+ T-cell-count becomes a prognostic factor after a longer follow-up period in human colorectal carcinoma: possible association with suppression of micrometastasis. Br J Cancer 91(9):1711–1717. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602201
Zlobec I, Lugli A, Baker K, Roth S, Minoo P, Hayashi S, Terracciano L, Jass JR (2007) Role of APAF-1, E-cadherin and peritumoral lymphocytic infiltration in tumour budding in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 212(3):260–268. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2164
Prall F, Duhrkop T, Weirich V, Ostwald C, Lenz P, Nizze H, Barten M (2004) Prognostic role of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in stage III colorectal cancer with and without microsatellite instability. Hum Pathol 35(7):808–816
Kazama Y, Watanabe T, Kanazawa T, Tanaka J, Tanaka T, Nagawa H (2007) Microsatellite instability in poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas of the colon and rectum: relationship to clinicopathological features. J Clin Pathol 60(6):701–704. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2006.039081
Lamberti C, Lundin S, Bogdanow M, Pagenstecher C, Friedrichs N, Buttner R, Sauerbruch T (2007) Microsatellite instability did not predict individual survival of unselected patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Color Dis 22(2):145–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-006-0131-8
Buckowitz A, Knaebel HP, Benner A, Blaker H, Gebert J, Kienle P, von Knebel DM, Kloor M (2005) Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer is associated with local lymphocyte infiltration and low frequency of distant metastases. Br J Cancer 92(9):1746–1753. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6602534
Schwitalle Y, Kloor M, Eiermann S, Linnebacher M, Kienle P, Knaebel HP, Tariverdian M, Benner A, von Knebel DM (2008) Immune response against frameshift-induced neopeptides in HNPCC patients and healthy HNPCC mutation carriers. Gastroenterology 134(4):988–997. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.015
Linnebacher M, Gebert J, Rudy W, Woerner S, Yuan YP, Bork P, von Knebel DM (2001) Frameshift peptide-derived T-cell epitopes: a source of novel tumor-specific antigens. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 93(1):6–11
Shapira S, Fokra A, Arber N, Kraus S (2014) Peptides for diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Curr Med Chem 21(21):2410–2416
Xiao H, Yoon YS, Hong SM, Roh SA, Cho DH, Yu CS, Kim JC (2013) Poorly differentiated colorectal cancers: correlation of microsatellite instability with clinicopathologic features and survival. Am J Clin Pathol 140(3):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1309/ajcp8p2dynkgrbvi
Thibodeau SN, Bren G, Schaid D (1993) Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science (New York, NY) 260(5109):816–819
Yoon YS, Kim J, Hong SM, Lee JL, Kim CW, Park IJ, Lim SB, Yu CS, Kim JC (2015) Clinical implications of mucinous components correlated with microsatellite instability in patients with colorectal cancer. Color Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.13027
Karahan B, Argon A, Yildirim M, Vardar E (2015) Relationship between MLH-1, MSH-2, PMS-2,MSH-6 expression and clinicopathological features in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(4):4044–4053
Soreide K, Slewa A, Stokkeland PJ, van Diermen B, Janssen EAM, Soreide JA, Baak JPA, Korner H (2009) Microsatellite instability and DNA ploidy in colorectal cancer: potential implications for patients undergoing systematic surveillance after resection. Cancer 115(2):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24024
Yun HR, Yi LJ, Cho YK, Park JH, Cho YB, Yun SH, Kim HC, Chun HK, Lee WY (2009) Double primary malignancy in colorectal cancer patients--MSI is the useful marker for predicting double primary tumors. Int J Color Dis 24(4):369–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-008-541-x
Hu H, Chang DT, Nikiforova MN, Kuan SF, Pai RK (2013) Clinicopathologic features of synchronous colorectal carcinoma: a distinct subset arising from multiple sessile serrated adenomas and associated with high levels of microsatellite instability and favorable prognosis. Am J Surg Pathol 37(11):1660–1670. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e31829623b8
Renkonen-Sinisalo L, Seppala TT, Jarvinen HJ, Mecklin JP (2017) Subtotal colectomy for colon cancer reduces the need for subsequent surgery in Lynch syndrome. Dis Colon Rectum 60(8):792–799. https://doi.org/10.1097/dcr.0000000000000802
Toh J, Chapuis PH, Bokey L, Chan C, Spring KJ, Dent OF (2017) Competing risks analysis of microsatellite instability as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 104(9):1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10542
Toh JW, de Souza P, Lim SH, Singh P, Chua W, Ng W, Spring KJ (2016) The potential value of immunotherapy in colorectal cancers: review of the evidence for programmed death-1 inhibitor therapy. Clin Colorectal Cancer 15(4):285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2016.07.007
Surveillance Research Program; National Cancer Institute. EaERP. [Accessed September 20, 2020]; Available from: http://seer.cancer.gov
Malesci A, Laghi L, Bianchi P, Delconte G, Randolph A, Torri V, Carnaghi C, Doci R, Rosati R, Montorsi M, Roncalli M, Gennari L, Santoro A (2007) Reduced likelihood of metastases in patients with microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13(13):3831–3839. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-0366
Zinselmeyer BH, Heydari S, Sacristan C, Nayak D, Cammer M, Herz J, Cheng X, Davis SJ, Dustin ML, McGavern DB (2013) PD-1 promotes immune exhaustion by inducing antiviral T cell motility paralysis. J Exp Med 210(4):757–774. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20121416
Schofield L, Watson N, Grieu F, Li WQ, Zeps N, Harvey J, Stewart C, Abdo M, Goldblatt J, Iacopetta B (2009) Population-based detection of Lynch syndrome in young colorectal cancer patients using microsatellite instability as the initial test. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 124(5):1097–1102. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23863
Stigliano V, Assisi D, Cosimelli M, Palmirotta R, Giannarelli D, Mottolese M, Mete LS, Mancini R, Casale V (2008) Survival of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer patients compared with sporadic colorectal cancer patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27(1):39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-9966-27-39
Drescher KM, Sharma P, Lynch HT (2010) Current hypotheses on how microsatellite instability leads to enhanced survival of Lynch syndrome patients. Hindawi Publishing Corporation, 410 Park Avenue, 15th Floor, 287 pmb, New York NY 10022, United States http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=emed12&NEWS=N&AN=359172101. Accessed (Drescher) Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Creighton University, School of Medicine, Omaha, NE 68178, United States 2010
Toon CW, Walsh MD, Chou A, Capper D, Clarkson A, Sioson L, Clarke S, Mead S, Walters RJ, Clendenning M, Rosty C, Young JP, Win AK, Hopper JL, Crook A, Von Deimling A, Jenkins MA, Buchanan DD, Gill AJ (2013) BRAFV600E immunohistochemistry facilitates universal screening of colorectal cancers for lynch syndrome. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, 530 Walnut Street,P O Box 327, Philadelphia PA 19106-3621, United States http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=emed15&NEWS=N&AN=369870141. Accessed (Toon, Clarkson, Sioson, Gill) Department of Anatomical Pathology, Darlinghurst, Australia 37
Toon CW, Chou A, Desilva K, Chan J, Patterson J, Clarkson A, Sioson L, Jankova L, Gill AJ (2014) BRAFV600E immunohistochemistry in conjunction with mismatch repair status predicts survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Nature Publishing Group, Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire RG21 6XS, United Kingdom http://www.nature.com/modpathol/index.htmlhttp://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=emed16&NEWS=N&AN=52834712. Accessed (Toon, Clarkson, Sioson, Gill) Department of Cancer Diagnosis and Pathology, Kolling Institute of Medical Research, St Leonards, NSW, Australia 27
Newton K, Jorgensen NM, Wallace AJ, Buchanan DD, Lalloo F, McMahon RF, Hill J, Evans DG (2014) Tumour MLH1 promoter region methylation testing is an effective prescreen for lynch syndrome (HNPCC). J Med Genet 51(12):789–796. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102552
Messerini L, Ciantelli M, Baglioni S, Palomba A, Zampi G, Papi L (1999) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in sporadic mucinous colorectal cancers. Hum Pathol 30(6):629–634
Kim SH, Shin SJ, Lee KY, Kim H, Kim TI, Kang DR, Hur H, Min BS, Kim NK, Chung HC, Roh JK, Ahn JB (2013) Prognostic value of mucinous histology depends on microsatellite instability status in patients with stage III colon cancer treated with adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol 20(11):3407–3413. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3169-1
Verhulst J, Ferdinande L, Demetter P, Ceelen W (2012) Mucinous subtype as prognostic factor in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Clin Pathol 65(5):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1136/jclinpath-2011-200340
Missiaglia E, Jacobs B, D'Ario G, Di Narzo AF, Soneson C, Budinska E, Popovici V, Vecchione L, Gerster S, Yan P, Roth AD, Klingbiel D, Bosman FT, Delorenzi M, Tejpar S (2014) Distal and proximal colon cancers differ in terms of molecular, pathological, and clinical features. Ann Oncol 25(10):1995–2001. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu275
Lim DR, Kuk JK, Kim T, Shin EJ (2017) Comparison of oncological outcomes of right-sided colon cancer versus left-sided colon cancer after curative resection: which side is better outcome? Medicine 96(42):e8241. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000008241
Ulanja MB, Rishi M, Beutler BD, Sharma M, Patterson DR, Gullapalli N, Ambika S (2019) Colon Cancer Sidedness, Presentation, and Survival at Different Stages. J Oncol 2019:4315032. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4315032
Petrelli F, Tomasello G, Borgonovo K, Ghidini M, Turati L, Dallera P, Passalacqua R, Sgroi G, Barni S (2017) Prognostic survival associated with left-sided vs right-sided colon cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 3(2):211–219. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.4227
Jernvall P, Makinen MJ, Karttunen TJ, Makela J, Vihko P (1999) Microsatellite instability: impact on cancer progression in proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 35(2):197–201
Meng WJ, Sun XF, Tian C, Wang L, Yu YY, Zhou B, Gu J, Xia QJ, Li Y, Wang R, Zheng XL, Zhou ZG (2007) Microsatellite instability did not predict individual survival in sporadic stage II and III rectal cancer patients. Oncology 72(1–2):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1159/000111107
Alex AK, Siqueira S, Coudry R, Santos J, Alves M, Hoff PM, Riechelmann RP (2017) Response to chemotherapy and prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer with DNA deficient mismatch repair. Clin Colorectal Cancer 16(3):228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2016.11.001
Aparicio T, Schischmanoff O, Poupardin C, Soufir N, Angelakov C, Barrat C, Levy V, Choudat L, Cucherousset J, Boubaya M, Lagorce C, Guetz GD, Wind P, Benamouzig R (2013) Deficient mismatch repair phenotype is a prognostic factor for colorectal cancer in elderly patients. Dig Liver Dis 45(3):245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2012.09.013
Andrici J, Farzin M, Sioson L, Clarkson A, Watson N, Toon CW, Gill AJ (2016) Mismatch repair deficiency as a prognostic factor in mucinous colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol 29(3):266–274. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2015.159
Bae JM, Kim JH, Rhee YY, Cho NY, Kim TY, Kang GH (2015) Annexin A10 expression in colorectal cancers with emphasis on the serrated neoplasia pathway. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 21(33):9749–9757. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9749
Banerjea A, Hands RE, Powar MP, Bustin SA, Dorudi S (2009) Microsatellite and chromosomal stable colorectal cancers demonstrate poor immunogenicity and early disease recurrence. Color Dis 11(6):601–608. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1318.2008.01639.x
Barault L, Charon-Barra C, Jooste V, de la Vega MF, Martin L, Roignot P, Rat P, Bouvier AM, Laurent-Puig P, Faivre J, Chapusot C, Piard F (2008) Hypermethylator phenotype in sporadic colon cancer: study on a population-based series of 582 cases. Cancer Res 68(20):8541–8546. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-1171
Barrasa Shaw A, Lopez-Guerrero JA, Calatrava Fons A, Garcia-Casado Z, Alapont Olavarrieta V, Campos Manez J, Vazquez Albaladejo C (2009) Value of the identification of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Clin Translational Oncol 11(7):465–469
Benatti P, Gafa R, Barana D, Marino M, Scarselli A, Pedroni M, Maestri I, Guerzoni L, Roncucci L, Menigatti M, Roncari B, Maffei S, Rossi G, Ponti G, Santini A, Losi L, Di Gregorio C, Oliani C, Ponz de Leon M, Lanza G (2005) Microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 11(23):8332–8340. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-05-1030
Bertagnolli MM, Redston M, Compton CC, Niedzwiecki D, Mayer RJ, Goldberg RM, Colacchio TA, Saltz LB, Warren RS (2011) Microsatellite instability and loss of heterozygosity at chromosomal location 18q: prospective evaluation of biomarkers for stages II and III colon cancer--a study of CALGB 9581 and 89803. J Clin Oncol 29(23):3153–3162. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.33.0092
Birgisson H, Edlund K, Wallin U, Påhlman L, Kultima HG, Mayrhofer M, Micke P, Isaksson A, Botling J, Glimelius B, Sundström M (2015) Microsatellite instability and mutations in BRAF and KRAS are significant predictors of disseminated disease in colon cancer. BMC Cancer 15:125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1144-x
Brenner BM, Swede H, Jones BA, Anderson GR, Stoler DL (2012) Genomic instability measured by inter-(simple sequence repeat) PCR and high-resolution microsatellite instability are prognostic of colorectal carcinoma survival after surgical resection. Ann Surg Oncol 19(1):344–350. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-011-1708-1
Carethers JM, Smith EJ, Behling CA, Nguyen L, Tajima A, Doctolero RT, Cabrera BL, Goel A, Arnold CA, Miyai K, Boland CR (2004) Use of 5-fluorouracil and survival in patients with microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 126(2):394–401
Chang SC, Lin JK, Yang SH, Wang HS, Li AF, Chi CW (2006) Relationship between genetic alterations and prognosis in sporadic colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 118(7):1721–1727. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21563
Chang EY, Dorsey PB, Johnson N, Lee R, Walts D, Johnson W, Anadiotis G, Kiser K, Frankhouse J (2006) A prospective analysis of microsatellite instability as a molecular marker in colorectal cancer. Am J Surg 191(5):646–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.02.015
Chouhan H, Sammour T, M LT, J WM (2019) Prognostic significance of BRAF mutation alone and in combination with microsatellite instability in stage III colon cancer. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol 15(1):69–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.13096
Curran B, Lenehan K, Mulcahy H, Tighe O, Bennett MA, Kay EW, O’Donoghue DP, Leader M, Croke DT (2000) Replication error phenotype, clinicopathological variables, and patient outcome in Dukes’ B stage II (T3,N0,M0) colorectal cancer. Gut 46(2):200–204
Des Guetz G, Lecaille C, Mariani P, Bennamoun M, Uzzan B, Nicolas P, Boisseau A, Sastre X, Cucherousset J, Lagorce C, Schischmanoff PO, Morere JF (2010) Prognostic impact of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer patients treated with adjuvant FOLFOX. Anticancer Res 30(10):4297–4301
Deschoolmeester V, Van Damme N, Baay M, Claes K, Van Marck E, Baert FJ, Wuyts W, Cabooter M, Weyler J, Vermeulen P, Lardon F, Vermorken JB, Peeters M (2008) Microsatellite instability in sporadic colon carcinomas has no independent prognostic value in a Belgian study population. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 44(15):2288–2295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.06.043
de Weger VA, Turksma AW, Voorham QJ, Euler Z, Bril H, van den Eertwegh AJ, Bloemena E, Pinedo HM, Vermorken JB, van Tinteren H, Meijer GA, Hooijberg E (2012) Clinical effects of adjuvant active specific immunotherapy differ between patients with microsatellite-stable and microsatellite-instable colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(3):882–889. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1716
Diep CB, Thorstensen L, Meling GI, Skovlund E, Rognum TO, Lothe RA (2003) Genetic tumor markers with prognostic impact in Dukes’ stages B and C colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 21(5):820–829
Donada M, Bonin S, Nardon E, De Pellegrin A, Decorti G, Stanta G (2011) Thymidilate synthase expression predicts longer survival in patients with stage II colon cancer treated with 5-flurouracil independently of microsatellite instability. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(2):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-010-0872-1
Drucker A, Arnason T, Yan SR, Aljawad M, Thompson K, Huang WY (2013) Ephrin b2 receptor and microsatellite status in lymph node-positive colon cancer survival. Transl Oncol 6(5):520–527
Du C, Zhao J, Xue W, Dou F, Gu J (2013) Prognostic value of microsatellite instability in sporadic locally advanced rectal cancer following neoadjuvant radiotherapy. Histopathology 62(5):723–730. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12069
Elsaleh H, Cserni G, Iacopetta B (2002) Extent of nodal involvement in stage III colorectal carcinoma: relationship to clinicopathologic variables and genetic alterations. Dis Colon Rectum 45(9):1218–1222. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.dcr.0000027039.89662.33
Emterling A, Wallin A, Arbman G, Sun XF (2004) Clinicopathological significance of microsatellite instability and mutated RIZ in colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 15(2):242–246
Eveno C, Lefevre JH, Svrcek M, Bennis M, Chafai N, Tiret E, Parc Y (2014) Oncologic results after multivisceral resection of clinical T4 tumors. Surgery 156(3):669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2014.03.040
Ferri M, Lorenzon L, Onelli MR, La Torre M, Mercantini P, Virgilio E, Balducci G, Ruco L, Ziparo V, Pilozzi E (2013) Lymph node ratio is a stronger prognostic factor than microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer patients: results from a 7 years follow-up study. Int J Surg (London, England) 11(9):1016–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2013.05.031
Fujiyoshi K, Yamamoto G, Takenoya T, Takahashi A, Arai Y, Yamada M, Kakuta M, Yamaguchi K, Akagi Y, Nishimura Y, Sakamoto H, Akagi K (2017) Metastatic pattern of stage IV colorectal Cancer with high-frequency microsatellite instability as a prognostic factor. Anticancer Res 37(1):239–247. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11313
Gafa R, Maestri I, Matteuzzi M, Santini A, Ferretti S, Cavazzini L, Lanza G (2000) Sporadic colorectal adenocarcinomas with high-frequency microsatellite instability. Cancer 89(10):2025–2037
Gavin PG, Colangelo LH, Fumagalli D, Tanaka N, Remillard MY, Yothers G, Kim C, Taniyama Y, Kim SI, Choi HJ, Blackmon NL, Lipchik C, Petrelli NJ, O’Connell MJ, Wolmark N, Paik S, Pogue-Geile KL (2012) Mutation profiling and microsatellite instability in stage II and III colon cancer: an assessment of their prognostic and oxaliplatin predictive value. Clin Cancer Res 18(23):6531–6541. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-0605
Gervaz P, Cerottini JP, Bouzourene H, Hahnloser D, Doan CL, Benhattar J, Chaubert P, Secic M, Gillet M, Carethers JM (2002) Comparison of microsatellite instability and chromosomal instability in predicting survival of patients with T3N0 colorectal cancer. Surgery 131(2):190–197
Ghanipour L, Jirström K, Sundström M, Glimelius B, Birgisson H (2017) Associations of defect mismatch repair genes with prognosis and heredity in sporadic colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 43(2):311–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2016.10.013
Gkekas I, Novotny J, Fabian P, Nemecek R, Palmqvist R, Strigard K, Pecen L, Svoboda T, Gurlich R, Gunnarsson U (2019) Deficient mismatch repair as a prognostic marker in stage II colon cancer patients. Eur J Surg Oncol 45(10):1854–1861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2019.05.023
Gryfe R, Kim H, Hsieh ET, Aronson MD, Holowaty EJ, Bull SB, Redston M, Gallinger S (2000) Tumor microsatellite instability and clinical outcome in young patients with colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 342(2):69–77. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200001133420201
Guidoboni M, Gafa R, Viel A, Doglioni C, Russo A, Santini A, Del Tin L, Macri E, Lanza G, Boiocchi M, Dolcetti R (2001) Microsatellite instability and high content of activated cytotoxic lymphocytes identify colon cancer patients with a favorable prognosis. Am J Pathol 159(1):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)61695-1
Gupta S, Ashfaq R, Kapur P, Afonso BB, Nguyen TP, Ansari F, Boland CR, Goel A, Rockey DC (2010) Microsatellite instability among individuals of Hispanic origin with colorectal cancer. Cancer 116(21):4965–4972. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25486
Hartman DJ, Nikiforova MN, Chang DT, Chu E, Bahary N, Brand RE, Zureikat AH, Zeh HJ, Choudry H, Pai RK (2013) Signet ring cell colorectal carcinoma: a distinct subset of mucin-poor microsatellite-stable signet ring cell carcinoma associated with dismal prognosis. Am J Surg Pathol 37(7):969–977. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182851e2b
Hemminki A, Mecklin JP, Jarvinen H, Aaltonen LA, Joensuu H (2000) Microsatellite instability is a favorable prognostic indicator in patients with colorectal cancer receiving chemotherapy. Gastroenterology 119(4):921–928
Hong SP, Min BS, Kim TI, Cheon JH, Kim NK, Kim H, Kim WH (2012) The differential impact of microsatellite instability as a marker of prognosis and tumour response between colon cancer and rectal cancer. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 48(8):1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.10.005
Hu J, Yan WY, Xie L, Cheng L, Yang M, Li L, Shi J, Liu BR, Qian XP (2016) Coexistence of MSI with KRAS mutation is associated with worse prognosis in colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(50):e5649. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000005649
Hutchins G, Southward K, Handley K, Magill L, Beaumont C, Stahlschmidt J, Richman S, Chambers P, Seymour M, Kerr D, Gray R, Quirke P (2011) Value of mismatch repair, KRAS, and BRAF mutations in predicting recurrence and benefits from chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(10):1261–1270. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.30.1366
Hveem TS, Merok MA, Pretorius ME, Novelli M, Baevre MS, Sjo OH, Clinch N, Liestol K, Svindland A, Lothe RA, Nesbakken A, Danielsen HE (2014) Prognostic impact of genomic instability in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 110(8):2159–2164. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.133
Imai Y (2015) Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the colon: subsite location and clinicopathologic features. Int J Color Dis 30(2):187–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-014-2070-0
Iachetta F, Domati F, Reggiani-Bonetti L, Barresi V, Magnani G, Marcheselli L, Cirilli C, Pedroni M (2016) Prognostic relevance of microsatellite instability in pT3N0M0 colon cancer: a population-based study. Intern Emerg Med 11(1):41–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1285-6
Jensen SA, Vainer B, Kruhoffer M, Sorensen JB (2009) Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer and association with thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression. BMC Cancer 9:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-25
Johannsdottir JT, Bergthorsson JT, Gretarsdottir S, Kristjansson AK, Ragnarsson G, Jonasson JG, Egilsson V, Ingvarsson S (1999) Replication error in colorectal carcinoma: association with loss of heterozygosity at mismatch repair loci and clinicopathological variables. Anticancer Res 19(3a):1821–1826
Jover R, Zapater P, Castells A, Llor X, Andreu M, Cubiella J, Balaguer F, Sempere L, Xicola RM, Bujanda L, Rene JM, Clofent J, Bessa X, Morillas JD, Nicolas-Perez D, Pons E, Paya A, Alenda C (2009) The efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer depends on the mismatch repair status. Eur J Cancer (Oxford, England : 1990) 45(3):365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.07.016
Jung SH, Kim SH, Kim JH (2016) Prognostic impact of microsatellite instability in colorectal Cancer presenting with mucinous, signet-ring, and poorly differentiated cells. Ann Coloproctol 32(2):58–65. https://doi.org/10.3393/ac.2016.32.2.58
Kakar S, Aksoy S, Burgart LJ, Smyrk TC (2004) Mucinous carcinoma of the colon: correlation of loss of mismatch repair enzymes with clinicopathologic features and survival. Mod Pathol 17(6):696–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800093
Kalady MF, Dejulius KL, Sanchez JA, Jarrar A, Liu X, Manilich E, Skacel M, Church JM (2012) BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with distinct clinical characteristics and worse prognosis. Dis Colon Rectum 55(2):128–133. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0b013e31823c08b3
Kang J, Lee HW, Kim IK, Kim NK, Sohn SK, Lee KY (2015) Clinical implications of microsatellite instability in T1 colorectal cancer. Yonsei Med J 56(1):175–181. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.1.175
Kang BW, Kim JG, Lee SJ, Chae YS, Moon JH, Sohn SK, Jeon SW, Jung MK, Lim KH, Jang YS, Park JS, Jun SH, Choi GS (2011) Clinical significance of microsatellite instability for stage II or III colorectal cancer following adjuvant therapy with doxifluridine. Med Oncol (Northwood, London, England) 28(Suppl 1):S214–S218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9701-2
Kevans D, Wang LM, Sheahan K, Hyland J, O’Donoghue D, Mulcahy H, O’Sullivan J (2011) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) protein expression in a cohort of stage II colorectal cancer patients with characterized tumor budding and mismatch repair protein status. Int J Surg Pathol 19(6):751–760. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066896911414566
Kim JE, Hong YS, Kim HJ, Kim KP, Kim SY, Lim SB, Park IJ, Kim CW, Yoon YS, Yu CS, Kim JC, Kim JH, Kim TW (2017) Microsatellite instability was not associated with survival in stage III colon cancer treated with adjuvant chemotherapy of oxaliplatin and infusional 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (FOLFOX). Ann Surg Oncol 24(5):1289–1294. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5682-5
Kim CG, Ahn JB, Jung M, Beom SH, Kim C, Kim JH, Heo SJ, Park HS, Kim JH, Kim NK, Min BS, Kim H, Koom WS, Shin SJ (2016) Effects of microsatellite instability on recurrence patterns and outcomes in colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer 115(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2016.161
Kim JE, Hong YS, Kim HJ, Kim KP, Lee JL, Park SJ, Lim SB, Park IJ, Kim CW, Yoon YS, Yu CS, Kim JC, Hoon KJ, Kim TW (2015) Defective mismatch repair status was not associated with DFS and OS in stage II Colon Cancer treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol 22(Suppl 3):S630–S637. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4807-6
Kim ST, Lee J, Park SH, Park JO, Lim HY, Kang WK, Kim JY, Kim YH, Chang DK, Rhee PL, Kim DS, Yun H, Cho YB, Kim HC, Yun SH, Lee WY, Chun HK, Park YS (2010) Clinical impact of microsatellite instability in colon cancer following adjuvant FOLFOX therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66(4):659–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-009-1206-3
Kim GP, Colangelo LH, Wieand HS, Paik S, Kirsch IR, Wolmark N, Allegra CJ (2007) Prognostic and predictive roles of high-degree microsatellite instability in colon cancer: a National Cancer Institute-National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Collaborative Study. J Clin Oncol 25(7):767–772. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.05.8172
Kim SH, Shin SJ, Lee KY, Kim H, Kim TI, Kang DR, Hur H, Min BS, Kim NK, Chung HC, Roh JK, Ahn JB (2013) Prognostic value of mucinous histology depends on microsatellite instability status in patients with stage III colon cancer treated with adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol 20(11):3407–3413. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-013-3169-1
Kim JE, Hong YS, Ryu MH, Lee JL, Chang HM, Lim SB, Kim JH, Jang SJ, Kim MJ, Yu CS, Kang YK, Kim JC, Kim TW (2011) Association between deficient mismatch repair system and efficacy to irinotecan-containing chemotherapy in metastatic colon cancer. Cancer Sci 102(9):1706–1711. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.02009.x
Klingbiel D, Saridaki Z, Roth AD, Bosman FT, Delorenzi M, Tejpar S (2015) Prognosis of stage II and III colon cancer treated with adjuvant 5-fluorouracil or FOLFIRI in relation to microsatellite status: results of the PETACC-3 trial. Ann Oncol 26(1):126–132. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu499
Korphaisarn K, Pongpaibul A, Limwongse C, Roothumnong E, Klaisuban W, Nimmannit A, Jinawath A, Akewanlop C (2015) Deficient DNA mismatch repair is associated with favorable prognosis in Thai patients with sporadic colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol: WJG 21(3):926–934. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.926
Lanza G, Gafa R, Maestri I, Santini A, Matteuzzi M, Cavazzini L (2002) Immunohistochemical pattern of MLH1/MSH2 expression is related to clinical and pathological features in colorectal adenocarcinomas with microsatellite instability. Mod Pathol 15(7):741–749. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mp.0000018979.68686.b2
Lanza G, Gafa R, Santini A, Maestri I, Guerzoni L, Cavazzini L (2006) Immunohistochemical test for MLH1 and MSH2 expression predicts clinical outcome in stage II and III colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 24(15):2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.03.2433
Lee SY, Kim DW, Lee HS, Ihn MH, Oh HK, Min BS, Kim WR, Huh JW, Yun JA, Lee KY, Kim NK, Lee WY, Kim HC, Kang SB (2015) Low-level microsatellite instability as a potential prognostic factor in sporadic colorectal cancer. Medicine 94(50):e2260. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000002260
Li P, Xiao ZT, Braciak TA, Ou QJ, Chen G, Oduncu FS (2017) Impact of age and mismatch repair status on survival in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med 6(5):975–981. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1007
Liang JT, Huang KC, Lai HS, Lee PH, Cheng YM, Hsu HC, Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Yeh KH, Wang SM, Tang C, Chang KJ (2002) High-frequency microsatellite instability predicts better chemosensitivity to high-dose 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin chemotherapy for stage IV sporadic colorectal cancer after palliative bowel resection. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 101(6):519–525. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.10643
Lim SB, Jeong SY, Lee MR, Ku JL, Shin YK, Kim WH, Park JG (2004) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in sporadic colorectal cancer. Int J Color Dis 19(6):533–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-004-0596-2
Lin CC, Lin JK, Lin TC, Chen WS, Yang SH, Wang HS, Lan YT, Jiang JK, Yang MH, Chang SC (2014) The prognostic role of microsatellite instability, codon-specific KRAS, and BRAF mutations in colon cancer. J Surg Oncol 110(4):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23675
Lin CC, Lai YL, Lin TC, Chen WS, Jiang JK, Yang SH, Wang HS, Lan YT, Liang WY, Hsu HM, Lin JK, Chang SC (2012) Clinicopathologic features and prognostic analysis of MSI-high colon cancer. Int J Color Dis 27(3):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1341-2
Maccaroni E, Bracci R, Giampieri R, Bianchi F, Belvederesi L, Brugiati C, Pagliaretta S, Del Prete M, Scartozzi M, Cascinu S (2015) Prognostic impact of mismatch repair genes germline defects in colorectal cancer patients: are all mutations equal? Oncotarget 6(36):38737–38748. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5395
MacQuarrie E, Arnason T, Gruchy J, Yan S, Drucker A, Huang WY (2012) Microsatellite instability status does not predict total lymph node or negative lymph node retrieval in stage III colon cancer. Hum Pathol 43(8):1258–1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2011.10.002
Maestro ML, Vidaurreta M, Sanz-Casla MT, Rafael S, Veganzones S, Martinez A, Aguilera C, Herranz MD, Cerdan J, Arroyo M (2007) Role of the BRAF mutations in the microsatellite instability genetic pathway in sporadic colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 14(3):1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-006-9111-z
Markovic S, Antic J, Dragicevic N, Hamelin R, Krivokapic Z (2012) High-frequency microsatellite instability and BRAF mutation (V600E) in unselected Serbian patients with colorectal cancer. J Mol Histol 43(2):137–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-011-9387-6
Meng WJ, Sun XF, Tian C, Wang L, Yu YY, Zhou B, Gu J, Xia QJ, Li Y, Wang R, Zheng XL, Zhou ZG (2007) Microsatellite instability did not predict individual survival in sporadic stage II and III rectal cancer patients. Oncology 72(1-2):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1159/000111107
Merok MA, Ahlquist T, Royrvik EC, Tufteland KF, Hektoen M, Sjo OH, Mala T, Svindland A, Lothe RA, Nesbakken A (2013) Microsatellite instability has a positive prognostic impact on stage II colorectal cancer after complete resection: results from a large, consecutive Norwegian series. Ann Oncol 24(5):1274–1282. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds614
Messerini L, Ciantelli M, Baglioni S, Palomba A, Zampi G, Papi L (1999) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in sporadic mucinous colorectal cancers. Hum Pathol 30(6):629–634
Mohan HM, Ryan E, Balasubramanian I, Kennelly R, Geraghty R, Sclafani F, Fennelly D, McDermott R, Ryan EJ, O'Donoghue D, Hyland JM, Martin ST, O'Connell PR, Gibbons D, Winter D, Sheahan K (2016) Microsatellite instability is associated with reduced disease specific survival in stage III colon cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 42(11):1680–1686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2016.05.013
Nazemalhosseini Mojarad E, Kashfi SM, Mirtalebi H, Taleghani MY, Azimzadeh P, Savabkar S, Pourhoseingholi MA, Jalaeikhoo H, Asadzadeh Aghdaei H, Kuppen PJ, Zali MR (2016) Low level of microsatellite instability correlates with poor clinical prognosis in stage II colorectal Cancer patients. J Oncol 2016:2196703. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2196703
Mouradov D, Domingo E, Gibbs P, Jorissen RN, Li S, Soo PY, Lipton L, Desai J, Danielsen HE, Oukrif D, Novelli M, Yau C, Holmes CC, Jones IT, McLaughlin S, Molloy P, Hawkins NJ, Ward R, Midgely R, Kerr D, Tomlinson IP, Sieber OM (2013) Survival in stage II/III colorectal cancer is independently predicted by chromosomal and microsatellite instability, but not by specific driver mutations. Am J Gastroenterol 108(11):1785–1793. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.292
Nakaji Y, Oki E, Nakanishi R, Ando K, Sugiyama M, Nakashima Y, Yamashita N, Saeki H, Oda Y, Maehara Y (2017) Prognostic value of BRAF V600E mutation and microsatellite instability in Japanese patients with sporadic colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143(1):151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2275-4
Nash GM, Gimbel M, Cohen AM, Zeng ZS, Ndubuisi MI, Nathanson DR, Ott J, Barany F, Paty PB (2010) KRAS mutation and microsatellite instability: two genetic markers of early tumor development that influence the prognosis of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 17(2):416–424. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0713-0
Nehls O, Hass HG, Okech T, Zenner S, Hsieh CJ, Sarbia M, Borchard F, Gruenagel HH, Gaco V, Porschen R, Gregor M, Klump B (2009) Prognostic implications of BAX protein expression and microsatellite instability in all non-metastatic stages of primary colon cancer treated by surgery alone. Int J Color Dis 24(6):655–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0635-0
Nopel-Dunnebacke S, Schulmann K, Reinacher-Schick A, Porschen R, Schmiegel W, Tannapfel A, Graeven U (2014) Prognostic value of microsatellite instability and p53 expression in metastatic colorectal cancer treated with oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy. Z Gastroenterol 52(12):1394–1401. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1366781
Nordholm-Carstensen A, Krarup PM, Morton D, Harling H (2015) Mismatch repair status and synchronous metastases in colorectal cancer: a nationwide cohort study. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 137(9):2139–2148. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29585
Ogino S, Nosho K, Kirkner GJ, Kawasaki T, Meyerhardt JA, Loda M, Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS (2009) CpG island methylator phenotype, microsatellite instability, BRAF mutation and clinical outcome in colon cancer. Gut 58(1):90–96. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.155473
Oh SY, Kim do Y, Kim YB, Suh KW (2013) Oncologic outcomes after adjuvant chemotherapy using FOLFOX in MSI-H sporadic stage III colon cancer. World J Surg 37(10):2497–2503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-2120-8
Ohrling K, Edler D, Hallstrom M, Ragnhammar P (2010) Mismatch repair protein expression is an independent prognostic factor in sporadic colorectal cancer. Acta Oncol (Stockholm, Sweden) 49(6):797–804. https://doi.org/10.3109/02841861003705786
Ooki A, Akagi K, Yatsuoka T, Asayama M, Hara H, Takahashi A, Kakuta M, Nishimura Y, Yamaguchi K (2014) Combined microsatellite instability and BRAF gene status as biomarkers for adjuvant chemotherapy in stage III colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 110(8):982–988. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.23755
Parc Y, Gueroult S, Mourra N, Serfaty L, Flejou JF, Tiret E, Parc R (2004) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability determined by immunohistochemical staining of MSH2 and MLH1 in sporadic T3N0M0 colon cancer. Gut 53(3):371–375
Park JW, Chang HJ, Park S, Kim BC, Kim DY, Baek JY, Kim SY, Oh JH, Choi HS, Park SC, Jeong SY (2010) Absence of hMLH1 or hMSH2 expression as a stage-dependent prognostic factor in sporadic colorectal cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 17(11):2839–2846. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-010-1135-8
Phipps AI, Lindor NM, Jenkins MA, Baron JA, Win AK, Gallinger S, Gryfe R, Newcomb PA (2013) Colon and rectal cancer survival by tumor location and microsatellite instability: the Colon Cancer Family Registry. Dis Colon Rectum 56(8):937–944. https://doi.org/10.1097/DCR.0b013e31828f9a57
Ribic CM, Sargent DJ, Moore MJ, Thibodeau SN, French AJ, Goldberg RM, Hamilton SR, Laurent-Puig P, Gryfe R, Shepherd LE, Tu D, Redston M, Gallinger S (2003) Tumor microsatellite-instability status as a predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 349(3):247–257. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa022289
Rosty C, Williamson EJ, Clendenning M, Walters RJ, Win AK, Jenkins MA, Hopper JL, Winship IM, Southey MC, Giles GG, English DR, Buchanan DD (2014) Should the grading of colorectal adenocarcinoma include microsatellite instability status? Hum Pathol 45(10):2077–2084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2014.06.020
Roth AD, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Yan P, Fiocca R, Klingbiel D, Dietrich D, Biesmans B, Bodoky G, Barone C, Aranda E, Nordlinger B, Cisar L, Labianca R, Cunningham D, Van Cutsem E, Bosman F (2010) Prognostic role of KRAS and BRAF in stage II and III resected colon cancer: results of the translational study on the PETACC-3, EORTC 40993, SAKK 60-00 trial. J Clin Oncol 28(3):466–474. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.23.3452
Salahshor S, Kressner U, Fischer H, Lindmark G, Glimelius B, Pahlman L, Lindblom A (1999) Microsatellite instability in sporadic colorectal cancer is not an independent prognostic factor. Br J Cancer 81(2):190–193. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6690676
Samowitz WS, Curtin K, Wolff RK, Tripp SR, Caan BJ, Slattery ML (2009) Microsatellite instability and survival in rectal cancer. Cancer Causes Control 20(9):1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10552-009-9410-3
Samowitz WS, Curtin K, Ma KN, Schaffer D, Coleman LW, Leppert M, Slattery ML (2001) Microsatellite instability in sporadic colon cancer is associated with an improved prognosis at the population level. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 10(9):917–923
Sargent DJ, Marsoni S, Monges G, Thibodeau SN, Labianca R, Hamilton SR, French AJ, Kabat B, Foster NR, Torri V, Ribic C, Grothey A, Moore M, Zaniboni A, Seitz JF, Sinicrope F, Gallinger S (2010) Defective mismatch repair as a predictive marker for lack of efficacy of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy in colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(20):3219–3226. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.27.1825
Saridaki Z, Papadatos-Pastos D, Tzardi M, Mavroudis D, Bairaktari E, Arvanity H, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, Souglakos J (2010) BRAF mutations, microsatellite instability status and cyclin D1 expression predict metastatic colorectal patients’ outcome. Br J Cancer 102(12):1762–1768. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6605694
Shima K, Morikawa T, Yamauchi M, Kuchiba A, Imamura Y, Liao X, Meyerhardt JA, Fuchs CS, Ogino S (2011) TGFBR2 and BAX mononucleotide tract mutations, microsatellite instability, and prognosis in 1072 colorectal cancers. PLoS One 6(9):e25062. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025062
Shin US, Cho SS, Moon SM, Park SH, Jee SH, Jung EJ, Hwang DY (2014) Is microsatellite instability really a good prognostic factor of colorectal cancer? Ann Coloproctol 30(1):28–34. https://doi.org/10.3393/ac.2014.30.1.28
Sinicrope FA, Shi Q, Smyrk TC, Thibodeau SN, Dienstmann R, Guinney J, Bot BM, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Goldberg RM, Mahoney M, Sargent DJ, Alberts SR (2015) Molecular markers identify subtypes of stage III colon cancer associated with patient outcomes. Gastroenterology 148(1):88–99. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.09.041
Sinicrope FA, Mahoney MR, Smyrk TC, Thibodeau SN, Warren RS, Bertagnolli MM, Nelson GD, Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Alberts SR (2013) Prognostic impact of deficient DNA mismatch repair in patients with stage III colon cancer from a randomized trial of FOLFOX-based adjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 31(29):3664–3672. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.48.9591
Sinicrope FA, Rego RL, Halling KC, Foster N, Sargent DJ, La Plant B, French AJ, Laurie JA, Goldberg RM, Thibodeau SN, Witzig TE (2006) Prognostic impact of microsatellite instability and DNA ploidy in human colon carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology 131(3):729–737. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2006.06.005
Sinicrope FA, Foster NR, Thibodeau SN, Marsoni S, Monges G, Labianca R, Kim GP, Yothers G, Allegra C, Moore MJ, Gallinger S, Sargent DJ (2011) DNA mismatch repair status and colon cancer recurrence and survival in clinical trials of 5-fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 103(11):863–875. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr153
Slik K, Kurki S, Korpela T, Carpen O, Korkeila E, Sundstrom J (2017) Ezrin expression combined with MSI status in prognostication of stage II colorectal cancer. PLoS One 12(9):e0185436. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185436
Srdjan M, Jadranka A, Ivan D, Branimir Z, Daniela B, Petar S, Velimir M, Zoran K (2016) Microsatellite instability & survival in patients with stage II/III colorectal carcinoma. Indian J Med Res 143(Supplement):S104–s111. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5916.191801
Sun Z, Yu X, Wang H, Zhang S, Zhao Z, Xu R (2014) Clinical significance of mismatch repair gene expression in sporadic colorectal cancer. Exp Ther Med 8(5):1416–1422. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1927
Taieb J, Zaanan A, Le Malicot K, Julie C, Blons H, Mineur L, Bennouna J, Tabernero J, Mini E, Folprecht G, Van Laethem JL, Lepage C, Emile JF, Laurent-Puig P (2016) Prognostic effect of BRAF and KRAS mutations in patients with stage III colon cancer treated with leucovorin, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin with or without cetuximab: a post hoc analysis of the PETACC-8 trial. JAMA Oncol 2(5):643–653. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.5225
Tan WJ, Hamzah JL, Acharyya S, Foo FJ, Lim KH, Tan IBH, Tang CL, Chew MH (2018) Evaluation of long-term outcomes of microsatellite instability status in an Asian cohort of sporadic colorectal cancers. J Gastrointest Cancer 49(3):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-017-9953-6
Thomas ML, Hewett PJ, Ruszkiewicz AR, Moore JW (2015) Clinicopathological predictors of benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy for stage C colorectal cancer: Microsatellite unstable cases benefit. Asia-Pac J Clin Oncol 11(4):343–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.12411
Tian S, Roepman P, Popovici V, Michaut M, Majewski I, Salazar R, Santos C, Rosenberg R, Nitsche U, Mesker WE, Bruin S, Tejpar S, Delorenzi M, Bernards R, Simon I (2012) A robust genomic signature for the detection of colorectal cancer patients with microsatellite instability phenotype and high mutation frequency. J Pathol 228(4):586–595. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4092
Tikidzhieva A, Benner A, Michel S, Formentini A, Link KH, Dippold W, von Knebel DM, Kornmann M, Kloor M (2012) Microsatellite instability and Beta2-Microglobulin mutations as prognostic markers in colon cancer: results of the FOGT-4 trial. Br J Cancer 106(6):1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2012.53
Toon CW, Chou A, DeSilva K, Chan J, Patterson J, Clarkson A, Sioson L, Jankova L, Gill AJ (2014) BRAFV600E immunohistochemistry in conjunction with mismatch repair status predicts survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Mod Pathol 27(5):644–650. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2013.200
Touchefeu Y, Provost-Dewitte M, Lecomte T, Morel A, Valo I, Mosnier JF, Bossard C, Eugene J, Duchalais E, Chetritt J, Guyetant S, Bezieau S, Senellart H, Caulet M, Cauchin E, Matysiak-Budnik T (2016) Clinical, histological, and molecular risk factors for cancer recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 28(12):1394–1399. https://doi.org/10.1097/meg.0000000000000725
Tran B, Kopetz S, Tie J, Gibbs P, Jiang ZQ, Lieu CH, Agarwal A, Maru DM, Sieber O, Desai J (2011) Impact of BRAF mutation and microsatellite instability on the pattern of metastatic spread and prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 117(20):4623–4632. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26086
Turner N, Wong HL, Templeton A, Tripathy S, Whiti Rogers T, Croxford M, Jones I, Sinnathamby M, Desai J, Tie J, Bae S, Christie M, Gibbs P, Tran B (2016) Analysis of local chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate combined with systemic inflammation improves prognostication in stage II colon cancer independent of standard clinicopathologic criteria. Int J Cancer J Intl Cancer 138(3):671–678. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29805
Venderbosch S, Nagtegaal ID, Maughan TS, Smith CG, Cheadle JP, Fisher D, Kaplan R, Quirke P, Seymour MT, Richman SD, Meijer GA, Ylstra B, Heideman DA, de Haan AF, Punt CJ, Koopman M (2014) Mismatch repair status and BRAF mutation status in metastatic colorectal cancer patients: a pooled analysis of the CAIRO, CAIRO2, COIN, and FOCUS studies. Clin Cancer Res 20(20):5322–5330. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-14-0332
Vogelaar FJ, Erning FNV, Reimers MS, Linden HV, Pruijt H, Brule A, Bosscha K (2016) The prognostic value of microsatellite instability, KRAS, BRAF and PIK3CA mutations in stage II Colon Cancer patients. Mol Med (Cambridge, Mass) 21(1):1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2015.00220
Wang C, van Rijnsoever M, Grieu F, Bydder S, Elsaleh H, Joseph D, Harvey J, Iacopetta B (2003) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability and Ki-ras mutation type in stage II colorectal cancer. Oncology 64(3):259–265 doi:69311
Wangefjord S, Brandstedt J, Lindquist KE, Nodin B, Jirstrom K, Eberhard J (2013) Associations of beta-catenin alterations and MSI screening status with expression of key cell cycle regulating proteins and survival from colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol 8:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-8-10
Ward RL, Turner J, Williams R, Pekarsky B, Packham D, Velickovic M, Meagher A, O’Connor T, Hawkins NJ (2005) Routine testing for mismatch repair deficiency in sporadic colorectal cancer is justified. J Pathol 207(4):377–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1851
Watanabe T, Wu TT, Catalano PJ, Ueki T, Satriano R, Haller DG, Benson AB 3rd, Hamilton SR (2001) Molecular predictors of survival after adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 344(16):1196–1206. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200104193441603
Westra JL, Schaapveld M, Hollema H, de Boer JP, Kraak MM, de Jong D, ter Elst A, Mulder NH, Buys CH, Hofstra RM, Plukker JT (2005) Determination of TP53 mutation is more relevant than microsatellite instability status for the prediction of disease-free survival in adjuvant-treated stage III colon cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 23(24):5635–5643. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.04.096
Wright CM, Dent OF, Barker M, Newland RC, Chapuis PH, Bokey EL, Young JP, Leggett BA, Jass JR, Macdonald GA (2000) Prognostic significance of extensive microsatellite instability in sporadic clinicopathological stage C colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 87(9):1197–1202. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2168.2000.01508.x
Yang L, Sun Y, Huang XE, Yu DS, Zhou JN, Zhou X, Li DZ, Guan X (2015) Carcinoma microsatellite instability status as a predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II rectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(4):1545–1551
Yoon YS, Yu CS, Kim TW, Kim JH, Jang SJ, Cho DH, Roh SA, Kim JC (2011) Mismatch repair status in sporadic colorectal cancer: immunohistochemistry and microsatellite instability analyses. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(12):1733–1739. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06784.x
Zaanan A, Flejou JF, Emile JF, Des GG, Cuilliere-Dartigues P, Malka D, Lecaille C, Validire P, Louvet C, Rougier P, de Gramont A, Bonnetain F, Praz F, Taieb J (2011) Defective mismatch repair status as a prognostic biomarker of disease-free survival in stage III colon cancer patients treated with adjuvant FOLFOX chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 17(23):7470–7478. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-11-1048
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 410 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toh, J.W.T., Phan, K., Reza, F. et al. Rate of dissemination and prognosis in early and advanced stage colorectal cancer based on microsatellite instability status: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis 36, 1573–1596 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-021-03874-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-021-03874-1