Abstract
Purpose
This study examined whether the apoptosis-related protein, BAX, or the microsatellite-instability phenotype provide prognostic information in patients with resected colon cancer.
Methods
A total of 371 stage I–III patients that previously underwent radical surgery were included (mean follow-up 51.8 months). BAX expression was examined by immunohistochemical staining; high-frequency microsatellite instability (MSI+) was determined by assessing the specific marker, BAT26, using single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-based analysis.
Results
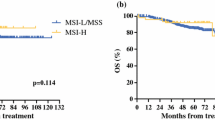
High BAX expression was found in 66.4% of patients. MSI+ tumors were observed in 14.8% of 344 patients. Univariate analysis showed that unlike MSI, low BAX expression was significantly correlated with poor disease-specific overall survival (OS) in stages I–III (p = 0.04). Multivariate subgroup analyses revealed that unlike MSI, low BAX was an independent predictor for OS in stage II (p = 0.009); however, in stages I or III, BAX or MSI were not independent predictors of OS.
Conclusions
In stage II colon cancer treated with surgery alone, BAX protein expression may be a predictor for prognosis.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ (2007) Cancer statistics 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Gill S, Loprinzi CL, Sargent DJ, Thomé SD, Alberts SR, Haller DG, Benedetti J, Francini G, shepherd LE, Seitz JF, Labianca R, Chen W, Cha SS, Heldebrant MP, Goldberg RM (2004) Pooled analysis of fluorouracil-based adjuvant therapy for stage II and III colon cancer: who benefits and by how much? J Clin Oncol 22:1797–1806
Wolpin BM, Meyerhardt JA, Mamon HJ, Mayer RJ (2007) Adjuvant treatment for colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin 57:168–185
Lindmark G, Bergström R, Pahlmann L, Glimelius B (1995) The association of preoperative serum tumor markers with Duke’s stage and survival in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 71:1090–1094
Greene FL, Stewart AK, Norton J (2002) A new TNM staging strategy for node positive (stage III) colon cancer. Ann Surg 4:416–421
Fearon ER, Vogelstein B (1990) A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 61:759–767
Perucho M (1996) Cancer of the microsatellite mutator phenotype. Biol Chem 377:675–684
Popat S, Hubner R, Houlston RS (2005) Systematic review of microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer prognosis. J Clin Oncol 23:609–618
Kerr J, Wyllie A, Currie A (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Miyashita T, Reed JC (1995) Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 80:293–299
Hoang JM, Cottu PH, Thuille B, Salmon RJ, Thomas G, Hamelin R (1997) BAT-26, an indicator of the replication error phenotype in colorectal cancers and cell lines. Cancer Res 57:300–303
Loukola A, Eklin K, Laiho P, Solovaara R, Kristo P, Järvinen H, Mecklin JP, Launonen V, Aaltonen LA (2001) Microsatellite marker analysis in screening for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). Cancer Res 61:4545–4549
Jansson A, Sun XF (2002) BAX expression decreases significantly from primary tumor to metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 20:811–816
Söreide K, Janssen EAM, Söiland H, Körner H, Baak JPA (2006) Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Br J Surgery 93:395–406
Sturm I, Köhne CH, Wolff G, Petrowsky H, Hillebrand T, Hauptmann S, Lorenz M, Dorken P, Daniel PT (1999) Analysis of the p53/BAX pathway in colorectal cancer: low BAX is a negative prognostic factor in patients with resected liver metastases. J Clin Oncol 17:1364–1374
Schelwies K, Sturm I, Grabowski P, Scherubl H, Schindler I, Hermann S, Stein H, Buhr HJ, Riecken EO, Zeitz M, Dorken P, Daniel PT (2002) Analysis of p53/BAX in primary colorectal carcinoma: low BAX protein expression is a negative prognostic factor in UICC stage III tumours. Int J Cancer 99:589–596
Nehls O, Okech T, Hsieh CJ, Sarbia M, Borchard F, Gruenagel HH, Gaco V, Porschen R, Gregor M, Klump B (2005) Low BAX protein expression correlates with disease-recurrence in preoperatively irradiated rectal carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:85–91
Nehls O, Okech T, Hsieh CJ, Enzinger T, Sarbia M, Borchard F, Gruenagel HH, Gaco V, Hass HG, Arkenau HAT, Hartmann JT, Porschen R, Gregor M, Klump B (2007) Studies on p53, BAX, and Bcl-2 protein expression in stage III (UICC) colon cancer treated by adjuvant chemotherapy: Major prognostic impact of proapoptotic BAX pronounced by intact p53. Br J Cancer 96:1409–1418
Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1997) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. UICC, International Union against cancer, 5th edn. Wiley-Liss, New York
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Stathopoulos GP, Fountzilas G, Kalofonos HP, Tsamandas A, Vrettou E, Scopa C, Polychronidis A, Simopoulos K, Koukourakis MI (2001) Bax protein expression in colorectal cancer: association with p53, bcl-2 and patterns of relapse. Anticancer Res 21:253–259
Koda M, Reszec J, Sulkowska M, Kanczuga-Koda L, Sulkowski S (2004) Expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and proapoptotic BAX and Bak proteins in human colorectal cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1030:377–383
Backus HHJ, van Groeningen CJ, Vos W, Dukers DF, Bloemena E, Wouters D, Pinedo HM, Peters GJ (2004) Differential expression of cell cycle and apoptosis related proteins in colorectal mucosa, primary colon tumours, and liver metastases. J Clin Pathol 55:206–211
Elsaleh H, Powell B, McCaul K, Grieu F, Grant R, Joseph D, Iacopetta B (2001) P53 alterations and microsatellite instability have predictive value for survival benefit from chemotherapy in stage III colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7:1343–1349
Evertson S, Wallin A, Arbman G, Rütten S, Emterling A, Zhang H, Sun XF (2003) Microsatellite instability and MBD4 mutation in unselected colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 23:3569–3574
Wang C, van Rijnsoever M, Grieu F, Bydder S, Elsaleh H, Joseph D, Harvey J, Iacopetta B (2003) Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability and Ki-ras mutation type in stage II colorectal cancer. Oncology 64:259–265
Minamoto T, Esumi H, Ochiai A, Belitsky G, Mai M, Sugimura T, Ronai Z (1997) Combined analysis of microsatellite instability and k-ras mutation increases detection of normal samples from colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 3:1413–1417
Gryfe R, Kim H, Hsieh ET, Aronson MD, Holowaty EJ, Bull SB, Redston M, Gallinger S (2000) Tumor microsatellite instability and clinical outcome in young patients with colorectal cancer. New Engl J Med 342:69–77
Ribic CM, Sargent DJ, Moore MJ, Thibodeau SN, French AJ, Goldberg RM, Hamilton SR, Laurent-Puig P, Gryfe R, Shepherd LE, Tu D, Redston M, Gallinger S (2003) Tumor microsatellite instability status as a predictor of benefit from fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer. New Engl J Med 349:247–257
Nakata B, Muguruma K, Hirakawa K, Chung YS, Yamashita Y, Inoue T, Matsuoka T, Onoda N, Kato Y, Sowa M (1998) Predictive value of Bcl-2 and BAX protein expression for chemotherapeutic effect in gastric cancer. A pilot study. Oncology 55:543–547
Kang SY, Han JH, Lee KJ, Choi J-H, Park JI, Kim HI, Lee H-W, Jang JH, Park JS, Kim HC, Kang S, Oh YT, Chun M, Kim JH, Sheen SS, Lim H-Y (2007) Low expression of BAX predicts poor prognosis in patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:4146–4153
Theodorakis P, Lomonosova E, Chinnadurai G (2002) Critical requirement of BAX manifestation of apoptosis induced by multiple stimuli in human epithelial cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 62:3373–3376
Schrag D, Cramer LD, Bach PB, Cohen AM, Warren JL, Begg CB (2000) Influence of hospital procedure volume on outcomes following surgery for colon cancer. JAMA 284:3028–3035
Rabeneck L, Davila JA, Thompson M, El-Serag HB (2004) Surgical volume and long-term survival following surgery for colorectal cancer in the Veterans Affairs Health-Care System. Am J Gastroenterol 99:668–675
Acknowledgements
The last author is supported by a grant of the Deutsche Krebshilfe (702601) and the Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research Tübingen (IZKF IIIB2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Oliver Nehls and Holger G. Hass contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nehls, O., Hass, H.G., Okech, T. et al. Prognostic implications of BAX protein expression and microsatellite instability in all non-metastatic stages of primary colon cancer treated by surgery alone. Int J Colorectal Dis 24, 655–663 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0635-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-009-0635-0