Abstract
The purpose of this study was to assess the prognostic value of abdominal color Doppler ultrasound (US) in determining predictors of early complications of NEC.
Methods
Fifty-one consecutive infants with stage Ia to IIIa NEC were prospectively included in the study between 2013 and July 2016. At least one abdominal US examination was performed in each patient.
Results
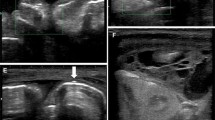
According to abdominal color Doppler US, neonates with NEC Ia stage in most cases (80%) found increased bowel wall perfusion. For the stage IIa typical signs were intramural gas and decreased bowel peristalsis. Patients in IIb stage had bowel wall thinning (less than 1 mm), decreased or absence of bowel peristalsis and absence of perfusion. In stage IIIa 71% of the cases had absence of bowel peristalsis and intramural gas. Absence of perfusion and bowel wall thinning less than 1 mm was found in 86% of neonates. One patient had portal venous gas. Nine patients with IIb and seven neonates with IIIa stage of NEC had laparotomy. In all 16 cases, US signs of bowel wall necrosis were verified intraoperative.
Conclusion
US provides an opportunity to image the bowel loops in cross section with dynamic evaluation of perfusion and peristalsis. Our study shows that abdominal US examination in neonates with NEC can highlight the presence of intestinal necrosis before the onset of intestinal perforation. Surgically intervening earlier in the clinical pathway of NEC may lead to improved outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell MJ, Ternberg JI, Feigin RD et al (1978) Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Ann Surg 187:1–7
Walsh MC, Kliegman RM (1986) Necrotizing enterocolitis: treatment based on staging criteria. Pediatr Clin N Am 33:179–201
Neu J, Walker WA (2011) Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med 364:255–264
Horbar JD, Badger GJ, Carpenter JH (2002) Trends in mortality and morbidity for very low birth weight infants, 1991–1999. Pediatrics 110:143–151
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF et al (2010) Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 126:443–456
Llanos AR, Moss ME, Pinzon MC et al (2002) Epidemiology of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis: a population-based study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 16:342–349
Guthrie SO, Gordon PV, Thomas V et al (2003) Necrotizing enterocolitis among neonates in the United States. J Perinatol 23:278–285
Luig M, Lui K, NICUS Group et al (2005) Epidemiology of necrotizing: enterocolitis: II. Risks and susceptibility of premature infants during the surfactant era: a regional study. J Pediatr Child Health 41:174–179
Holman RC, Stoll BJ, Clarke MJ et al (1997) The epidemiology of necrotizing enterocolitis infant mortality in the United States. Am J Public Health 87:2026–2031
Kasivajjula H, Maheshwari A (2014) Pathophysiology and current management of necrotizing enterocolitis. Indian J Pediatr 81(5):489–497
Braccini G, Lamacchia M, Boraschi P, Bertellotti L, Marrucci A, Goletti O, Perri G (1996) Ultrasound versus plain film in the detection of pneumoperitoneum. Abdom Imaging 21:404–412
Faingold R, Daneman A, Tomlinson G, Babyn PS, Manson DE, Mohanta A, Moore AM, Hellmann J, Smith C, Gerstle T, Kim JH (2005) Necrotizing enterocolitis: assessment of bowel viability with color Doppler US. Radiology 235:587–594
Kim WY, Kim WS, Kim IO, Kwon TH, Chang W, Lee EK (2005) Sonographic evaluation of neonates with early-stage necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Radiol 35:1056–1061
Kim WY, Kim IO, Kim WS et al (2007) Sonographic findings in a model of ischemia-induced necrotizing enterocolitis with pathological correlations. Invest Radiol 42:312–318
Epelman M, Daneman A, Navarro OM, Morag I, Moore AM, Kim JH, Faingold R, Taylor G, Gerstle JT (2007) Necrotizing enterocolitis: review of state-of-the-art imaging findings with pathologic correlation. Radiographics 27:285–305
Silva CT, Daneman A, Navarro OM, Faingold R, Epelman M (2007) Comparison of accuracy of radiographs and ultrasound for the detection of free intraperitoneal gas in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Radiol 37(Suppl 1):S52
Silva CT, Daneman A, Navarro OM, Moore AM, Moineddin R, Gerstle JT, Mittal A, Brindle M, Epelman M (2007) Correlation of sonographic findings and outcome in necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Radiol 37:274–282
Franco A, Ramji FG (2008) Utility of abdominal sonography to diagnose necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur J Radiol Extra 65:13–16
Dilli D, Suna Oğuz S, Erol R, Ozkan-Ulu H, Dumanlı H, Dilmen U (2011) Does abdominal sonography provide additional information over abdominal plain radiography for diagnosis of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates? Pediatr Surg Int 27:321–327
Bohnhorst B (2013) Usefulness of abdominal ultrasound in diagnosing necrotising enterocolitis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 98:F445–F450
Muchantef K, Epelman M, Darge K, Kirpalani H, Laje P, Anupindi SA (2013) Sonographic and radiographic imaging features of the neonate with necrotizing enterocolitis: correlating findings with outcomes. Pediatr Radiol 43(1444–1452):1240
Silva CT, Daneman A, Navarro OM, Moineddin R, Levine D, Moore AM (2013) A prospective comparison of intestinal sonography and abdominal radiographs in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Radiol 43:1453–1463
Yikilmaz A, Nigel JH, Daneman A, Gerstle JT, Oscar M, Navarro et al (2014) Prospective evaluation of the impact of sonography on the management and surgical intervention of neonates with necrotizing enterocolits. Pediatr Surg Int 30:1231–1240
Dekhkonbaev AA, Aliev MM, Adylova GS, Yuldashev RZ (2015) Ultrasonogrophic predictors of early complications of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatriya 3:62–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliev, M.M., Dekhqonboev, A.A. & Yuldashev, R.Z. Advantages of abdominal ultrasound in the management of infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Surg Int 33, 213–216 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-4017-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-016-4017-8