Abstract
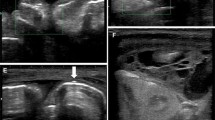
Background: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most common gastrointestinal emergency in neonatal intensive care units. Ultrasonographic findings in early-stage NEC have not been described. Objective: To assess the diagnostic value of ultrasonography for the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with NEC. Materials and methods: We evaluated the sonographic findings of early stages of NEC in 40 neonates who were clinically diagnosed with NEC when they were 2–28 days old. Their average gestational age was 32 weeks, and their mean weight was 1,850 g. All of the patients showed signs of bowel distention on abdominal radiography, with no evidence of pneumatosis intestinalis. We performed bowel sonography in all patients (n = 40), as well as in ten healthy neonates who served as a control group. The studies were conducted with a 10-MHz linear transducer from February 2003 to January 2004. We evaluated the echogenicity of the bowel wall, involved region, ascites, and portal venous gas at both initial and follow-up examinations. We divided the patients into two groups according to the bowel wall echogenicity pattern, group I with echogenic dots in the bowel wall and group II with dense granular echogenicities in the bowel wall. In order to identify any correlations between the ultrasonography and clinical findings, we evaluated the duration of parenteral feeding (NPO) in each group and compared two groups by means of a statistical analysis (Mann–Whitney test). Results: All of the neonates in the control group (n = 10) presented normal bowel wall echogenicity; the patients with NEC presented echogenic dots in 16 patients (40%) and dense granular echogenicities in 24 patients (60%). Portal venous gas was absent in all patients. On the follow-up examinations, the echogenicity of the bowel wall and ascites decreased in 37 patients (93%). The duration of NPO was 11.1 ± 6.6 days in group I and 16.5 ± 7.2 days in group II (P < 0.05). Conclusion: Echogenic dots or dense granular echogenicities in the bowel wall can be seen in patients with early-stage NEC. Bowel sonography can be helpful for the early diagnosis and monitoring of patients with NEC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buonomo C (1999) The radiology of necrotizing enterocolitis. Radiol Clin North Am 37:1187–1198
Berdon W, Grossman H, Baker D, et al (1964) Necrotizing enterocolitis in the premature infant. AJR 83:879–887
Bell MJ, Ternberg J, Feigin R, et al (1978) Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis: therapeutic decisions based on clinical staging. Ann Surg 187:1–7
Goske MJ, Goldblum JR, Applegate KE, et al (1999) The “circle sign”: a new sonographic sign of pneumatosis intestinalis—clinical, pathologic, and experimental findings. Pediatr Radiol 29:530–535
Kohzaki S, Hayashi K, Fukuda T, et al (1994) Case report: the “aurora sign”—a new sonographic sign of pneumatosis cystoids intestinalis. Br J Radiol 67:1275–1277
Sato M, Ishida H, Konno K, et al (1999) Sonography of pneumatosis cystoids intestinalis. Abdom Imaging 24:559–561
Dahms BB (2001) The gastrointestinal tract. In: Thomas Stocker J, Louis P. Dehner (eds) Pediatric pathology, vol 1, 2nd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 679–681
Kazez A, Kucukaydin N, Kucikaydin M, et al (1997) A model of hypoxia-induced necrotizing enterocolitis: the role of distension. J Pediatr Surg 32:1466–1469
Pear BL (1998) Pneumatosis intestinalis: a review. Radiology 207:13–19
Heng Y, Schuffler MD, Haggit RC, et al (1995) Pneumatosis intestinalis: a review. Am J Gastroenterol 90:1747–1758
Fenton LZ, Buonomo C (2000) Benign pneumatosis in children. Pediatr Radiol 30:786–793
Vernacchia FS, Jeffrey RB, Laing FC, et al (1985) Sonographic recognition of pneumatosis intestinalis. AJR 145:51–52
Sigel B, Machi J, Ramos JR, et al (1985) Ultrasonic features of pneumatosis intestinalis. J Clin Ultrasound 13:675–678
Wilson SR, Burns PN, Wilkinson LM, et al (1999) Gas at abdominal US: appearance, relevance, and analysis of artifacts. Radiology 210:113–123
Vijayaraghavan SB (1990) Sonographic features of pneumatosis of the small bowel. J Clin Ultrasound 18:579–581
Jaile J, Levin T, Wung J, et al (1992) Benign gaseous distention of the bowel in premature infants treated with nasal continuous airway pressure: a study of contributing factors. AJR 158:125–127
Soboleski D, Chait P, Shuckett B, et al (1995) Sonographic diagnosis of systemic venous gas in a patient with pneumatosis intestinalis. Pediatr Radiol 25:480–481
Molik KA, West KW, Rescorla FJ, et al (2001) Portal venous air: the poor prognosis persists. J Pediatr Surg 36:1143–1145
Bohnhorst B, Muller S, Dordelmann M, et al (2003) Early feeding after necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. J Pediatr 143:484–487
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Kyu Jin Chang, MD, for the statistical analysis and the artist Woo Young Kim for help in the professional improvement of the images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, WY., Kim, W.S., Kim, IO. et al. Sonographic evaluation of neonates with early-stage necrotizing enterocolitis . Pediatr Radiol 35, 1056–1061 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1533-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1533-4