Abstract
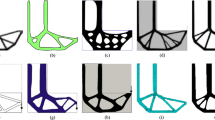
This paper, based on an extended bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method, proposes a design approach to minimize the maximum von Mises stress of continuum structures subject to both material use and casting constraints. The stress singularity phenomenon is avoided naturally by the technique of discrete variable of the bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. The maximum von Mises stress is approximated by the global p-norm stress aggregation approach, and the adjoint method is adopted to derive the sensitivity numbers. Both sensitivity numbers and topological variables are filtered to overcome the highly nonlinear stress behavior and stabilize the optimization procedure. A series of comparison studies have been conducted to validate the effectiveness and practicability of the method on several benchmark design problems. Both two and four parting directions are investigated in this paper. The examples exhibit significant difference in the final topologies for designs with casting constraints. The casting constraints limit the range of solutions to topology optimization problems. Designs with casting constraints seek to satisfy manufacturability of the optimized structure at the expense of structural strength performance. The study demonstrates the importance of strength criteria for the design of continuum structures under casting constraints.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deaton JD, Grandhi RV (2014) A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(1):1–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0956-z
Liang X, To AC, Du JB, Zhang YJ (2021) Topology optimization of phononic-like structures using experimental material interpolation model for additive manufactured lattice infills. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg 377:113717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.113717
Gai YD, Zhu XF, Zhang YJ, Hou WB, Hu P (2020) Explicit isogeometric topology optimization based on moving morphable voids with closed B-spline boundary curves. Struct Multidiscip Optim 61(3):963–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02398-1
Zhu JH, Zhang WH, Xia L (2016) Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Arch Comput Methods Eng 23(4):595–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-015-9151-2
Li ZH, Shi TL, Xia Q (2017) Eliminate localized eigenmodes in level set based topology optimization for the maximization of the first eigenfrequency of vibration. Adv Eng Softw 107:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.12.001
Wei P, Wang MY (2009) Piecewise constant level set method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78(4):379–402. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.2478
Xia L, Xia Q, Huang X, Xie YM (2018) Bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization on advanced structures and materials: a comprehensive review. Arch Comput Methods Eng 25(2):437–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-016-9203-2
Duysinx P, Bendsøe MP (1998) Topology optimization of continuum structures with local stress constraints. Int J Numer Methods Eng 43(8):1453–1478. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19981230)43:8%3c1453::AID-NME480%3e3.0.CO;2-2
Le C, Norato J, Bruns T, Ha C, Tortorelli D (2010) Stress-based topology optimization for continua. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(4):605–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-009-0440-y
Svärd H (2015) Interior value extrapolation: a new method for stress evaluation during topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51(3):613–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1171-2
Bruggi M (2016) Topology optimization with mixed finite elements on regular grids. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 305:133–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.03.010
Xu B, Han YS, Zhao L (2020) Bi-directional evolutionary topology optimization of geometrically nonlinear continuum structures with stress constraints. Appl Math Model 80:771–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.12.009
Xu B, Han YS, Zhao L (2021) Bi-directional evolutionary stress-based topology optimization of material nonlinear structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 63(3):1287–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02757-3
Cheng G, Guo X (1997) Epsilon-relaxed approach in structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 13(4):258–266. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01197454
Bruggi M (2008) On an alternative approach to stress constraints relaxation in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 36:125–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-007-0203-6
Bruggi M, Duysinx P (2012) Topology optimization for minimum weight with compliance and stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(3):369–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-012-0759-7
Yang R, Chen C (1996) Stress-based topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 12(2):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196941
Xia L, Zhang L, Xia Q, Shi TL (2018) Stress-based topology optimization using bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 333:356–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.01.035
Zhao F, Xia L, Lai WX, Xia Q, Shi TL (2019) Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures with stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 59:647–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2090-4
Luo Y, Wang MY, Kang Z (2013) An enhanced aggregation method for topology optimization with local stress constraints. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 254:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2012.10.019
Zhou M, Sigmund O (2017) On fully stressed design and p-norm measures in structural optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 56(3):731–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1731-3
van Miegroet L, Duysinx P (2007) Stress concentration minimization of 2d filets using x-fem and level set description. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4):425–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-006-0091-1
Allaire G, Jouve F (2008) Minimum stress optimal design with the level set method. Eng Anal Bound Elem 32:909–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2007.05.007
van Dijk NP, Maute K, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0912-y
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput Struct 49:885–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-7949(93)90035-c
Huang X, Xie YM (2007) Convergent and mesh-independent solutions for bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Finite Elem Anal Des 43:1039–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2007.06.006
Fritzen F, Xia L, Leuschner M, Breitkopf P (2016) Topology optimization of multiscale elastoviscoplastic structures. Inter J Numer Methods Eng 106(6):430–453. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5122
Xia L, Fritzen F, Breitkopf P (2017) Evolutionary topology optimization of elastoplastic structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55(2):569–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1523-1
Xia L, Da D, Yvonnet J (2018) Topology optimization for maximizing the fracture resistance of quasi-brittle composites. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg 332:234–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2017.12.021
Han YS, Xu B, Wang Q, Liu YH (2021) Bi-directional evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures subjected to inertial loads. Adv Eng Softw 155:102897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2020.102897
Xu B, Han YS, Zhao L, Xie YM (2019) Topology optimization of continuum structures for natural frequencies considering casting constraints. Eng Optimiz 51(6):941–960. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2018.1506771
Han YS, Xu B, Zhao L, Xie YM (2019) Topology optimization of continuum structures under hybrid additive-subtractive manufacturing constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 60(6):2571–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02334-3
Xu B, Han YS, Zhao L, Xie YM (2020) Topological optimization of continuum structures for additive manufacturing considering thin feature and support structure constraints. Eng Optimiz. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215X.2020.1849170
Zuo KT, Chen LP, Zhang YQ, Yang J (2006) Manufacturing-and machining-based topology optimization. Int J Adv Manuf Tech 27(5):531–536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2210-8
Ishii K, Aomra S (2004) Topology optimization for the extruded three dimensional structure with constant cross section. JSME Int J A-Solid M 47(2):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1299/jsmea.47.198
Li H, Li PG, Gao L, Zhang L, Wu T (2015) A level set method for topological shape optimization of 3D structures with extrusion constraints. Comput Method Appl M 283:615–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2014.10.006
Sørensen S, Lund E (2013) Topology and thickness optimization of laminated composites including manufacturing constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(2):249–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0904-y
Wan F, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0602-y
Asberg B, Blanco G, Bose P, Garcia-Lopez J, Overmars M et al (1997) Feasibility of design in stereolithography. Algorithmica 19(1):61–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00014421
Bose P, van Kreveld M, Toussaint G (1998) Filling polyhedral molds. Comput Aided Design 30(4):245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-4485(97)00075-4
Harzheim L, Graf G (2006) A review of optimization of cast parts using topology optimization. II-topology optimization with manufacturing constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 31(5):388–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-005-0554-9
Schramm U, Zhou M (2006) Recent developments in the commercial implementation of topology optimization. In: IUTAM symposium on machines and materials: status and perspectives. Solid mechanics and its applications, vol 137. Springer, New York, pp 239–248
Hui KC, Tan ST (1992) Mould design with sweep operations-a heuristic search approach. Comput Aided Design 24(2):81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-4485(92)90002-R
Kwong KK (1992) Computer-aided parting line and parting surface generation in mould design. Ph.D. thesis, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Gersborg AR, Andreasen CS (2011) An explicit parameterization for casting constraints in gradient driven topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(6):875–881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-011-0632-0
Zhu JH, Gu XJ, Zhang WH, Beckers P (2013) Structural design of aircraft skin stretch-forming die using topology optimization. J Comput Appl Math 246:278–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2012.09.001
Duysinx P, Sigmund O (1998) New development in handling stress constraints in optimal material distribution. In: Proc. 7th AIAA/USAF/NASA/ISSMO Symposium on multidisciplinary analysis and optimization. A collection of technical papers (held in St. Louis, Missouri), vol 3, pp 1501–1509
Han YS, Xu B, Liu YH (2021) An efficient 137-line Matlab code for geometrically nonlinear topology optimization using bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 63(5):2571–2588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-020-02816-9
Sigmund O (2001) A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21(2):120–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001580050176
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the Innovation Foundation for Doctor Dissertation of Northwestern Polytechnical University (CX2021014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Availability of data and materials
The necessary information for replication of the results is present in the manuscript. The interested reader may contact the corresponding author for further implementation details.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Wang, Q. Numerical simulation of stress-based topological optimization of continuum structures under casting constraints. Engineering with Computers 38, 4919–4945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01512-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01512-6