Abstract
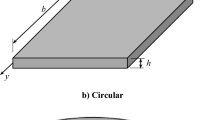
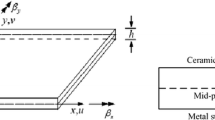
We propose a size-dependent moving Kriging meshfree approach for bending, free vibration and buckling analyses of functionally graded (FG) microplates using the refined plate theory (RPT) and modified strain gradient theory (MSGT). The RPT retains only four variables and reduces one variable when comparing to the original higher order shear deformation theory. For microstructures, three length-scale parameters (LSPs) related to size effects are enhanced in the classical RPT. Material properties of FG microplates are calculated by a rule of mixture. The virtual work principle is used to form the weak forms, and the displacements, natural frequencies and buckling loads of FG microplates are then determined using moving Kriging meshfree method. Numerical validations are shown to evaluate effects of geometrical parameters, boundary conditions, volume fraction and LSPs on displacements, natural frequencies and buckling loads of FG microplates. As observed results, an increase and decrease of natural frequencies, buckling loads and displacements of FG microplates are respectively confirmed. In addition, the modified couple stress model or classical RPT model is recovered when a few LSPs are negligible.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lam DCC, Yang F, Chong ACM, Wang J, Tong P (2003) Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. J Mech Phys Solids 51(8):1477–1508
Toupin RA (1962) Elastic materials with couple-stresses. Arch Ration Mech Anal 11(1):385–414
Mindlin RD, Tiersten HF (1962) Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity. Arch Ration Mech Anal 11(1):415–448
Yang F, Chong ACM, Lam DCC, Tong P (2002) Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 39(10):2731–2743
Mindlin RD, Eshel NN (1968) On first strain-gradient theories in linear elasticity. Int J Solids Struct 4(1):109–124
Kahrobaiyan MH, Rahaeifard M, Tajalli SA, Ahmadian MT (2012) A strain gradient functionally graded Euler-Bernoulli beam formulation. Int J Eng Sci 52:65–76
Akgöz B, Civalek Ö (2013) Buckling analysis of functionally graded microbeams based on the strain gradient theory. Acta Mech 224(9):2185–2201
Ansari R, Gholami R, Sahmani S (2011) Free vibration analysis of size-dependent functionally graded microbeams based on the strain gradient Timoshenko beam theory. Compos Struct 94(1):221–228
Sahmani S, Bahrami M, Ansari R (2014) Nonlinear free vibration analysis of functionally graded third-order shear deformable microbeams based on the modified strain gradient elasticity theory. Compos Struct 110:219–230
Zhang B, He Y, Liu D, Gan Z, Shen L (2013) A novel size-dependent functionally graded curved mircobeam model based on the strain gradient elasticity theory. Compos Struct 106:374–392
Karamanli A, Vo TP (2020) Size-dependent behaviour of functionally graded sandwich microbeams based on the modified strain gradient theory. Compos Struct 246:112401
Karamanli A, Vo TP (2021) A quasi-3D theory for functionally graded porous microbeams based on the modified strain gradient theory. Compos Struct 257:113066
Ansari R, Gholami R, Faghih Shojaei M, Mohammadi V, Sahmani S (2015) Bending, buckling and free vibration analysis of size-dependent functionally graded circular/annular microplates based on the modified strain gradient elasticity theory. Eur J Mech A Solids 49:251–267
Mirsalehi M, Azhari M, Amoushahi H (2017) Buckling and free vibration of the FGM thin micro-plate based on the modified strain gradient theory and the spline finite strip method. Eur J Mech A Solids 61:1–13
Zhang B, He Y, Liu D, Shen L, Lei J (2015) An efficient size-dependent plate theory for bending, buckling and free vibration analyses of functionally graded microplates resting on elastic foundation. Appl Math Model 39(13):3814–3845
Zhang B, He Y, Liu D, Lei J, Shen L, Wang L (2015) A size-dependent third-order shear deformable plate model incorporating strain gradient effects for mechanical analysis of functionally graded circular/annular microplates. Compos B Eng 79:553–580
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Nguyen-Xuan H (2018) Isogeometric analysis of size-dependent isotropic and sandwich functionally graded microplates based on modified strain gradient elasticity theory. Compos Struct 192:274–288
Farzam A, Hassani B (2019) Size-dependent analysis of FG microplates with temperature-dependent material properties using modified strain gradient theory and isogeometric approach. Compos B Eng 161:150–168
Thai S, Thai H-T, Vo TP, Patel VI (2017) Size-dependant behaviour of functionally graded microplates based on the modified strain gradient elasticity theory and isogeometric analysis. Comput Struct 190:219–241
Thai S, Thai H-T, Vo TP, Nguyen-Xuan H (2017) Nonlinear static and transient isogeometric analysis of functionally graded microplates based on the modified strain gradient theory. Eng Struct 153:598–612
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H (2018) Size-dependent analysis of FG-CNTRC microplates based on modified strain gradient elasticity theory. Eur J Mech A Solids 72:521–538
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Phung-Van P (2019) Size dependent free vibration analysis of multilayer functionally graded GPLRC microplates based on modified strain gradient theory. Compos Part B Eng 169:174–188
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Phung-Van P (2020) Free vibration analysis of functionally graded anisotropic microplates using modified strain gradient theory. Eng Anal Bound Elem 117:284–298
Li Q, Wu D, Gao W, Tin-Loi F (2020) Size-dependent instability of organic solar cell resting on Winkler-Pasternak elastic foundation based on the modified strain gradient theory. Int J Mech Sci 177:105306
Li Q, Wu D, Gao W, Tin-Loi F, Liu Z, Cheng J (2019) Static bending and free vibration of organic solar cell resting on Winkler-Pasternak elastic foundation through the modified strain gradient theory. Eur J Mech A Solids 78:103852
Salehipour H, Shahsavar A (2018) A three dimensional elasticity model for free vibration analysis of functionally graded micro/nano plates: modified strain gradient theory. Compos Struct 206:415–424
Natarajan S, Manickam G (2012) Bending and vibration of functionally graded material sandwich plates using an accurate theory. Finite Elem Anal Des 57:32–42
Natarajan S, Baiz PM, Bordas S, Rabczuk T, Kerfriden P (2011) Natural frequencies of cracked functionally graded material plates by the extended finite element method. Compos Struct 93(11):3082–3092
Natarajan S, Baiz PM, Ganapathi M, Kerfriden P, Bordas S (2011) Linear free flexural vibration of cracked functionally graded plates in thermal environment. Comput Struct 89(15):1535–1546
Nguyen-Xuan H, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Thanh N, Nguyen-Thoi T, Bordas S (2010) A node-based smoothed finite element method with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plates. Comput Mech 46(5):679–701
Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thanh N, Nguyen-Xuan H, Rabczuk T, Bordas S (2011) A cell — based smoothed finite element method for free vibration and buckling analysis of shells. KSCE J Civ Eng 15(2):347–361
Natarajan S, Ferreira AJM, Bordas S, Carrera E, Cinefra M, Zenkour AM (2014) Analysis of functionally graded material plates using triangular elements with cell-based smoothed discrete shear gap method. Math Probl Eng 2014:247932
Nguyen-Xuan H, Liu GR, Thai-Hoang C, Nguyen-Thoi T (2010) An edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM) with stabilized discrete shear gap technique for analysis of Reissner-Mindlin plates. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:471–489
Atroshchenko E, Tomar S, Xu G, Bordas SP (2018) Weakening the tight coupling between geometry and simulation in isogeometric analysis: from sub-and super-geometric analysis to Geometry-Independent Field approximaTion (GIFT). Int J Numer Methods Eng 114(10):1131–1159
Marussig B, Zechner J, Beer G, Fries T-P (2015) Fast isogeometric boundary element method based on independent field approximation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 284:458–488
Yu P, Anitescu C, Tomar S, Bordas SPA, Kerfriden P (2018) Adaptive isogeometric analysis for plate vibrations: an efficient approach of local refinement based on hierarchical a posteriori error estimation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 342:251–286
Videla J, Anitescu C, Khajah T, Bordas SP, Atroshchenko E (2019) h-and p-adaptivity driven by recovery and residual-based error estimators for PHT-splines applied to time-harmonic acoustics. Comput Math Appl 77:2369–2395
Hu Q, Chouly F, Hu P, Cheng G, Bordas SP (2018) Skew-symmetric Nitsche’s formulation in isogeometric analysis: Dirichlet and symmetry conditions, patch coupling and frictionless contact. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 341:188–220
Nguyen VP, Anitescu C, Bordas SP, Rabczuk T (2015) Isogeometric analysis: an overview and computer implementation aspects. Math Comput Simul 117:89–116
Valizadeh N, Natarajan S, Gonzalez-Estrada OA, Rabczuk T, Bui TQ, Bordas SPA (2013) NURBS-based finite element analysis of functionally graded plates: static bending, vibration, buckling and flutter. Compos Struct 99:309-326.
Nguyen-Thanh N, Nguyen-Xuan H, Bordas SPA, Rabczuk T (2011) Isogeometric analysis using polynomial splines over hierarchical T-meshes for two-dimensional elastic solids. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(21):1892–1908
Rabczuk T, Belytschko T (2007) A three dimensional large deformation meshfree method for arbitrary evolving cracks. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196:2777–2799
Rabczuk T, Areias PMA, Belytschko T (2007) A meshfree thin shell method for non-linear dynamic fracture. Int J Numer Methods Eng 72(5):524–548
Samaniego E, Anitescu C, Goswami S, Nguyen-Thanh VM, Guo H, Hamdia K et al (2020) An energy approach to the solution of partial differential equations in computational mechanics via machine learning: concepts, implementation and applications. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 362:112790
Anitescu C, Atroshchenko E, Alajlan N, Rabczuk T (2019) Artificial neural network methods for the solution of second order boundary value problems. Comput Mater Contin 59(1):345–359
Guo H, Zhuang X, Rabczuk T (2019) A deep collocation method for the bending analysis of Kirchhoff plate. Comput Mater Contin 59(2):433–456
Rabczuk T, Ren H, Zhuang X (2019) A nonlocal operator method for partial differential equations with application to electromagnetic waveguide problem. Comput Mater Contin 59(1):31–55
Vu-Bac N, Lahmer T, Zhuang X, Nguyen-Thoi T, Rabczuk T (2016) A software framework for probabilistic sensitivity analysis for computationally expensive models. Adv Eng Softw 100:19–31
Gu L (2003) Moving kriging interpolation and element-free Galerkin method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56(1):1–11
Thai CH, Do VNV, Nguyen-Xuan H (2016) An improved moving Kriging-based meshfree method for static, dynamic and buckling analyses of functionally graded isotropic and sandwich plates. Eng Anal Bound Elem 64:122–136
Thai CH, Nguyen TN, Rabczuk T, Nguyen-Xuan H (2016) An improved moving Kriging meshfree method for plate analysis using a refined plate theory. Comput Struct 176:34–49
Thai CH, Phung-Van P (2020) A meshfree approach using naturally stabilized nodal integration for multilayer FG GPLRC complicated plate structures. Eng Anal Bound Elem 117:346–358
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Wahab MA, Nguyen-Xuan H (2018) A moving Kriging meshfree method with naturally stabilized nodal integration for analysis of functionally graded material sandwich plates. Acta Mech 229(7):2997–3023
Thai CH, Tran TD, Phung-van P (2020) A size-dependent moving Kriging meshfree model for deformation and free vibration analysis of functionally graded carbon nanotube-reinforced composite nanoplates. Eng Anal Bound Elem 115:52–63
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Nguyen-Xuan H, Phung-Van P (2021) A size dependent meshfree model for functionally graded plates based on the nonlocal strain gradient theory. Compos Struct 272:114169
Reddy JN (2000) Analysis of functionally graded plates. Int J Numer Methods Eng 47(1–3):663–684
Senthilnathan N, Lim S, Lee K, Chow ST (1987) Buckling of shear-deformable plates. AIAA J 25(9):1268–1271
Thai CH, Ferreira AJM, Nguyen-Xuan H (2017) Naturally stabilized nodal integration meshfree formulations for analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates. Compos Struct 178:260–276
Thai H-T, Kim S-E (2013) A size-dependent functionally graded Reddy plate model based on a modified couple stress theory. Compos B Eng 45(1):1636–1645
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 107.02-2019.35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thai, C.H., Nguyen-Xuan, H., Nguyen, L.B. et al. A modified strain gradient meshfree approach for functionally graded microplates. Engineering with Computers 38 (Suppl 5), 4545–4567 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01493-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01493-6