Abstract
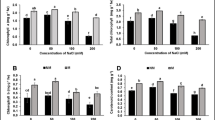
Endophytic microbes promote plant growth through various biochemical mechanisms and assist plants in resuming their morpho-physiological traits under abiotic stresses. The current study was conducted to investigate the plant growth promotion properties and biochemical characterization of Bacillus safensis (SCAL1) under various heat stress regimes. Further investigations aimed to understand the potential of heat-tolerant B. safensis (SCAL1) in amelioration of heat stress in two varieties of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Riogrande and Sweetie). Properties characterized include 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase (ACC deaminase) (0.84–0.96 μM/mg protein/h) and exopolysaccharide (EPS) (0.73–0.92 mg ml−1) under normal and heat stressed conditions. An increased level of ACC deaminase (12.5%) and EPS (20.65%) was observed under heat stress as compared to normal conditions. B. safensis also produced plant growth regulators such as indole acetic acid (IAA) (0.71, 0.57, and 0.49 μg ml−1), gibberellic acid (GA3) (19.4, 18.2, and 19.2 μg ml−1), and kinetin (32.07, 27.3, and 26.8 μg ml−1) under heat stress and control conditions. IAA and kinetin production were slightly reduced under heat stress conditions compared to control conditions. A greenhouse experiment was carried out to analyze the bacterial potential to promote plant growth under heat stress conditions. Inoculation of both tomato varieties with B. safensis significantly improved plant growth parameters, antioxidant enzyme activities, and chlorophyll content under heat stress. The results suggest that inoculating tomato with thermo-tolerant plant growth-promoting endophytic bacterium may provide an eco-friendly management strategy to mitigate heat stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afridi MS, Amna S, Mahmood T, Salam A, Mukhtar T, Mehmood S, Ali J, Khatoon Z, Bibi M, Javed MT, Sultan T (2019) Induction of tolerance to salinity in wheat genotypes by plant growth-promoting endophytes: involvement of ACC deaminase and antioxidant enzymes. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.041
Afridi MS, Van Hamme JD, Bundschuh J, Khan MN, Salam A, Waqar M, Chaudhary HJ (2021) Biotechnological approaches in agriculture and environmental management-bacterium Kocuria rhizophila 14ASP as heavy metal and salt-tolerant plant growth-promoting strain. Biologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00826-6
Ahammed GJ, Xu W, Liu A, Chen S (2018) COMT1 silencing aggravates heat stress-induced reduction in photosynthesis by decreasing chlorophyll content, photosystem II activity, and electron transport efficiency in tomato. Front Plant Sci 9:998. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00998
Ahammed GJ, Guang Y, Yang Y, Chen J (2021) Mechanisms of elevated CO2-induced thermotolerance in plants: the role of phytohormones. Plant Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-021-02751-z
Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Asghar HN, Ghafoor U, Shahid M (2015a) Differential effects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on maize growth and cadmium uptake. J Plant Growth Regul 35:303–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9534-5
Ahmad I, Akhtar MJ, Mehmood S, Akhter K, Tahir M, Saeed MF, Hussain S (2015b) Combined application of compost and Bacillus sp. CIK-512 ameliorated the lead toxicity in radish by regulating the homeostasis of antioxidants and lead. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:805–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.054
Ali SZ, Sandhya V, Grover M, Kishore N, Rao LV, Venkateswarlu B (2009) Pseudomonas sp. strain AKM-P6 enhances tolerance of sorghum seedlings to elevated temperatures. Biol Fertils 46:45–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-009-0404-9
Ali SZ, Sandhya V, Grover M, RaoVenkateswarlu LVB (2011) Effect of inoculation with a thermo-tolerant plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas putida strain AKMP7 on growth of wheat (Triticum spp.) under heat stress. J Plant Interact 6:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2010.545147
Ali B, Amna JMT, Ali H, Munis MFH, Chaudhary HJ (2017) Influence of endophytic Bacillus pumilus and EDTA on the phytoextraction of Cu from soil by using Cicer arietinum. Int J Phytoremediat 19:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2016.1216075
Al-Whaibi MH (2011) Plant heat-shock proteins: a mini review. J King Saud Univ-Sci 23(2):139–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2010.06.022
Amna SS, Din B, Xia Y, Kamran MA, Javed MT, Sultan T, Chaudhary HJ (2019) Mechanistic elucidation of germination potential and growth of wheat inoculated with exopolysaccharide and ACC-deaminase producing Bacillus strains under induced salinity stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109466
Ashraf M, Harris PJC (2013) Photosynthesis under stressful environments: an overview. Photosynthetica 51:163–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-013-0021-6
Azcon R, Barea J (1975) Synthesis of auxins, gibberellins and cytokinins by Azotobacter vinelandii and Azotobacter bijerinkii related to effects produced on tomato plants. Plant Soil 43:609–619
Bano A, Fatima M (2009) Salt tolerance in Zea mays (L.) following inoculation with Rhizobium and Pseudomonas. Biol Fertil Soils 45:405–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-008-0344-9
Barea JM, Brown ME (1974) Effects on plant growth produced by Azotobacter paspali related to synthesis of plant growth regulating substances. J Appl Bacteriol 37:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1974.tb00483.x
Bárzana G, Aroca R, Paz JA, Chaumont F, Martinez-Ballesta MC, Carvajal M (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis increases relative apoplastic water flow in roots of the host plant under both well-watered and drought stress conditions. Ann Bot 109:1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs007
Bita C, Gerats T (2013) Plant tolerance to high temperature in a changing environment: scientific fundamentals and production of heat stress-tolerant crops. Front Plant Sci 4:273. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00273
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chakraborty U, Pradhan B (2011) Drought stress-induced oxidative stress and antioxidative responses in four wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties. Arch Agron Soil Sci 58:617–630. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2010.533660
Cornic G (2000) Drought stress inhibits Photosynthesis By decreasing stomatal aperture-not by affecting ATP synthesis. Trends Plant Science 5:187–198
Dinesh R, Anandaraj M, Kumar A, Bini YK, Subila KP, Aravind R (2015) Isolation, characterization, and evaluation of multi-trait plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for their growth-promoting and disease suppressing effects on ginger. Microbiol Res 173:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.01.014
Etesami H, Hosseini HM, Alikhani HA (2014) Bacterial biosynthesis of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-caboxylate (ACC) deaminase, a useful trait to elongation and endophytic colonization of the roots of rice under constant flooded conditions. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 20:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-014-0251-5
Fahad S, Bajwa AA, Nazir U, Anjum SA, Farooq A, Zohaib A, Huang J (2017) Crop production under drought and heat stress: plant responses and management options. Front Plant Sci 8:1147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01147
FAOSTAT (2013). http://faostat3.fao.org/home/E.
Feng B, Liu P, Li G, Dong ST, Wang FH, Kong LA, Zhang JW (2014) Effect of heat stress on the photosynthetic characteristics in flag leaves at the grain-filling stage of different heat-resistant winter wheat varieties. J Agron Crop Sci 200(2):143–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12045
Ferreira AS, Silva IN, Oliveira VH, Cunha R, Moreira LM (2011) Insights into the role of extracellular polysaccharides in Burkholderia adaptation to different environments. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 1:16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2011.00016
Garbero M, Pedranzani H, Zirulnik F, Molina A, Perez-Chaca MV, Vigliocco A, Abdala G (2011) ´ Short-term cold stress in two cultivars of Digitaria eriantha: effects on stress-related hormones and antioxidant defense system. Acta Physiol Plant 33:497–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0573-z
Gerszberg A, Hnatuszko-Konka K, Kowalczyk T, Kononowicz AK (2015) Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) in the service of biotechnology. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 120(3):881–902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0664-4
Gill SS, Tuteja N (2010) Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:909–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2010.08.016
Gill SS, Gill R, Trivedi DK, Anjum NA, Sharma KK, Ansari MW, Ansar AA, Johri AK, Prasad R, Pereira E, Varma A, Tuteja N (2016) Piriformospora indica: potential and significance in plant stress tolerance. Front Microbiol 7:332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00332
Glick BR (2014) Bacteria with ACC deaminase can promote plant growth and help to feed the world. Microbiol Res 169:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.009
Gupta M, Kiran S, Gulati A, Singh B, Tewari R (2012) Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing bacteria able to enhance the growth and aloin-a biosynthesis of Aloe barbadensis Miller. Microbiol Res 167:358–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.02.004
Han QQ, Lu XP, Bai JP, Qiao Y, Pare PW, Wang SM, Zhang JL, Wu YN (2014) Beneficial soil bacterium Bacillus subtilis (GB03) augments salt tolerance of white clover. Front Plant Sci 5:525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00525
Hazra P, Samsul HA, Sikder D, Peter KV (2007) Breeding tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) resistant to high temperature stress. Int J Plant Breed 1(1):31–40
Humaira Y, Bano A (2011) Isolation and characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria from rhizosphere soil of weeds of khewra salt range. Pak J Bot 43:1663–1668
Hussain A, Kamran MA, Javed MT, Hayat K, Farooq MA, Ali N, Chaudhary HJ (2019) Individual and combinatorial application of Kocuria rhizophila and citric acid on phytoextraction of multi-metal contaminated soils by Glycine max L. Environ Exp Bot 159:23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.12.006
Iqbal A, Hasnain S (2013) Aeromonas punctata PNS-1: a promising candidate to change the root morphogenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana in MS and sand system. Act Physiol Plant 35:657–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1106-8
Jahan MS, Shu S, WangY CZ, He M, Tao M, Guo S (2019a) Melatonin alleviates heat-induced damage of tomato seedlings by balancing redox homeostasis and modulating polyamine and nitric oxide biosynthesis. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1992-7
Jahan MS, Wang Y, Shu S, Zhong M, Chen Z, Wu J, Guo S (2019b) Exogenous salicylic acid increases the heat tolerance in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by enhancing photosynthesis efficiency and improving antioxidant defense system through scavenging of reactive oxygen species. Sci Hortic 247:421–4290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.12.047
Jahan MS, Shu S, Wang Y, Hasan M, El-Yazied AA, Alabdallah NM, Guo S (2021) Melatonin pretreatment confers heat tolerance and repression of heat-induced senescence in tomato through the modulation of ABA-and GA-mediated pathways. Front Plant Sci 12:381. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.650955
Kang SM, Khan AL, You YH, Kim JG, Kamran M, Lee IJ (2014) Gibberellin production by newly isolated strain Leifsonia soli SE134 and its potential to promote plant growth. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:106–112. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1304.04015
Khan AL, Waqas M, Kang SM, Al-Harrasi A, Hussain J, Al-Rawahi A (2014) Bacterial endophyte Sphingomonas sp. LK11 produces gibberellins and IAA and promotes tomato plant growth. J Microbiol 52:689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-4002-7
Khan AL, Ahmed Halo B, Elyassi A, Ali S, Al-Hosni K, Hussain J et al (2016) Indole acetic acid and ACC-deaminase from endophytic bacteria improves the growth of Solanum lycopersicum Electron. J Biotechnol 19:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbt.2016.02.001
Khan MA, Asaf S, Khan AL, Jan R, Kang SM, Kim KM, Lee IJ (2020) Thermotolerance effect of plant growth-promoting Bacillus cereus SA1 on soybean during heat stress. BMC Microbiol 20(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01822-7
Khoshru B, Mitra D, Khoshmanzar E, Myo EM, Uniyal N, Mahakur B, Rani A (2020) Current scenario and future prospects of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: an economic valuable resource for the agriculture revival under stressful conditions. J Plant Nutr 43(20):3062–3092. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2020.1799004
Kim M, Lee U, Small I, des Francs Small CC, Vierling E (2012) Mutations in an Arabidopsis mitochondrial transcription termination factor-related protein enhance thermo-tolerance in the absence of the major molecular chaperone HSP101. Plant Cell 24:3349–3365. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.101006
Kinet JM, Peet MM (1997) Tomato. In: Wien HC (ed) The physiology of vegetable crops. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 207–258
Kruasuwan T (2016) Diversity of culturable plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes associated with sugarcane roots and their effect of growth by co-inoculation of diazotrophs and actinomycetes. J Plant Growth Regul 35:1074–1087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-016-9604-3
Kumar P, Dubey RC, Maheshwari DK (2012) Bacillus strains isolated from rhizosphere showed plant growth-promoting and antagonistic activity against phytopathogens. Microbiol Res 167:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2012.05.002
Liu J, Luo J, Ye H, Sun Y, Lu Z, Zeng X (2009) Production, characterization and antioxidant activities in vitro of exopolysaccharides from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Carbohydr Polym 78:275–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.03.046
Liu J, Luo J, Ye H, Zeng X (2012) Preparation, antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro of different derivatives of levan from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Food Chem Toxicol 50:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2011.11.016
Liu F, Xing S, Ma H, Du Z, Ma B (2013) Cytokinin-producing, plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that confer resistance to drought stress in Platycladus orientalis container seedlings. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9155–9164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5193-2
Louden BC, Haarmann D, Lynne AM (2011) Use of blue agar CAS assay for siderophores detection. J Microbiol Biol Educ JMBE 12:51. https://doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v12i1.249
Mahapatra S, Banerjee D (2013) Evaluation of in vitro antioxidant potency of exopolysaccharide from endophytic Fusarium solani SD5. Int J Biol Macromol 53:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.11.003
Mahapatra S, Banerjee D (2016) Production and structural elucidation of exopolysaccharide from endophytic Pestalotiopsis sp. BC55. Int J Biol Macromol 82:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.035
Maqbool S, Amna MS, Suhaib M, Sultan T, Munis MFH (2021) Interaction of Acc deaminase and antioxidant enzymes to induce drought tolerance in enterobacter cloacae 2wc2 inoculated maize genotypes. Pak J Bot 53:3
Mehmood S, Khan AA, Shi F, Tahir M, Sultan T, Munis MFH, Chaudhary HJ (2021a) Alleviation of salt stress in wheat seedlings via multifunctional Bacillus aryabhattai PM34: an in-vitro study. Sustainability 13(14):8030. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13148030
Mehmood S, Muneer MA, Tahir M, Javed MT, Mahmood T, Afridi MS, Paripaker N, Abbasia HA, Munisa MFH, Chaudhary HJ (2021b) Deciphering distinct biological control and growth promoting potential of multi-stress tolerant Bacillus subtilis PM32 for potato stem canker. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 27(9):2101–2114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-021-01067-2
Mehmood S, Khatoon Z, Amnaa AI, Muneer MA, Kamrane MA, Ali J, Ali B, Chaudhary HJ (2021c) Bacillus sp. PM31 harboring various plant growth-promoting activities regulates Fusarium dry rot and wilt tolerance in potato. Arch Agron Soil Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2021.1971654
Mirzaei M, Pascovici D, Atwell BJ, Haynes PA (2012) Differential regulation of aquaporins, small GTPases and V-ATPases proteins in rice leaves subjected to drought stress and recovery. Proteomics 12:864–877. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201100389
Mukhtar T, Afridi MS, McArthur R, Van Hamme JD, Rineau F, Mahmood T, Zahid M, SalamKhan A (2019) Draft genome sequence of Bacillus safensis SCAL1, an endophytic heat-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacterium. Microbiol Resour Announc 8:50. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00306-18
Mukhtar T, Smith D, Sultan T, Seleiman MF, Alsadon AA, Ali S, Saad MA (2020) Mitigation of heat stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by ACC-deaminase and exopolysaccharide producing Bacillus cereus: effects on biochemical profiling. Sustainability 12(6):2159. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062159
Mu’minah B, SubairFahruddin H (2015) Isolation and screening bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS) from potato rhizosphere in highland and the potential as a producer indole acetic acid (IAA). Procedia Food Sci 3:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.profoo.2015.01.007
Namasivayam E, Ravindar JD, Mariappan K, Akhil J, Mukesh K, Jayaraj R (2011) Production of extracellular pectinase by Bacillus cereus isolated from market solid waste. J Bioanal Biomed 3:70–75. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-593X.1000046
Narayan VV, Hatha MA, Morgan HW, Rao D (2008) Isolation and characterization of aerobic thermophilic bacteria from the Savusavu hot springs in Fiji. Microbes Environ 23:350–352. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME08105
Penrose DM, Glick BR (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase- containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plantarum 118:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2003.00086.x
Raklami A, Oufdou K, Tahiri AI, Mateos-Naranjo E, Navarro-Torre S, Rodríguez-Llorente ID, Pajuelo E (2019) Safe cultivation of Medicago sativa in metal-polluted soils from semi-arid regions assisted by heat-and metallo-resistant PGPR. Microorganisms 7(7):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7070212
Rehem BC, ZanelatoBertolde F, Furtado de Almeida AA (2012) Regulation of gene expression in response to abiotic stress in plants. In: Bubulya P (ed) Cell metabolism—cell homeostasis and stress response. InTech, Rijeka
Ruan YL, Jin Y, Yang YJ, Li GJ, Boyer JS (2010) Sugar input, metabolism, and signaling mediated by invertase: roles in development, yield potential, and response to drought and heat. Mol Plant 3:942–955. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssq044
Saber MAF, Abdelhafez AA, Hassan EA, Ramadan EM (2015) Characterization of fluorescent pseudomonads isolates and their efficiency on the growth promotion of tomato plant. Ann Agric Sci 60:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2015.04.007
Sarma RK, Saikia R (2014) Alleviation of drought stress in mung bean by strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa GGRJ21. Plant Soil 377:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1981-9
Sato S, Kamiyama M, Iwata T, Makita N, Furukawa H, Ikeda H (2006) Moderate increase of mean daily temperature adversely affects fruit set of Lycopersicon esculentum by disrupting specific physiological processes in male reproductive development. Ann Bot 97:731–738. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcl037
Satyanarayana SD, Krishna MSR, Kumar PP (2017) Optimization of high-yielding protocol for DNA extraction from the forest rhizosphere microbes. 3 Biotech 7(2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0737-2
Shahzad SM, Arif MS, Riaz M, Iqbal Z, Ashraf M (2013) PGPR with varied ACC-deaminase activity induced different growth and yield response in maize (Zea mays L.) under fertilized conditions. Eur J Soil Biol 57:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2013.04.002
Smith S, Read D (2008) Mycorrhiza symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072.x
Spaepen S, Bossuyt S, Engelen K, Marchal K, Vanderleyden J (2014) Phenotypical and molecular responses of A. thaliana roots as a result of inoculation with the auxin producing bacterium Azospirillum brasilense. New Phytol 201:850–861. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12590
Stoltzfus JR, So R, Malarvizhi PP, Ladha JK, de Bruijn FJ (1997) Isolation of endophytic bacteria from rice and assessment of their potential for supplying rice with biologically fixed nitrogen. Plant Soil 194:25–36
Tien TM, Gaskins MH, Hubbell DH (1979) Plant growth substances produced by Azospirillum brasilense and their effect on the growth of pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum L.). Appl Microbiol 37L:1016–1024. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.37.5.1016-1024.1979
Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot 61:199–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.05.011
Wang ET, Tan ZY, Guo XW, Rodríguez-Duran R, Boll G, Martínez-Romero E (2006) Diverse endophytic bacteria isolated from a leguminous tree Conzattia multiflora grown in Mexico. Arch Microbiol 186(4):251–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0141-5
Zainab N, Din BU, Javed MT, Afridi MS, Mukhtar T, Kamran MA, Chaudhary HJ (2020) Deciphering metal toxicity responses of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) with exopolysaccharide and ACC-deaminase producing bacteria in industrially contaminated soils. Plant Physiol Biochem 152:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.04.039
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Richal Baker who critically reviewed and improved its English. The authors would like to thank the National Agriculture Research Centre Islamabad, Pakistan, Department of Plant Sciences, Quaid-i-Azam University, Islamabad, Pakistan and McGill University Canada for the facilitation of laboratories and services.
Funding
Funding was provided by Pakistan Agricultural Research Council (Grant No. ALP Project # CS374).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept of work: TM, HJC, and DS. Data arrangement: TM, FA, MR, MSA, and AS. Formal analysis of manuscript: HJC, TM, SM, and A. Proof reading: GJ, TS, JA, and FHM. Statistical analysis: MR, SM, and FA. Supervision: HJC.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no financial conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Golam Jalal Ahammed.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhtar, T., Ali, F., Rafique, M. et al. Biochemical Characterization and Potential of Bacillus safensis Strain SCAL1 to Mitigate Heat Stress in Solanum lycopersicum L.. J Plant Growth Regul 42, 523–538 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10571-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10571-4