Abstract
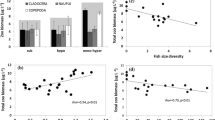
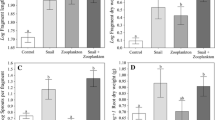
To explore the size-dependent responses of zooplankton to submerged macrophyte restoration, we collected macrophyte, zooplankton and water quality samples seasonally from a subtropical shallow lake from 2010 to 2012. Special attention was given to changes in rotifers and crustaceans (cladocerans and copepods). The rotifers were grouped into three size classes (<200 μm, 200 μm–400 μm, >400 μm) to explore their size-related responses to macrophyte restoration. The results showed that during the restoration, the annual mean biomass and macrophyte coverage increased significantly from 0 to 637 g/m2 and 0 to 27%, respectively. In response, the density and biomass of crustaceans and the crustacean-to-rotifer ratio increased significantly, while the rotifer density decreased significantly. Moreover, rotifers showed significant sizedependent responses to macrophyte restoration. Specially, rotifers <400 μm were significantly suppressed, while those ≥400 μm were significantly encouraged. Overall, the population of large-sized zooplankton tended to boom, while that of small rotifers was inhibited during macrophyte restoration. Redundancy analysis (RDA) revealed positive correlations between macrophytes and crustaceans, rotifers and COD or Chl-a, but negative correlations between macrophytes and COD or Chl-a, and between crustaceans and Chl-a. Moreover, the results indicate that increased predation on phytoplankton by large-sized zooplankton might be an important mechanism for macrophyte restoration during development of aquatic ecosystems, and that this mechanism played a very important role in promoting the formation of a clear-water state in subtropical shallow lakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Y, Chen G X. 1979. Cyclopoida. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Copepoda. Science Press, Beijing, China. 450p. (in Chinese)
Agasild H, Zingel P, Tõnno I, Haberman J, Nõges T. 2007. Contribution of different zooplankton groups in grazing on phytoplankton in shallow eutrophic Lake Võrtsjärv (Estonia). Hydrobiologia, 584 (1): 167–177.
Beklioglu M, Gozen A G, Yildirim F, Zorlu P, Onde S. 2008. Impact of food concentration on diel vertical migration behaviour of Daphnia pulex under fish predation risk. Hydrobiologia, 614 (1): 321–327.
Beklioglu M, Romo S, Kagalou I, Quintana X, Bécares E. 2007. State of the art in the functioning of shallow Mediterranean lakes: workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia, 584 (1): 317–326.
Blanck A, Lamouroux N. 2007. Large-scale intraspecific variation in life-history traits of European freshwater fish. J. Biogeogr., 34 (5): 862–875.
Brönmark C, Weisner S E B. 1992. Indirect effects of fish community structure on submerged vegetation in shallow, eutrophic lakes: an alternative mechanism. Hydrobiologia, 243-244: 293–301.
Burks R L, Lodge D M, Jeppesen E, Lauridsen T L. 2002. Diel horizontal migration of zooplankton: costs and benefits of inhabiting the littoral. Freshwater Biol., 47 (3): 343–365.
Castro B B, Marques S M, Gonçalves F. 2007. Habitat selection and diel distribution of the crustacean zooplankton from a shallow Mediterranean lake during the turbid and clear water phases. Freshwater Biol., 52 (3): 421–433.
Cazzanelli M, Warming T P, Christoffersen K S. 2008. Emergent and floating-leaved macrophytes as refuge for zooplankton in a eutrophic temperate lake without submerged vegetation. Hydrobiologia, 605 (1): 113–122.
Chang X X, Eigemann F, Hilt S. 2012. Do macrophytes support harmful cyanobacteria? Interactions with a green alga reverse the inhibiting effects of macrophyte allelochemicals on Microcystis aeruginosa. Harmful Algae, 19: 76–84.
Cyr H, Curtis J M. 1999. Zooplankton community size structure and taxonomic composition affects size-selective grazing in natural communities. Oecologia, 118 (3): 306–315.
Editorial Board of Monitoring and Determination Methods for Water and Wastewater, State Environmental Protection Administration of China. 2002. Monitoring and Determination Methods for Water and Wastewater. 4 th edn. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China. 836p. (in Chinese)
Espinosa-Rodríguez C A, Valencia-del Toro G, Sarma S S S, Nandini S. 2016. Allelopathic activity and chemical analysis of crude extracts from the macrophyte egeria densa on selected phytoplankton species. Allelopathy J., 39(1): 147–160.
Estlander S, Nurminen L, Olin M, Vinni M, Horppila J. 2009. Seasonal fluctuations in macrophyte cover and water transparency of four brown-water lakes: implications for crustacean zooplankton in littoral and pelagic habitats. Hydrobiologia, 620 (1): 109–120.
Fernandes R, Gomes L C, Pelicice F M, Agostinho A A. 2009. Temporal organization of fish assemblages in floodplain lagoons: the role of hydrological connectivity. Environ. Biol. Fish., 85 (2): 99–108.
Gulati R D, Pires L M D, van Donk E. 2008. Lake restoration studies: failures, bottlenecks and prospects of new ecotechnological measures. Limnologica, 38 (3-4): 233–247.
Gulati R D, van Donk E. 2002. Lakes in the Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: state-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia, 478 (1-3): 73–106.
James W F, Barko J W, Butler M G. 2004. Shear stress and sediment resuspension in relation to submersed macrophyte biomass. Hydrobiologia, 515 (1-3): 181–191.
Jeppesen E, Jensen J P, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T, Pedersen L J, Jensen L. 1997. Top-down control in freshwater lakes: the role of nutrient state, submerged macrophytes and water depth. Hydrobiologia, 342-343: 151–164.
Jeppesen E, Jensen J P, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T L. 2005b. Response of fish and plankton to nutrient loading reduction in Eight shallow Danish lakes with special emphasis on seasonal dynamics. Freshwater Biol., 50 (10): 1616–1627.
Jeppesen E, Meerhoff M, Jacobsen B A, Hansen R S, Søndergaard M, Jensen J P, Lauridsen T L, Mazzeo N, Branco C W C. 2007b. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation—the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia, 581 (1): 269–285.
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Jensen H S, Ventäla A M. 2009. Lake and reservoir Management. In: Likens G E ed. Encyclopedia of Inland Waters. Elsevier, Oxford.
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen T L, Davidson T A, Liu Z W, Mazzeo N, Trochine C, Özkan K, Jensen H S, Trolle D, Starling F, Lazzaro X, Johansson L S, Bjerring R, Liboriussen L, Larsen S E, Landkildehus F, Egemose S, MeerhoffM. 2012. Chapter 6—biomanipulation as a restoration tool to combat eutrophication: recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Ecol. Res., 47: 411–488.
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Mazzeo N, MeerhoffM, Branco C W C, Huszar V L M, Scasso F. 2005a. Lake restoration and biomanipulation in temperate lakes: relevance for subtropical and tropical lakes. In: Reddy V ed. Tropical Eutrophic Lakes: Their Restoration and Management. Oxford Publishing, I.B.H Publishing, New Hampshire. p.331–359.
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, MeerhoffM, Lauridsen T L, Jensen J P. 2007a. Shallow lake restoration by nutrient loading reduction—some recent findings and challenges ahead. Hydrobiologia, 584 (1): 239–252.
Jiang S, Du N. 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea, Freshwater Cladocera. Science Press, Academia Sinica, Beijing, China. 297p. (in Chinese)
Kõiv T, Nõges T, Laas A. 2011. Phosphorus retention as a function of external loading, hydraulic turnover time, area and relative depth in 54 lakes and reservoirs. Hydrobiologia, 660 (1): 105–115.
Kufel L, Kufel I. 2002. Chara beds acting as nutrient sinks in shallow lakes—a review. Aquat. Bot., 72 (3-4): 249–260.
Lacerot G, Kruk C, Lürling M, Scheffer M. 2013. The role of subtropical zooplankton as grazers of phytoplankton under different predation levels. Freshwater Biol., 58 (3): 494–503.
Lauridsen T L, Jensen J P, Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M. 2003. Response of submerged macrophytes in Danish lakes to nutrient loading reductions and biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia, 506-509 (1-3): 641–649.
Li E H, Li W, Liu G H, Yuan L Y. 2008. The effect of different submerged macrophyte species and biomass on sediment resuspension in a shallow freshwater lake. Aquat. Bot., 88 (2): 121–126.
Meerhoff M, Clemente J M, de Mello F T, Iglesias C, Pedersen A R, Jeppesen E. 2007. Can warm climate-related structure of littoral predator assemblies weaken the clear water state in shallow lakes?. Global Change Biol., 13 (9): 1888–1897.
Miranda L E. 2008. Extending the scale of reservoir management. In: Allen M S, Sammons S, Maceina M J, eds. Balancing Fisheries Management and Water Uses for Impounded River Systems. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda.
Mulderij G, van Donk E, Roelofs J G M. 2003. Differential sensitivity of green algae to allelopathic substances from Chara. Hydrobiologia, 491 (1-3): 261–271.
Peretyatko A, Teissier S, De Backer S, Triest L. 2009. Restoration potential of biomanipulation for eutrophic peri-urban ponds: the role of zooplankton size and submerged macrophyte cover. Hydrobiologia, 634 (1): 125–135.
Pluntke T, Kozerski H P. 2003. Particle trapping on leaves and on the bottom in simulated submerged plant stands. Hydrobiologia, 506 (1-3): 575–581.
Reitzel K, Hansen J, Andersen F Ø, Hansen K S, Jensen H S. 2005. Lake restoration by dosing aluminum relative to mobile phosphorus in the sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39 (11): 4134–4140.
Romo S, Villena MJ, Sahuquillo M, Soria J M, Gimenez M, Alfonso T, Vicente E, Miracle M R. 2005. Response of a shallow Mediterranean lake to nutrient diversion: does it follow similar patterns as in northern shallow lakes? Freshw ater Biol., 50 (10): 1706–1717.
Sachse R, Petzoldt T, Blumstock M, Moreira S, Pätzig M, Rücker J, Janse J H, Mooij W M, Hilt S. 2014. Extending one-dimensional models for deep lakes to simulate the impact of submerged macrophytes on water quality. Environ. Modell. Sof., 61: 410–423.
Sagrario G, De Losángeles M, Balseiro E, Ituarte R, Spivak E. 2009. Macrophytes as refuge or risky area for zooplankton: a balance set by littoral predacious macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Biol., 54 (5): 1042–1053.
Schriver P, Bøgestrand J, Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M. 1995. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplanlphytoplankton interactions: large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshwater Biol., 33 (2): 255–270.
Søndergaard M, Jensen J P, Jeppesen E, Møller P H. 2002. Seasonal dynamics in the concentrations and retention of phosphorus in shallow Danish lakes after reduced loading. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag., 5 (1): 19–29.
Søndergaard M, Jeppesen E, Jensen J P, Amsinck S L. 2005. Water framework directive: ecological classification of Danish lakes. J. Appl. Ecol., 42 (4): 616–629.
Špoljar M, Dražina T, Habdija I, Meseljevic M Grcic Z. 2011. Contrasting zooplankton assemblages in two oxbow lakes with low transparencies and narrow emergent macrophyte belts (Krapina River, Croatia). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol., 96 (2): 175–190.
Špoljar M, Dražina T, Šargac J, Kralj Borojevic K Žutinic P. 2012. Submerged macrophytes as a habitat for zooplankton development in two reservoirs of a flow-through system (Papuk Nature Park, Croatia). Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Lim., 48 (2): 161–175.
Špoljar M, Tomljanovic T, Dražina T, Lajtner J, Štulec H, Matulic D, Jelena F. 2016. Zooplankton structure in two interconnected ponds: similarities and differences. Croat. J. Fish., 74 (1): 6–13.
Teixeira-de Mello F, Meerhoff M, Pekcan-Hekim Z, Jeppesen E. 2009. Substantial differences in littoral fish community structure and dynamics in subtropical and temperate shallow lakes. Freshwater Biol., 54 (6): 1202–1215.
van Leeuwen E, Lacerot G, van Nes E H, Hemerik L, Scheffer M. 2007. Reduced top-down control of phytoplankton in warmer climates can be explained by continuous fish reproduction. Ecol. Model., 206 (1-2): 205–212.
Wang J J. 1961. Freshwater Rotifer Fauna in China. Science Press, Beijing, China. 288p. (in Chinese)
Xu H, Paerl H W, Qin B Q, Zhu G W, Gao G. 2010. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr., 55 (1): 420–432.
Zhang S Y, Liu A F, Ma J M, Zhou Q H, Xu D, Chen S P, Zhao Q, Wu Z B. 2010b. Changes in physicochemical and biological factors during regime shifts in a restoration demonstration of macrophytes in a small hypereutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol. Eng., 36 (12): 1611–1619.
Zhang S Y, Zhou Q H, Xu D, Lin J D, Chen S P, Wu Z B. 2010a. Effects of sediment dredging on water quality and zooplankton community structure in a shallow of eutrophic lake. J. Environ. Sci., 22 (2): 218–224.
Acknowledgement
We thank Prof. QIU Dongru and Dr. WANG Yafen for their valuable comments and advice. Thanks are also given to other laboratory colleagues for field and laboratory work assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China 12th Five-Year Plan (No. 2012ZX07101007-005) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51178452, 51208498, 51308530)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, L., He, F., Zhang, Y. et al. Size-dependent responses of zooplankton to submerged macrophyte restoration in a subtropical shallow lake. J. Ocean. Limnol. 36, 376–384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-6192-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-6192-z