Abstract
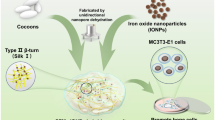
Bone tissue engineering is developed over decades and various materials and techniques are introduced to produce an improved scaffold for bone growth and regeneration. The polymeric scaffolds composed of bioceramics are prospective candidates for treating bone defects. The applications of coaxial electrospinning in tissue engineering are growing due to the increased functionality of the fibrous scaffolds compared to basic electrospinning. In this study, a biodegradable and biocompatible polycaprolactone (PCL)/polyacrylonitrile (PAN) core–shell nanofibrous structure composed of oyster shell (OS) as a bioceramic has been used to prepare a new scaffold for bone tissue engineering. The adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) were cultured on the fabricated scaffolds to examine their potential for cell support, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation. (1) The electrospun nanofibers present a highly porous with interconnected pore structure. (2) There was no cytotoxicity of the prepared scaffolds towards ADMSCs. (3) The ADMSCs cultured on the PCL@PAN/OS scaffold present a higher level of biomineralization analyzed by calcium content and alizarin red S assays. (4) In addition, it shows the highest osteocalcin, ALP, and Runx2 gene expression. The excellent biological properties of the core–shell PCL@PAN/OS nanofibrous structure have been promising to have potential applications in bone tissue engineering.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
C. Xu, P. Su, X. Chen, Y. Meng, W. Yu, A.P. Xiang, Y. Wang, Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of biomimetic Bioglass-Collagen-Phosphatidylserine composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 32, 1051–1058 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.09.068
B. Sun, J. Li, W. Liu, B.M. Aqeel, H. El-Hamshary, S.S. Al-Deyab, X. Mo, Fabrication and characterization of mineralized P(LLA-CL)/SF three-dimensional nanoyarn scaffolds. Iran. Polym. J. 24, 29–40 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-014-0297-9
J. Venkatesan, S.-K. Kim, Nano-hydroxyapatite composite biomaterials for bone tissue engineering—a review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 10, 3124–3140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2014.1893
C. Yang, Q. Shao, Y. Han, Q. Liu, L. He, Q. Sun, S. Ruan, Fibers by electrospinning and their emerging applications in bone tissue engineering. Appl. Sci. 11, 9082 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199082
Y. Yu, S. Hua, M. Yang, Z. Fu, S. Teng, K. Niu, Q. Zhao, C. Yi, Fabrication and characterization of electrospinning/3D printing bone tissue engineering scaffold. RSC Adv. 6, 110557–110565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA17718B
K. Rezwan, Q.Z. Chen, J.J. Blaker, A.R. Boccaccini, Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 27, 3413–3431 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.039
S.S. Liao, F.Z. Cui, W. Zhang, Q.L. Feng, Hierarchically biomimetic bone scaffold materials: nano-HA/collagen/PLA composite. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 69B, 158–165 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.20035
M. Kandeel, Bioinformatics of thymidine metabolism in Trypanosoma evansi: exploring nucleoside deoxyribosyltransferase (NDRT) as a drug target. Trop. Biomed. 38, 311–317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.47665/tb.38.3.071
M. Alquhaidan, M. Kandeel, Gene expression of multidrug-resistant ATP-binding cassette transporter (MDR1/ABCB1) in bovine mastitis. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 17, 2335 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v17i12.3
A. Gupta, S. Gupta, R. Mani, P. Durgapal, B. Goyal, D. Rajput, S. Rao, P. Dhar, M. Gupta, S. Kishore, R. Kant, Expression of Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, Survivin, Enhancer of zeste homolog -2, Cyclooxygenase-2, p53 and p16 molecular markers in Gall bladder carcinoma. J. Carcinogen. 20, 7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.4103/jcar.JCar_4_21
J. Li, H. Sun, D. Sun, Y. Yao, F. Yao, K. Yao, Biomimetic multicomponent polysaccharide/nano-hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. Carbohyd. Polym. 85, 885–894 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.04.015
M. Khalili, A. Khalili, D.O. Bokov, M. Golmirzaei, M.S. Oleneva, N. Naghiaei, M. Radmehr, E. Esmaeili, Preparation and characterization of bi-layered polycaprolactone/polyurethane nanofibrous scaffold loaded with titanium oxide and curcumin for wound dressing applications. Appl. Phys. A 128, 497 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05646-2
M. Piran, M. Shiri, M. SoufiZomorrod, E. Esmaeili, M. SoufiZomorrod, N. VazifehShiran, H. Mahboudi, H. Daneshpazhouh, N. Dehghani, S. Hosseinzadeh, Electrospun triple-layered PLLA/gelatin. PRGF/PLLA scaffold induces fibroblast migration. J. Cell. Biochem. 120, 11441–11453 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28422
N. Fazeli, E. Arefian, S. Irani, A. Ardeshirylajimi, E. Seyedjafari, 3D-printed PCL scaffolds coated with nanobioceramics enhance osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. ACS Omega 6, 35284–35296 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c04015
R. Xue, Y. Qian, L. Li, G. Yao, L. Yang, Y. Sun, Polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffold enhances the osteogenic differentiation potency of various human tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 8, 148 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0588-0
M.-Y. Bai, F.-Y. Ku, J.-F. Shyu, T. Hayashi, C.-C. Wu, Evaluation of polyacrylonitrile nonwoven mats and silver-gold bimetallic nanoparticle-decorated nonwoven mats for potential promotion of wound healing in vitro and in vivo and bone growth in vitro. Polymers 13, 516 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040516
Y. Altaher, M. Kandeel, Structure-activity relationship of anionic and cationic polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers against Staphylococcus aureus. J. Nanomater. 2022, 1–5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4013016
W.R. Kadhum, S.A.S. Al-Zuhairy, M.B.M. Mohamed, A.Y. Abdulrahman, M.M. Kadhim, Z. Alsadoon, T.C. Teoh, A nanotechnological approach for enhancing the topical drug delivery by newly developed liquid crystal formulations. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 11, 716–720 (2021). https://doi.org/10.25258/ijddt.11.3.11
S.A.S. Al-Zuhairy, W.R. Kadhum, M. Alhijjaj, M.M. Kadhim, A.S. Al-Janabi, A.W. Salman, H.K.R. Al-Sharifi, A.A. Khadom, Development and evaluation of biocompatible topical petrolatum-liquid crystal formulations with enhanced skin permeation properties. J. Oleo Sci. 71, ess21344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess21344
W.R. Kadhum, G.L. See, M. Alhijjaj, M.M. Kadhim, F.J. Arce, A.S. Al-Janabi, R.R. Al-Rashidi, A.A. Khadom, Evaluation of the skin permeation-enhancing abilities of newly developed water-soluble self-assembled liquid crystal formulations based on hexosomes. Crystals 12, 1238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst12091238
M. Seyyedi, A. Molajou, Nanohydroxyapatite loaded-acrylated polyurethane nanofibrous scaffolds for controlled release of paclitaxel anticancer drug, J. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 9, 50–61 (2021). http://journals.researchub.org/index.php/jrset/article/view/1213.
E. Esmaeili, M.A. Ghiass, M. Vossoughi, M. Soleimani, Hybrid magnetic-DNA directed immobilisation approach for efficient protein capture and detection on microfluidic platforms. Sci. Rep. 7, 194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00268-8
M. Sabet, M. Salavati-Niasari, E. Esmaeili, Synthesis of zinc sulfide nanostructures with different sulfur sources via mild hydrothermal route: investigation of crystal phase and morphology. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 26, 738–743 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-016-0374-y
E. Esmaeili, M. Sabet, M. Salavati-Niasari, Z. Zarghami, S. Bagheri, Effect of sulfur source on cadmium sulfide nanostructures morphologies via simple hydrothermal route. J. Clust. Sci. 27, 351–360 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-015-0934-2
R. Didekhani, M.R. Sohrabi, E. Seyedjafari, M. Soleimani, H. Hanaee-Ahvaz, Electrospun composite PLLA/Oyster shell scaffold enhances proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. Biologicals 54, 33–38 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biologicals.2018.04.006
S. Dorozhkin, Calcium orthophosphate-based bioceramics. Materials. 6, 3840–3942 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6093840
W. Luo, S. Zhang, Y. Lan, C. Huang, C. Wang, X. Lai, H. Chen, N. Ao, 3D printed porous polycaprolactone/oyster shell powder (PCL/OSP) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Res. Express. 5, 045403 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab916
G.-L. Yoon, B.-T. Kim, B.-O. Kim, S.-H. Han, Chemical–mechanical characteristics of crushed oyster-shell. Waste Manage. 23, 825–834 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00159-9
E. Razeghian, R. Margiana, S. Chupradit, D.O. Bokov, W.K. Abdelbasset, F. Marofi, S. Shariatzadeh, F. Tosan, M. Jarahian, Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a vehicle for cytokine delivery: an emerging approach for tumor immunotherapy. Front. Med. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.721174
R. Margiana, A. Markov, A.O. Zekiy, M.U. Hamza, K.A. Al-Dabbagh, S.H. Al-Zubaidi, N.M. Hameed, I. Ahmad, R. Sivaraman, H.H. Kzar, M.E. Al-Gazally, Y.F. Mustafa, H. Siahmansouri, Clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell in regenerative medicine: a narrative review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13, 366 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-03054-0
S.A. Jasim, A.V. Yumashev, W.K. Abdelbasset, R. Margiana, A. Markov, W. Suksatan, B. Pineda, L. Thangavelu, S.H. Ahmadi, Shining the light on clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13, 101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02782-7
H. Huldani, R. Margiana, F. Ahmad, M.J.C. Opulencia, M.J. Ansari, D.O. Bokov, N.N. Abdullaeva, H. Siahmansouri, Immunotherapy of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) through mesenchymal stem cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 107, 108698 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108698
R. Margiana, R.A. Aman, J.A. Pawitan, A.A. Jusuf, N. Ibrahim, H. Wibowo, The effect of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on the peripheral nerve regeneration of injured rats. Electron. J. Gen. Med. 16, 171 (2019). https://doi.org/10.29333/ejgm/115468
M. Khalili, H. Keshvari, R. Imani, A.N. Sohi, E. Esmaeili, M. Tajabadi, Study of osteogenic potential of electrospun <scp>PCL</scp> incorporated by dendrimerized superparamagnetic nanoparticles as a bone tissue engineering scaffold. Polym. Adv. Technol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5555
E. Esmaeili, Z. Malaie-Balasi, M. Kabiri, A. Khojasteh, F. Mohamadyar-Toupkanlou, N. Sadeghzadeh, Z. Zarei-Behjani, S. Hosseinzadeh, Optimization of nanoclay/polyacrylonitrile scaffold using response surface method for bone differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. ASAIO J (2021). https://doi.org/10.1097/MAT.0000000000001355
W. Liu, S. Thomopoulos, Y. Xia, Electrospun nanofibers for regenerative medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 1, 10–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201100021
E. Esmaeili, T. Eslami-Arshaghi, S. Hosseinzadeh, E. Elahirad, Z. Jamalpoor, S. Hatamie, M. Soleimani, The biomedical potential of cellulose acetate/polyurethane nanofibrous mats containing reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites and curcumin: antimicrobial performance and cutaneous wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 152, 418–427 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.295
J. Dolgin, S.N. Hanumantharao, S. Farias, C.G. Simon, S. Rao, Mechanical properties and morphological alterations in fiber-based scaffolds affecting tissue engineering outcomes. Fibers. 11, 39 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/fib11050039
B. Abderrahim, E. Abderrahman, A. Mohamed, T. Fatima, T. Abdesselam, O. Krim, Kinetic thermal degradation of cellulose, polybutylene succinate and a green composite: comparative study. World J. Environ. Eng. 3, 95–110 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1269/wjee-3-4-1
J. Li, S. Su, L. Zhou, V. Kundrát, A.M. Abbot, F. Mushtaq, D. Ouyang, D. James, D. Roberts, H. Ye, Carbon nanowalls grown by microwave plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition during the carbonization of polyacrylonitrile fibers. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 024313 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4774218
S. An, Y. Gao, J. Ling, X. Wei, Y. Xiao, Calcium ions promote osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of human dental pulp cells: implications for pulp capping materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 23, 789–795 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-011-4531-0
T. Narai, R. Watase, Y. Nakayama, I. Kodani, T. Inoue, K. Kokura, Establishment of human immortalized mesenchymal stem cells lines for the monitoring and analysis of osteogenic differentiation in living cells. Heliyon 6, e05398 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05398
Y.-T. Tsao, Y.-J. Huang, H.-H. Wu, Y.-A. Liu, Y.-S. Liu, O. Lee, Osteocalcin mediates biomineralization during osteogenic maturation in human mesenchymal stromal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18, 159 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18010159
T. Komori, Regulation of osteoblast and odontoblast differentiation by RUNX2. J. Oral Biosci. 52, 22–25 (2010). https://doi.org/10.2330/joralbiosci.52.22
N. Andalib, M. Kehtari, E. Seyedjafari, N. Motamed, M.M. Matin, In vivo bone regeneration using a bioactive nanocomposite scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells, Cell and Tissue. Banking 22, 467–477 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-020-09894-5
R.J. Miron, Y.F. Zhang, Osteoinduction: a review of old concepts with new standards. J. Dent. Res. 91, 736–744 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034511435260
Y. Shen, S. Yang, J. Liu, H. Xu, Z. Shi, Z. Lin, X. Ying, P. Guo, T. Lin, S. Yan, Q. Huang, L. Peng, Engineering scaffolds integrated with calcium sulfate and oyster shell for enhanced bone tissue regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6, 12177–12188 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/am501448t
Acknowledgements
Hereby, we extend our gratitude to the stem cell technology research center. The authors are grateful to Dr. Iman Rad and Mr. Jafar Meghdadi for their technical support.
Funding
There are no funders to report for this submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EE: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, resources, formal analysis, validation, writing. RD: investigation, methodology, validation, visualization. ZG: investigation, methodology, writing—original draft. MK: investigation, methodology, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeili, E., Didekhani, R., Gohari, Z. et al. Fabrication and characterization of PCL@PAN nanofibrous scaffold containing nature-derived oyster shell for bone tissue engineering applications. Appl. Phys. A 129, 670 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06943-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-023-06943-0