Abstract
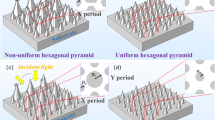
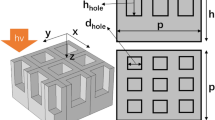
This paper focuses on the geometry of GaN nanomaterials and subsequent absorption rate analysis performed to optimize ultraviolet photocathode for operation in the wavelength range of 200–400 nm. COMSOL Multiphysics commercial software were used to numerically simulate the optical properties of GaN (gallium nitride) nanomaterials. Based on the concept of light trapping mechanism and radial mode resonance absorption, we study GaN nanomaterials with various arrangements and geometric features to obtain unified broadband light absorption in the ultraviolet region. In radial mode, we investigated the light-trapping efficiency of symmetrical and asymmetrical six-side pyramid structure nanoarrays, demonstrating broadband light absorption in two nanostructure periodic arrays (square periods and hexagonal periods) of absorbing efficiency. In the axial mode, the light absorption efficiencies of the hierarchical structures of different geometric parameters and characteristic structures are calculated and analyzed. It is interesting that GaN cylindrical–hemispherical layered nanostructure (R = 140 nm, H = 640 nm) exhibits size-dependent absorption bands and high absorption efficiency in the ultraviolet region. All the results provide an effective solution for designing GaN cathode materials in the ultraviolet omnidirectional absorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
V.E. Kudryashov, S.S. Mamakin, A.N. Turkin et al., Luminescence spectra and efficiency of GaN-based quantum-well heterostructure light emitting diodes: current and voltage dependence. Semiconductors 35(7), 827–834 (2001)
Y.K. Kuo, T.H. Wang, J.Y. Chang et al., Advantages of blue InGaN light-emitting diodes with InGaN–AlGaN–InGaN barriers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100(3), 031112–031113 (2012)
S.J. Pearton, J.C. Zopler, R.J. Shurl et al., Processing defects and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 86(1), 1–78 (1999)
Z. Yi et al., Gallium clusters gan (n = 1−6): structures, thermochemistry, and electron affinities. Cheminform 35(45), 579–598 (2004)
H.M. Manasevit, F.M. Erdman, W.I. Simpson, The use of metalorganics in the preparation of semiconductor materials: growth on insulating substrates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 13–14, 118–1864 (1971)
X. Zhang, V.G. Dubrovskii, N.V. Sibirev, G.E. Cirlin, C. Sartel, M. Tchernycheva, J.C. Harmand, F. Glas, Growth of inclined GaAs nanowires by molecular beam epitaxy: theory and experiment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5(10), 1692–1697 (2010)
T.W. Ho, F.C.N. Hong, A reliable method to grow vertically-aligned silicon nanowires by a novel ramp-cooling process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(20), 7989–7996 (2012)
J. Noborisaka, J. Motohisa, T. Fukui, Catalyst-free growth of GaAs nanowires by selective-area metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(213102), 1–3 (2005)
T. Mårtensson, P. Carlberg, M. Borgstrom, L. Montelius, W. Seifert, L. Samuelson, Nanowire arrays defined by nanoimprint lithography. Nano Lett. 4(4), 699–702 (2004)
I.G. Kavakli, K. Kantarli, Single and double-layer antireflection coatings on silicon. Turk. J. Phys. 26, 349–354 (2002)
S.E. Lee, S.W. Choi, J. Yi, Double-layer anti-reflection coating using MgF2 and CeO2 films on a crystalline silicon substrate. Thin Solid Films 376(1–2), 208–213 (2000)
J. Li, H. Yu, S.M. Wong, X. Li, G. Zhang, P.G. Lo, D.L. Kwong, Design guidelines of periodic Si nanowire arrays for solar cell application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(243113), 1–3 (2009)
L. Wen, Z. Zhao, X. Li, Y. Shen, H. Guo, Y. Wang, Theoretical analysis and modeling of light trapping in high efficiency GaAs nanowire array solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 99(143116), 1–3 (2011)
L. Hu, G. Chen, Analysis of optical absorption in silicon nanowire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nano Lett. 7(11), 3249–3252 (2007)
R. Debnath, C.M. Hangarter, D. Josell, 3D geometries: enabling optimization toward the inherent limits of thin-film photovoltaics. Springer Ser. Mater. Sci. 218, 1–24 (2016)
W. Zhou, M. Tao, L. Chen, H. Yang, Microstructured surface design for omnidirectional antireflection coatings on solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 102(10), 103–105 (2007)
C.H. Sun, W.L. Min, N.C. Linn, P. Jiang, B. Jiang, Templated fabrication of large area subwavelength antireflection gratings on silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91(23), 231105 (2007)
Z. Fan, R. Kapadia, P.W. Leu, X. Zhang, Y.L. Chueh, K. Takei, K. Yu, A. Jamshidi, A.A. Rathore, D.J. Ruebusch, M. Wu, A. Javey, Ordered arrays of dual-diameter nanopillars for maximized optical absorption. Nano Lett. 10(10), 3823–3827 (2010)
K. Zhou, S.W. Jee, Z. Guo, S. Liu, J.H. Lee, Enhanced absorptive characteristics of metal nanoparticle-coated silicon nanowires for solar cell applications. Appl. Opt. 50(31), G63–G68 (2011)
Z. Xu, H. Huangfu, L. He, J. Wang, D. Yang, J. Guo et al., Light-trapping properties of the si inclined nanowire arrays. Opt. Commun. 382, 332–336 (2017)
H. Lu, H. Zhao, Surface antireflection properties of GaN nanostructures with various effective refractive index profiles. Opt. Express 22(26), 31907 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province-China (Grant no.2017-AD41779), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities-China (Grant no.30916011206) and the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province-China (Grant no.2015-XCL-008). Qinghua Lv of Hubei University of Technology is greatly appreciated for the help with COMSOL Multiphysics Business Package calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Z., Liu, L., Zhangyang, X. et al. Enhanced absorptive characteristics of GaN nanowires for ultraviolet (UV) photocathode. Appl. Phys. A 126, 152 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3312-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-020-3312-3