Abstract
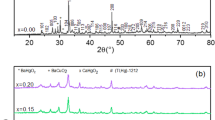
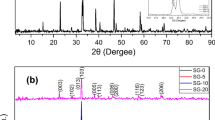
This work reveals the influence of lead fluoride substitution and liquid nitrogen immersion on the mechanical properties of high-temperature superconductor samples \(\left( {{\text{Cu}}_{0.5 - x} {\text{Tl}}_{0.5} {\text{Pb}}_{x} } \right){\text{Ba}}_{2} {\text{Ca}}_{2} {\text{Cu}}_{3} {\text{O}}_{10 - \delta - y} {\text{F}}_{y}\), with (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.10). The samples under investigation were synthesized by solid-state reaction method at normal pressure. The samples were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The X-ray data have indicated that the partial replacement of \({\text{Cu}}^{2 + }\) ions by Pb2+ ions and oxygen by fluorine in the reservoir layer do not alter the tetragonal structure of the samples. On the other hand, the values of the lattice parameters a and c were found to be varied with x according to the difference in the ionic radii of \({\text{Pb}}^{2 + } {\text{and Cu}}^{2 + }\) as well as to the oxygen content. SEM analysis has revealed that lead fluoride substitutions improve the inter-grains connectivity of the prepared samples. The values of the superconducting transition temperature (\(T_{\text{c}}\)) were determined using ac magnetic susceptibility measurements. Vickers microhardness \((H_{\text{v}} )\) was measured as a function of applied loads and the immersion time in liquid nitrogen (t). It was found that \(H_{\text{v}}\) values have recorded enhancements after one-hour immersion in liquid nitrogen. Moreover, the variation of \(H_{\text{v}}\) has shown an enhancement about 34% for x = 0.06. Furthermore, various models were employed to interpret the load dependence behavior of Hv.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ihara, Y. Sekita, H. Tateai, N.A. Khan, K. Ishida, E. Harashima et al., IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 9(2), 1551–1554 (1999)
M.A. Rahman, M.Z. Rahaman, M.N. Samsuddoha, Am. J. Phys. Appl. 3(2), 39–56 (2015)
N.H. Mohammed, A.I. Abou-Aly, I.H. Ibrahim, R. Awad, M. Rekaby, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 24(5), 1463–1472 (2011)
A. Srour, W. Malaeb, M. Rekaby, R. Awad, Phys. Scr. 92(10), 104002 (2017)
R. Awad, A.A. Aly, M. Kamal, M. Anas, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 24(6), 1947–1956 (2011)
N.M. Hamdan, K.A. Ziq, A.S. Al-Harthi, Physica C Supercond. 314(1–2), 125–132 (1999)
T.M. Chen, J.S. Ho, Physica C Supercond. 282, 915–916 (1997)
A. Lenders, M. Mich, H.C. Freyhard, Physica C Supercond. 279(3–4), 173–180 (1997)
M. Kühberger, G. Gritzner, Physica C Supercond. 390(3), 263–269 (2003)
K. Sangwal, B. Surowska, Mater. Res. Innov. 7(2), 91–104 (2003)
C.E. Foerster, E. Lima, P. Rodrigues Jr., F.C. Serbena, C.M. Lepienski, M.P. Cantão et al., Braz. J. Phys. 38(3A), 341–345 (2008)
A.I. Abou-Aly, M.A. Gawad, R. Awad, I. G-Eldeen, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 24(7), 2077 (2011)
S.M. Khalil, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64(5), 855–861 (2003)
S. Zhirafar, A. Rezaeian, M. Pugh, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 186(1–3), 298–303 (2007)
N.M. Anas, W.L. Quah, H. Zuhailawati, A.S. Anasyida, Procedia Chem. 19, 241–246 (2016)
H.A. Cetinkara, M. Yilmazlar, O. Ozturk, M. Nursoy, C. Terzioglu, J. Phys. Confer. Ser. 153(1), 012038 (2009). (IOP Publishing)
B.W. Mott, Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, UK (1956)
M.M. Barakat, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30(10), 2945–2955 (2017)
R. Terzioglu, S. Polat Altintas, A. Varilci, C. Terzioglu, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 1–7 (2019)
K. Sangwal, Cryst. Res. Technol. 44(10), 1019–1037 (2009)
K. Yoda, T.A. Sualatu, N. Nomura, Y. Tsutsumi, H. Doi, S. Kurosu, A. Chiba, Y. Igarashi, T. Hanawa, Acta Bio. Mater. 8(7), 2856–2862 (2012)
C. Hays, E.G. Kendall, Metallography 6(4), 275–282 (1973)
B.R. Lawn, V.R. Howes, J. Mater. Sci. 16(10), 2745–2752 (1981)
H. Li, R.C. Bradt, J. Mater. Sci. 28(4), 917–926 (1993)
H. Li, R.C. Bradt, J. Mater. Sci. 31(4), 1065–1070 (1996)
O. Ozturk, E. Asikuzun, A.T. Tasci, T. Gokcen, H. Ada, H. Koralay, S. Cavdar, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29(5), 3957–3966 (2018)
J.B. Quinn, D.G. Quinn, J. Mater. Sci. 32(16), 4331–4346 (1997)
O. Ozturk, R.A.M. Arebat, A.R.A. Nefrow, F. Bulut, G. Guducu, E. Asikuzun, S. Celik, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(8), 7400–7409 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was performed in the Materials Science lab, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Beirut Arab University, in cooperation with the Superconductivity and metallic-glass lab, Faculty of Science, Alexandria University, Egypt, American University of Beirut (AUB) and Accelerator Laboratory, Lebanese Atomic Energy Commission, CNRS, Beirut, Lebanon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AbuHlaiwa, H., Basma, H., Rekaby, M. et al. Influence of lead fluoride on the mechanical properties of (\(\text{Cu}_{0.5} \text{Tl}_{0.5}\)): 1223 Phase. Appl. Phys. A 125, 715 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2972-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2972-3