Abstract
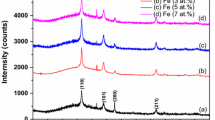
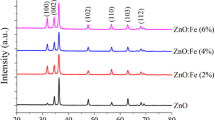
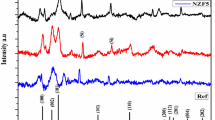
This article reports the fabrication and characterization of thin films of pure and cobalt doped ZnO (Co at 4% and 7%), a transparent diluted magnetic semiconductor (DMS) grown on ‘Si’ and glass substrates by RF magnetron sputtering technique. The crystalline structure and phase of the grown thin films were analyzed by using X-ray diffraction (XRD) method which confirmed the hexagonal wurtzite structure of the ZnO with slight lattice strain and change in orientation of the planes. The XRD also confirmed that, the films exhibit prominent peaks of (1 0 1) and (1 0 3) with polycrystalline nature. The morphology of the grown thin films was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) which confirmed the variation of micro-structure and size of the polycrystalline film’s surface. The energy dispersive X-ray spectra (EDS) from SEM have confirmed the presence of constituent elements in the films and concentration (in %) of each element. The crystalline properties and morphology of the film’s cross-section were studied by high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM). The average thickness of the films was found to be about 600 nm from the cross-section electron microscopic images. The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern from TEM was recorded for the Co (7%) doped ZnO film which has good polycrystalline quality. The optical transmittance of the films coated on corning glass substrates was investigated by UV–Visible spectrophotometer for pure, 4% and 7% Co doped ZnO films, which revealed the optical transparency of 85%, 75% and 65%, respectively. The room temperature ferromagnetism of the doped films was analysed by vibrating sample magnetometry and magneto optic Kerr effect. It was found that the ferromagnetic behaviour of films increases with ‘Co’ content and the results were discussed in detail.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Salavati-Niasari, N. Mir, F. Davar, ZnO nanotriangles: synthesis, characterization and optical properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 476, 908–912 (2009)
M.H. Huang, S. Mao, H. Feick, H. Yan, Y. Wu, H. Kind et al., Room-Temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292, 1897–1899 (2001)
N.H. Al-Hardan, M.J. Abdullah, N.M. Ahmed, F.K. Yam, A. Abdul Aziz, UV photodetector behavior of 2D ZnO plates prepared by electrochemical deposition. Superlattice Microstruct. 51, 765–771 (2012)
A.A. Bergh, P.J. Dean, Light emitting diodes (Clarendon, Oxford, 1976). (Mir, Moscow, 1987)
H. Han, N.D. Theodore, T.L. Alford, Improved conductivity and mechanism of carrier transport in zinc oxide with embedded silver layer. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 013708 (2008)
A.P. Abiyasa, S.F. Yu, S.P. Lau, E.S.P. Leong, H.Y. Yang, Enhancement of ultraviolet lasing from Ag-coated highly disordered ZnO films by surface-plasmon resonance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90(23), 231106–231113 (2007)
M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Z. Fereshteh, Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanocrystals from thermolysis of new precursor. Chem. Eng. J. 146, 498–502 (2009)
A.K. Babaheydari, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Khansari, Solvent-less synthesis of zinc oxide nanostructures from Zn(salen) as precursor and their optical properties. Particuology 10, 759–764 (2012)
M. Goudarzi, M. Mousavi-Kamazani, M. Salavati-Niasari, Zinc oxide nanoparticles: solvent-free synthesis, characterization and application as heterogeneous nanocatalyst for photodegradation of dye from aqueous phase. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 8423–8428 (2017)
M. Yousefi, E. Noori, D. Ghanbari, M. Salavati-Niasari, T. Gholami, A facile room temperature synthesis of zinc oxide nanostructure and its influence on the flame retardancy of poly vinyl alcohol. J. Cluster Sci. 25, 397–408 (2014)
A.P. Bhirud, S.D. Sathaye, R.P. Waichal, L.K. Nikam, B.B. Kale, An eco-friendly, highly stable and efficient nanostructured p-type N-doped ZnO photocatalyst for environmentally benign solar hydrogen production. Green Chem. 14, 2790–2798 (2012)
F. Soofivand, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Mohandes, Novel precursor-assisted synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles/nanofibers. Mater. Lett. 98, 55–58 (2013)
H. Cao, J.Y. Xu, E.W. Seelig, R.P.H. Chang, Microlaser made of disordered media. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2997 (2000)
Z.K. Tang, G.K.L. Wong, P. Yu, M. Kawasaki, A. Ohtomo, H. Koinuma, Y. Segawa, Room-temperature ultraviolet laser emission from self-assembled ZnO microcrystallite thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 3270 (1998)
H.Y. Xu, Y.C. Liu, Y.X. Liu, C.S. Xu, C.L. Shao, R. Mu, Ultraviolet electroluminescence from p-GaN/i-ZnO/n-ZnO heterojunction light-emitting diodes. Appl. Phys. B Laser Optic. 80(7), 871 (2005)
P.F. Carcia, R.S. McLean, M.H. Reilly, G. Nunes, High-performance ZnO thin-film transistors on gate dielectrics grown by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1117 (2003)
H.Y. Xu, Y.C. Liu, R. Mu, C.L. Shao, Y.M. Lu, D.Z. Shen, X.W. Fan, F-doping effects on electrical and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystalline films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 123107 (2005)
M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, A. Khansari, Nanosphericals and nanobundles of ZnO: Synthesis and characterization. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 61–65 (2011)
Y. Yang, S. Niu, D. Han, T. Liu, G. Wang, Y. Li, Progress in developing metal oxide nanomaterials for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700555 (2017)
V. Galstyan, E. Comini, C. Baratto, G. Faglia, G. Sberveglieri, Nanostructured ZnO chemical gas sensors. Ceram. Int. 41, 14239–14244 (2015)
N. Mir, M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, Preparation of ZnO nanoflowers and Zn glycerolate nanoplates using inorganic precursors via a convenient rout and application in dye sensitized solar cells. Chem. Eng. J. 181, 779–789 (2012)
A.B. Djurisic, Y.H. Leung, A.M.C. Ng, Strategies for improving the efficiency of semiconductor metal oxide photocatalysis. Mater. Horiz. 1, 400 (2014)
M. Salavati-Niasari, F. Davar, M. Mazaheri, Preparation of ZnO nanoparticles from [bis(acetylacetonato)zinc(II)]–oleylamine complex by thermal decomposition. Mater. Lett. 62, 1890–1892 (2008)
J.K. Furdyna, Diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 64, R29 (1988)
G. Mihály, M. Csontos, S. Bordács, I. Kézsmárki, T. Wojtowicz, X. Liu, B. Jankó, J.K. Furdyna, Anomalous hall effect in the (In, Mn)Sb dilute magnetic semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 1–4 (2008)
J.S. Kulkarni, O. Kazakova, J.D. Holmes, Dilute magnetic semiconductor nanowires. Appl. Phys. A 85, 277–286 (2006)
C. Claude, A. Fert, F.N. Van Dau, The emergence of spin electronics in data storage. Nat. Mater. 6, 813–823 (2007)
S.B. Ogale, Dilute doping, defects, and ferromagnetism in metal oxide systems. Adv. Mater. 22, 3125–3155 (2010)
B.T. Jonker, Y.D. Park, B.R. Bennett, H.D. Cheong, G. Kioseoglou, A. Petrou, Robust electrical spin injection into a semiconductor heterostructure. Phys. Rev. B 62, 8180 (2000)
I. Appelbaum, B. Huang, D.J. Monsma, Electronic measurement and control of spin transport in silicon. Nature 447, 295–298 (2007)
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand, Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science 287, 1019 (2000)
P. Sharma, A. Gupta, K.V. Rao, F.J. Owens, R. Sharma, R. Ahuja, J.M.O. Guillen, B. Johansson, G.A. Gehring, Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO. Nat. Mater. 2, 673 (2003)
S.A. Wolf, A.A. Awschalom, R.A. Buhrman, J.M. Daughton, S. Molnar, M.L. Roukes, A.Y. Chtchelkanova, D.M. Treger, Spintronics: A spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294, 1488 (2001)
M. Hassanpour, H. Safardoust-Hojaghan, M. Salavati-Niasari, Degradation of methylene blue and Rhodamine B as water pollutants via green synthesized Co3O4/ZnO nanocomposite. J. Mol. Liq. 229, 293–299 (2017)
B. Panigrahy, M. Aslam, D. Bahadur, Controlled optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanorods by Ar ion irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 183109 (2011)
P. Bandyopadhyay, A. Dey, R. Basu, S. Das, P. Nandy, Synthesis and characterization of copper doped zinc oxide nanoparticles and its application in energy conversion. Curr. Appl. Phys. 14, 1149–1155 (2014)
F. Pan, C. Song, X. Liu, Y. Yang, F. Zeng, Ferromagnetism and possible application in spintronics of transition-metal-doped ZnO films. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 62, 1–35 (2008)
B.P. Kafle, S. Acharya, S. Thapa, S. Poudel, Structural and optical properties of Fe-doped ZnO transparent thin films. Ceram. Int. 42, 1133–1139 (2016)
S.M. Hosseini, I.A. Sarsari, P. Kameli, H. Salamati, Effect of Ag doping on structural, optical, and photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy Compd. 640, 408–415 (2015)
K. Sato, H. Katayama-Yoshida, First principles materials design for semiconductor spintronics. Semicond. Sci. Tech. 17, 367 (2002)
P.A. Wolff, R.N. Bhatt. A.C. Durst, Polaron‐polaron interactions in diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 5196 (1996)
A. Kaminski, S. Das Sarma, Polaron percolation in diluted magnetic semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 247202 (2002)
D. Akcan, S. Ozharar, E. Ozugurlu, L. Arda, The effects of Co/Cu Co-doped ZnO thin films: An optical study. J. Alloy. Compd. 797, 253–261 (2019)
P. Shukla, S. Tiwari, S. Ram Joshi, V.R. Akshay, M. Vasundhara, S. Varma, J. Singh, A. Chanda, Investigation on structural, morphological and optical properties of Co-doped ZnO thin films. Phys. B Condens. Matter 550, 303–310 (2018)
A. Ali, A. Luiz Pinto, R. Henda, R. Fagerberg, Influence of Co loading on structural and morphological properties of Co-doped ZnO thin films grown by pulsed electron beam ablation. J. Alloy. Compd. 731, 181–188 (2018)
Z. Jin, T. Fukumura, M. Kawasaki, K. Ando, H. Saito, T. Sekiguchi, Y.Z. Yoo, M. Murakami, Y. Matsumoto, T. Hasegawa, H. Koinuma, High throughput fabrication of transition-metal-doped epitaxial ZnO thin films: A series of oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors and their properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3824 (2001)
S. Ge, B. Zhang, C. Yang, Characterization of Er-doped AlN films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 358, 404–408 (2019)
C.-Y. Guo, X. Qi, RF magnetron sputter deposition and electrical properties of La and Y doped SrTiO3 epitaxial films. Mater. Des. 179, 107888 (2019)
A. Zdyb, E. Krawczak, S. Gułkowski, The influence of annealing on the properties of ZnO: Al layers obtained by RF magnetron sputtering. Opto Electron Rev 26(3), 247–251 (2018)
H. Mehmood, G. Bektaş, İ. Yıldız, T. Tauqeer, H. Nasser, R. Turan, Electrical, optical and surface characterization of reactive RF magnetron sputtered molybdenum oxide films for solar cell applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 101, 46–56 (2019)
T. Welzel, K. Ellmer, The influence of the target age on laterally resolved ion distributions in reactive planar magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 205, S294–S298 (2011)
R. Siddheswaran, R. Medlin, P. Calta, P. Sutta, Preparation of Nc-Si/A-SiO2 multi-layer thin film specimens for TEM cross-section observation by Cryo Argon ion slicing. JOJ Mater. Sci. 1(5), 555574 (2017)
J.L. Lábár, Consistent indexing of a (set of) single crystal SAED pattern(s) with the process diffraction program. Ultramicroscopy 103, 237–249 (2005)
T.F. Jaramillo, S. Baeck, A.K. Shwarsctein, K.S. Choi, G.D. Stucky, E.W. McFarland, J. Comb. Chem. 7, 264–271 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The corresponding and first author R.S acknowledges Tamilnadu State Council for Science and Technology (TNSCST), India for the award Young Scientist Fellowship (YSF) scheme 2018–2019, No. TNSCST/YSFS/VR/01/2018-2019/7108, dated 25/05/2019 for the partial financial support to carry out the research work. One of the authors, R.M acknowledges the CEDAMNF project, Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000358, co-funded by the ERDF as part of the MSMT, for the partial financial support towards the development of results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddheswaran, R., Medlín, R., Jeyanthi, C.E. et al. Structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of RF sputtered Co doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor for spintronic applications. Appl. Phys. A 125, 592 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2886-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2886-0