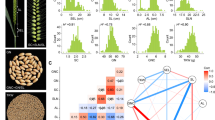
Abstract
Key message
A total of 104 foxtail millet accessions were evaluated for 11 nutrients in three environments and 67 high-confidence marker–trait associations (MTAs) were identified. Six SNPs showed pleiotropic effect and associated with two or more nutrients, whereas 24 candidate genes were identified for 28 MTAs involving seven traits.
Abstract
Millets are known for their better nutritional profiles compared to major cereals. Foxtail millet (Setaria italica) is rich in nutrients essential to circumvent malnutrition and hidden hunger. However, the genetic determinants underlying this trait remain elusive. In this context, we evaluated 104 diverse foxtail millet accessions in three different environments (E1, E2, and E3) for 11 nutrients and genotyped with 30K SNPs. The genome-wide association study showed 67 high-confidence (Bonferroni-corrected) marker–trait associations (MTAs) for the nutrients except for phosphorus. Six pleiotropic SNPs were also identified, which were associated with two or more nutrients. Around 24 candidate genes (CGs) were identified for 28 MTAs involving seven nutrients. A total of 17 associated SNPs were present within the gene region, and five (5) were mapped in the exon of the CGs. Significant SNPs, desirable alleles and CGs identified in the present study will be useful in breeding programmes for trait improvement.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adeva C, Yun Y-T, Shim K-C, Luong NH, Lee H-S, Kang J-W, Kim H-J, Ahn S-N (2023) QTL mapping of mineral element contents in rice using introgression lines derived from an interspecific cross. Agronomy 13:76
Alseekh S, Kostova D, Bulut M, Fernie AR (2021) GenomE-wide association studies: assessing trait characteristics in model and crop plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:5743–5754
Anuradha N, Satyavathi CT, Bharadwaj C, Nepolean T, Sankar SM, Singh SP, Meena MC, Singhal T, Srivastava RK (2017) Deciphering genomic regions for high grain iron and zinc content using association mapping in pearl millet. Front Plant Sci 8:412
Aranzana MJ, Kim S, Zhao K, Baller E, Horton M, Jacob J et al (2005) Genome wide association mapping in Arabidopsis identifies previously known flowering time and pathogen resistance genes. PLoS Genet 1:e60
Badakhshan H, Moradi N, Mohammadzadeh H, Zakeri MR (2013) Genetic variability analysis of grains Fe, Zn and beta-carotene concentration of prevalent wheat varieties in Iran. Intl J Agri Crop Sci 6:57–62
Bandyopadhyay T, Jaiswal V, Prasad M (2017a) Nutrition potential of foxtail millet in comparison to other millets and major cereals. In: Prasad M (ed) The foxtail millet genome. Compendium of plant genomes. Springer, Cham, pp 123–135
Bandyopadhyay T, Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M (2017b) Millets for next generation climatE−smart agriculture. Front Plant Sci 8:1266
Basnet B, Khanal S (2022) Quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for iron and zinc bio-fortification in genetically diverse germplasm of maize (Zea mays L): a systematic review. Heliyon 8:e12593
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Dixit S, Singh UM, Abbai R, Ram T, Singh VK, Paul A, Virk PS, Kumar A (2019) Identification of genomic region(s) responsible for high iron and zinc content in rice. Sci Rep 9:8136
Doust AN, Devos KM, Gadberry MD, Gale MD, Kellogg EA (2004) Genetic control of branching in foxtail millet. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9045–9050
Fang X, Dong K, Wang X, Liu T, Jihong H, Ren R et al (2016) A high density genetic map and QTL for agronomic and yield traits in Foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.]. BMC Genom 17:1–12
FAO (2022) https://www.fao.org
Govindaraj M, Kanatti A, Rai KN, Pfeiffer WH, Shivade H (2022) Association of grain iron and zinc content with other nutrients in pearl millet germplasm, breeding lines, and hybrids. Front Nutr 8:746625
Gupta PK, Kulwal PL, Jaiswal V (2014a) Association mapping in crop plants, opportunities and challenges. Adv Genet 85:109–148
Gupta S, Kumari K, Muthamilarasan M, Parida SK, Prasad M (2014b) Population structure and association mapping of yield contributing agronomic traits in foxtail millet. Plant Cell Rep 33:881–893
He Q, Zhi H, Tang S, Xing L, Wang S, Wang H et al (2021) QTL mapping for foxtail millet plant height in multi-environment using an ultra-high density bin map. Theor Appl Genet 134:557–572
Islam MZ, Arifuzzaman M, Banik S, Hossain MA, Ferdous J, Khalequzzaman M, Pittendrigh BR, Tomita M, Ali MP (2020) Mapping QTLs underpin nutrition components in aromatic rice germplasm. PLoS ONE 15:e0234395
Jaiswal V, Gupta S, Gahlaut V, Muthamilarasan M, Bandyopadhyay T, Ramchiary N, Prasad M (2019a) GenomE-wide association study of major agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) using ddRAD sequencing. Sci Rep 9:5020
Jaiswal V, Bandyopadhyay T, Gahlaut V, Gupta S, Dhaka A, Ramchiary N, Prasad M (2019b) GenomE-wide association study (GWAS) delineates genomic loci for ten nutritional elements in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). J Cereal Sci 85:48–55
Jia G, Huang X, Zhi H, Zhao Y, Zhao Q, Li W et al (2013) A haplotype map of genomic variations and genomE-wide association studies of agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Nat Genet 45:957–961
Kotla A, Phuke R, Hariprasanna K, Mehtre SP, Rathore A, Gorthy S et al (2019) Identification of QTLs and candidate genes for high grain Fe and Zn concentration in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. J Cereal Sci 90:102850
Kumar S, Hash CT, Thirunavukkarasu N, Singh G, Rajaram V, Rathore A, Senapathy S, Mahendrakar MD, Yadav RS, Srivastava RK (2016) Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling high iron and zinc content in self and open pollinated grains of pearl millet [Pennisetum glaucum (L.) R. Br.]. Front Plant Sci 7:1636
Kumar A, Tomer V, Kaur A et al (2018a) Millets: a solution to agrarian and nutritional challenges. Agric Food Secur 7:31
Kumar S, Hash CT, Neponean T, Mahendrakar MD, Satyavathi CT, Singh G, Rathore A, Yadav RS (2018b) Mapping grain iron and zinc content quantitative trait loci in an Iniadi-derived immortal population of pearl millet. Genes 9:248
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genomE-wide association studies. PLoS Genet 12:1–24
Liu J, Wu B, Singh RP, Velu G (2019) QTL mapping for micronutrients concentration and yield component traits in a hexaploid wheat mapping population. J Cereal Sci 88:57–64
Liu T, He J, Dong K, Wang X, Wang W, Yang P et al (2020) QTL mapping of yield component traits on bin map generated from resequencing a RIL population of foxtail millet (Setaria italica). BMC Genom 21:1–13
Liu J, Huang L, Li T, Liu Y, Yan Z, Tang G, Zheng Y, Liu D, Wu B (2021) GenomE-wide association study for grain micronutrient concentrations in wheat advanced lines derived from wild emmer. Front Plant Sci 12:651283
Moulick D, Ghosh D, Skalicky M, Gharde Y, Mazumder MK, Choudhury S, Biswas JK, Santra SC, Brestic M, Vachova P, Hossain A (2022) Interrelationship among rice grain arsenic, micronutrients content and grain quality attributes: an investigation from genotype × environment perspective. Front Environ Sci 10:857629
Nadeem F, Ahmad Z, Wang R, Han J, Shen Q, Chang F et al (2018) Foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) Beauv.] grown under low nitrogen shows a smaller root system, enhanced biomass accumulation, and nitrate transporter expression. Front Plant Sci 9:205
Nadeem F, Ahmad Z, Ul Hassan M, Wang R, Diao X, Li X (2020) Adaptation of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) to abiotic stresses: a special perspective of responses to nitrogen and phosphate limitations. Front Plant Sci 11:187
Nazari L, Ropelewska E, Zadeh MA (2022) Micronutrient content and geometrical features of grain sorghum subjected to water stress. Chem Proc 10:25
Puranik S, Sahu PP, Beynon S et al (2020) GenomE-wide association mapping and comparative genomics identifies genomic regions governing grain nutritional traits in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gaertn.). Plants People Planet 2:649
Rana S, Pramitha L, Aggarwal PR, Muthamilarasan M (2021) Genomic designing for biotic stress tolerance in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). In: Kole C (ed) Genomic designing for biotic stress resistant cereal crops. Springer, Cham
Rathan ND, Krishna H, Ellur RK, Sehgal D, Govindan V, Ahlawat AK, Krishnappa G, Jaiswal JP, Singh JB, Sv S, Ambati D, Singh SK, Bajpai K, Mahendru-Singh A (2022) GenomE-wide association study identifies loci and candidate genes for grain micronutrients and quality traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci Rep 12:7037
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5:69–76
Singh RK, Muthamilarasan M, Prasad M (2022) SiHSFA2e regulated expression of SisHSP21.9 maintains chloroplast proteome integrity under high temperature stress. Cell Mol Life Sci 79:580
Singhal T, Satyavathi CT, Singh SP, Kumar A, Sankar SM, Bhardwaj C, Mallik M, Bhat J, Anuradha N, Singh N (2021) Multi-environment quantitative trait loci mapping for grain iron and zinc content using bi-parental recombinant inbred line mapping population in pearl millet. Front Plant Sci 12:659789
Srivastava RK, Satyavathi CT, Mahendrakar MD, Singh RB, Kumar S, Govindaraj M, Ghazi IA (2021) Addressing iron and zinc micronutrient malnutrition through nutrigenomics in pearl millet: advances and prospects. Front Genet 12:723472
Tian B, Zhang L, Liu Y, Wu P, Wang W, Zhang Y et al (2021) Identification of QTL for resistance to leaf blast in foxtail millet by genome resequencing analysis. Theor Appl Genet 134:743–754
Wang J, Wang ZL, Du XF, Yang HQ, Han F, Han YH et al (2017) A high-density genetic map and QTL analysis of agronomic traits in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] using RAD-seq. PLoS ONE 12:e0179717
Wang Y, Xu X, Hao Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Pu Z, Tian Y, Xu D, Xia X, He Z, Zhang Y (2021) QTL mapping for grain zinc and iron concentrations in bread wheat. Front Nutr 8:680391
Wang M, Zhang R, Zhao Y, Yao J, Li W, Yang Z, Sun F, Yang X (2022) Identifying QTL and candidate genes for prolificacy in maize. Crop J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2022.08.007
WHO (2021) https://www.who.int/news-room/factsheets/detail/malnutrition
Xue WT, Gianinetti A, Wang R et al (2016) Characterizing barley seed macro- and micro-nutrients under multiple environmental conditions. Cereal Res Commun 44:639–649
Yoshitsu Y, Takakusagi M, Abe A, Takagi H, Uemura A, Yaegashi H et al (2017) QTL-seq analysis identifies two genomic regions determining the heading date of foxtail millet, Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv Breed Sci 67:518–527
Zhang Y, Gao X, Li J, Gong X, Yang P, Gao J et al (2019) Comparative analysis of proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) leaf transcriptomes for insight into drought tolerance mechanisms. BMC Plant Biol 19:1–17
Zhang B, Liang Z, Wang X (2023) Genetic and genomic research in foxtail millet. Plant Growth Regul 99:1–2
Zhao Y, Zhao W, Jiang C, Wang X, Xiong H, Todorovska EG et al (2018) Genetic architecture and candidate genes for deep-sowing tolerance in rice revealed by non-syn GWAS. Front Plant Sci 9:332
Zhi H, He Q, Tang S, Yang J, Zhang W, Liu H et al (2021) Genetic control and phenotypic characterization of panicle architecture and grain yield-related traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Theor Appl Genet 134:3023–3036
Zhu C, Kobayashi K, Loladze I, Zhu J, Jiang Q, Xu X, Liu G, Seneweera S, Ebi KL, Drewnowski A et al (2018) Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels this century will alter the protein, micronutrients and vitamin content of rice grains with potential health consequences for the poorest ricE−dependent countries. Sci Adv 4:1–9
Acknowledgements
MP acknowledges the financial support received through the National Bioscience Award (2015) from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India. VJ [CSIR-IHBT publication number is 5445] and VG acknowledge the DST-INSPIRE Faculty Awards received from Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India. VJ also thank the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) for the Early Career Research Award. The authors are thankful to DBT-eLibrary Consortium (DeLCON) for providing access to E−resources.
Funding
Department of Science and Technology (DST) for the INSPIRE faculty award (File no. DST/INSPIRE/04/2016/001189).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MP and VJ conceived and designed the experiments. VJ, TB, RKS, and VG performed the experiments. VJ and VG analysed the results. VJ and MM wrote the manuscript. MP approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Om Parkash Parkash Dhankher.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jaiswal, V., Bandyopadhyay, T., Singh, R.K. et al. Multi-environment GWAS identifies genomic regions underlying grain nutrient traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Plant Cell Rep 43, 6 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03127-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-023-03127-1