Abstract
Key message
Eleven Alfin-like (AL) genes were obtained from apple and MdAL4 was selected for improving drought stress tolerance of transgenic apple callus and Arabidopsis.
Abstract
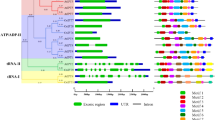
Drought is an important environmental factor affecting plant growth all over the world. Alfin-like (AL) have well-documented functions in abiotic stress response, but their drought stress tolerance in apple (Malus domestica) are poorly understood. According to the transcriptome data, 11 MdAL genes containing conserved Alfin and PHD-finger domain were identified in apple and divided into three subgroups with a total of 35 members from different species. Subsequently, gene structures, conserved amino acid sequences, promoter cis-acting elements, and gene evolution events were analyzed. Based on differential expression of MdALs in response to abiotic stresses, MdAL4, which was highly expressed under drought, was further cloned and investigated. MdAL4 encoding nuclear-localized protein conferred enhanced drought tolerance in overexpressing transgenic calli of apple ‘Orin’. Moreover, the ectopic expression of MdAL4 improved the drought tolerance of transgenic Arabidopsis, as judged from remarkably decreased malonaldehyde (MDA) content and electrolyte leakage in MdAL4 overexpressing plants relative to WT. Furthermore, MdAL4 possibly could bind to promoter regions of ROS-scavenging and stress-related genes to improve drought tolerance. Additionally, we found in silico evidence that three proteins containing the WD40 domain that interact with MdAL4. Based on these results, MdAL4 was identified as a positive regulator for improving drought stress of apple.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper.
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Bancroft I (2001) Duplicate and diverge: the evolution of plant genome microstructure. Trends Genet 17:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(00)02179-X
Bashline L, Li S, Zhu X, Gu Y (2015) The TWD40-2 protein and the AP2 complex cooperate in the clathrin-mediated endocytosis of cellulose synthase to regulate cellulose biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:12870–12875. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1509292112
Bastola DR, Pethe VV, Winicov I (1998) Alfin1, a novel zinc-finger protein in alfalfa roots that binds to promoter elements in the salt-inducible MsPRP2 gene. Plant Mol Biol 38:1123–1135. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006081926699
Bermúdez ICV, Schmidt W (2021) Chromatin enrichment for proteomics in plants (ChEP-P) implicates the histone reader ALFIN-LIKE 6 in jasmonate signalling. BMC Genom 22:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.02.446857
Bradford W, Buckholz A, Morton J, Price C, Jones AM, Urano D (2013) Eukaryotic G protein signaling evolved to require G protein-coupled receptors for activation. Sci Signal 6:ra37
Celton JM, Gaillard S, Bruneau M, Pelletier S, Aubourg S, Martin-Magniette ML, Navarro L, Faurens L, Renou JP (2014) Widespread anti-sense transcription in apple is correlated with siRNA production and indicates a large potential for transcriptional and/or post-transcriptional control. New Phytol 203:287–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12787
Chandrika NNP, Sundaravelpandian K, Yu SM, Wolfgang S (2013) Alfin-like 6 is involved in root hair elongation during phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 8(3):709–720. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.24381
Cheng MC, Liao PM, Kuo WW, Lin TP (2013) The Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 regulates abiotic stress responsive gene expression by binding to different cis-acting elements in response to different stress signals. Plant Physiol 162:1566–1582. https://doi.org/10.2307/41943499
Devoto A, Hartmann HA, Piffanelli P, Elliott C, Simmons C, Taramino G, Goh CS, Cohen FE, Emerson BC, Schulze-Lefert P (2003) Molecular phylogeny and evolution of the plant-specific seven-transmembrane MLO family. J Mol Evol 56:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.10064
Eichler EE, Sankoff D (2003) Structural dynamics of eukaryotic chromosome evolution. Science 301:793–797. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086132
Fruh K, Mansouri M, Bartee E, Gouveia K, Nerenberg BTH, Barrett J, Thomas L, Thomas G, McFadden G (2003) The PHD/LAP-domain protein M153R of myxomavirus is a ubiquitin ligase that induces the rapid internalization and lysosomal destruction of CD4. J Virol 77:1427–1440. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.77.2.1427-1440.2003
Guk JY, Jang MJ, Kim S (2022) Identification of novel PHD-finger genes in pepper by genomic re-annotation and comparative analyses. BMC Plant Biol 22(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-022-03580-2
Hao YJ, Wei W, Song QX, Chen HW, Zhang YQ, Wang F, Zou HF, Gang L, Tian AG, Zhang WK (2011) Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J 68:302–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04687.x
Hu W, Huang C, Deng XM, Zhou SY, Chen LH, Li Y, Wang C, Ma ZB, Yuan QQ, Wang Y, Cai R, Liang XY, Yang GX, He GY (2013) TaASR1, a transcription factor gene in wheat, confers drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Environ 36:1449–1464. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12074
Hunter T, Lu ZM, Xu SC, Joazeiro C, Cobb MH (2002) The PHD domain of MEKK1 acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase and mediates ubiquitination and degradation of ERK1/2. Mol Cell 9:945–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00519-1
Kong HZ, Landherr LL, Frohlich MW, Leebens-Mack J, Ma H, dePamphilis CW (2007) Patterns of gene duplication in the plant SKP1 gene family in angiosperms: evidence for multiple mechanisms of rapid gene birth. Plant J 50:873–885. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03097.x
Kong X, Lv W, Jiang S, Zhang D, Cai G, Pan J, Li D (2013) Genome wide identification and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase in maize. BMC Genom 14:433. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-433
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lee WY, Lee D, Chung WI, Kwon CS (2009) Arabidopsis ING and Alfin1-like protein families localize to the nucleus and bind to H3K4me3/2 via plant homeodomain fingers. Plant J 58:511–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03795.x
Liao Y, Zou HF, Wang HW, Zhang WK, Ma B, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008a) Soybean GmMYB76, GmMYB92, and GmMYB177 genes confer stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Cell Res 18:1047–1060. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.280
Liao Y, Zou HF, Wei W, Hao YJ, Tian AG, Huang J, Liu YF, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2008b) Soybean GmbZIP44, GmbZIP62 and GmbZIP78 genes function as negative regulator of ABA signaling and confer salt and freezing tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 228:225–240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0731-3
Linder B, Newman R, Jones LK, Debernardi S, Young BD, Freemont P, Verrijzer CP, Saha V (2000) Biochemical analyses of the AF10 protein: the extended LAP/PHD-finger mediates oligomerisation. J Mol Biol 299:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.3766
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001
Mehdi S, Derkacheva M, Ramstro M, Kralemann L, Bergquist J, Hennig L (2016) The WD40 domain protein MSI1 functions in a histone deacetylase complex to fine-tune abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 28:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00763
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Miura K, Na R, Suzaki T (2020) The PHD finger of Arabidopsis SIZ1 recognizes trimethylated histone H3K4 mediating SIZ1 function and abiotic stress response. Commun Biol 3(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-019-0746-2
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(16):6309–6314. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401572101
Nakashima K, Ito Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2009) Transcriptional regulatory networks in response to abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis and grasses. Plant Physiol 149:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.129791
Niu CF, Wei W, Zhou QY, Tian AG, Chen SY (2012) Wheat WRKY genes TaWRKY2 and TaWRKY19 regulate abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Environ 35:1156–1170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02480.x
Prakash JB, Shweta P (2018) WD40 repeat proteins: signalling scaffold with diverse functions. Protein J 37:391–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10930-018-9785-7
Qian F, Zhao QY, Zhang TN, Li YL, Su YN, Li L, Sui JH, Chen S, He XJ (2021) A histone H3K27me3 reader cooperates with a family of PHD finger-containing proteins to regulate flowering time in Arabidopsis. Acta Bot Sin 63(4):787–802. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13067
Ramani AK, Marcotte EM (2003) Exploiting the co-evolution of interacting proteins to discover interaction specificity. J Mol Biol 327:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00114-1
Ruiz-Lozano JM, Porcel R, Azcón C, Aroca R (2012) Regulation by arbuscular mycorrhizae of the integrated physiological response to salinity in plants: new challenges in physiological and molecular studies. J Exp Bot 63:4033–4044. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers126
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Taji T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2010) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–8292. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01359.x
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3(3):217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(00)80068-0
Song Y, Gao J, Yang FX, Kua CS, Liu JX, Cannon CH, Tuller T (2013) Molecular evolutionary analysis of the Alfin-like protein family in Arabidopsis lyrata, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Thellungiella halophila. PLoS ONE 8(7):e66838
Spoel SH, Ooijen GV (2014) Circadian redox signaling in plant immunity and abiotic stress. Antioxid Redox Sign 20:3024–3039. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5530
Tao JJ, Wei W, Pan WJ, Lu L, Zhang JS (2018) An Alfin-like gene from Atriplex hortensis enhances salt and drought tolerance and abscisic acid response in transgenic Arabidopsis. Sci Rep 8(1):2707. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-21148-9
Thu SW, Rai KM, Sandhu D, Rajangam A, Balasubramanian VK, Palmer RG, Mendu V (2019) Mutation in a PHD-finger protein MS4 causes male sterility in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 19(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1979-4
Townsley FM, Thompson B, Bienz M (2004) Pygopus residues required for its binding to Legless are critical for transcription and development. J Biol Chem 278:5177–5183. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309722200
Uljon S, Xu X, Durzynska I, Stein S, Adelmant G, Marto JA, Pear WS, Blacklow SC (2016) Structural basis for substrate selectivity of the E3 ligase COP1. Structure 24:687–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.03.002
Vinocur B, Altman A (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr Opin Biotech 16:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2005.02.001
Wang F, Chen HW, Li QT, Wei W, Li W, Zhang WK, Ma B, Bi YD, Lai YC, Liu XL, Man WQ, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2015) GmWRKY27 interacts with GmMYB174 to reduce expression of GmNAC29 for stress tolerance in soybean plants. Plant J 83:224–236. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12879
Waziri A, Singh K, Sharma T, Chatterjee S, Purty RS (2020) Genome-wide analysis of PHD finger gene family and identification of potential miRNA and their PHD finger gene specific targets in Oryza sativa indica. Non-Coding RNA 5(4):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.10.002
Wei W, Huang J, Hao YJ, Zou HF, Wang HW, Zhao JY, Liu XY, Zhang WK, Ma B, Zhang JS (2009) Soybean GmPHD-type transcription regulators improve stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. PLoS ONE 4:e7209. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007209
Wei W, Zhang YQ, Tao JJ, Chen HW, Li QT, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lin Q, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2015) The Alfin-like homeodomain finger protein AL5 suppresses multiple negative factors to confer abiotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J 81:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12773
Winicov I (1993) cDNA encoding putative zinc finger motifs from salt-tolerant alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cells. Plant Physiol 102:681–682. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.2.681
Winicov I (2000) Alfin1 transcription factor overexpression enhances plant root growth under normal and saline conditions and improves salt tolerance in alfalfa. Planta 210:416–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008150
Winicov II, Bastola DR (1999) Transgenic overexpression of the transcription factor alfin1 enhances expression of the endogenous MsPRP2 gene in alfalfa and improves salinity tolerance of the plants. Plant Physiol 120:473–480. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.120.2.473
Wu T, Pi EX, Tsai SN, Lam HM, Sun SM, Kwan YW, Ngai SM (2011) GmPHD5 acts as an important regulator for crosstalk between histone H3K4 di-methylation and H3K14 acetylation in response to salinity stress in soybean. BMC Plant Biol 11:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-178
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (1994) A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell 6:251–264. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.6.2.251
Yang Z, Zhou Y, Wang X, Gu S, Yu J, Liang G, Yan C, Xu C (2008) Genome-wide comparative phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary analysis of tubby-like protein family in Arabidopsis, rice, and poplar. Genomics 92:246–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.06.001
Zhang L, Li Z, Quan R, Li G, Wang R, Huang R (2011) An AP2 domain-containing gene, ESE1, targeted by the ethylene signaling component EIN3 is important for the salt response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 157:854–865. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.111.179028
Zhu YF, Chen QJ, Liu XD, Qu YY (2021) The Conringia planisiliqua Alfin-like2 gene enhances drought and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Theor Exp Plant Phys 33(4):427–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-021-00223-z
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31860530) and College Industry Support and Guidance Project of Gansu Province (2019C11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PW performed the analyses and wrote the manuscript. SL participated in the discussion on picture drawing of this manuscript. BC, JM, WL, and ZM revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Marcelo Menossi.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Lu, S., Li, W. et al. Genome-wide characterization of Alfin-like (AL) genes in apple and functional identification of MdAL4 in response to drought stress. Plant Cell Rep 42, 395–408 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02966-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-022-02966-8