Abstract
Key message
SbNAC genes (131) encoding 183 proteins were identified from the sorghum genome and characterized. The expression patterns of SbSNACs were evaluated at three sampling time points under post-flowering drought stress.
Abstract
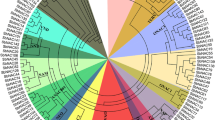
NAC proteins are specific transcription factors in plants, playing vital roles in development and response to various environmental stresses. Despite the fact that Sorghum bicolor is well-known for its drought-tolerance, it suffers from grain yield loss due to pre and post-flowering drought stress. In the present study, 131 SbNAC genes encoding 183 proteins were identified from the sorghum genome. The phylogenetic trees were constructed based on the NAC domains of sorghum, and also based on sorghum with Arabidopsis and 8 known NAC domains of other plants, which classified the family into 15 and 19 subfamilies, respectively. Based on the obtained results, 13 SbNAC proteins joined the SNAC subfamily, and these proteins are expected to be involved in response to abiotic stresses. Promoter analysis revealed that all SbNAC genes comprise different stress-associated cis-elements in their promoters. UTRs analysis indicated that 101 SbNAC transcripts had upstream open reading frames, while 39 of the transcripts had internal ribosome entry sites in their 5′UTR. Moreover, 298 miRNA target sites were predicted to exist in the UTRs of SbNAC transcripts. The expression patterns of SbSNACs were evaluated in three genotypes at three sampling time points under post-flowering drought stress. Based on the results, it could be suggested that some gene members are involved in response to drought stress at the post-flowering stage since they act as positive or negative transcriptional regulators. Following further functional analyses, some of these genes might be perceived to be promising candidates for breeding programs to enhance drought tolerance in crops.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afifi A, May S, Clark V (2003) Computer-aided multivariate analysis. CRC Press, London
Aida M, Ishida T, Fukaki H et al (1997) Genes involved in organ separation in Arabidopsis: an analysis of the cup-shaped cotyledon mutant. Plant Cell 9:841–857. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.6.841
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA et al (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
Bashirullah A, Cooperstock RL, Lipshitz HD (2001) Spatial and temporal control of RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7025–7028. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.111145698
Benson DA, Boguski MS, Lipman DJ, Ostell J (1997) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 25:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.1.1
Blum A (2004) Sorghum physiology. In: Nguyen HT, Blum A (eds) Physiology and biotechnology integration for plant breeding. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 141–223
Casa AM, Mitchell SE, Hamblin MT et al (2005) Diversity and selection in sorghum: Simultaneous analyses using simple sequence repeats. Theor Appl Genet 111:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-1952-5
Cenci A, Guignon V, Roux N, Rouard M (2014) Genomic analysis of NAC transcription factors in banana (Musa acuminata) and definition of NAC orthologous groups for monocots and dicots. Plant Mol Biol 85:63–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0169-2
Chen X, Wang Y, Lv B et al (2014) The NAC family transcription factor OsNAP confers abiotic stress response through the ABA pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 55:604–619. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pct204
Collinge M, Boller T (2001) Differential induction of two potato genes, Stprx2 and StNAC, in response to infection by Phytophthora infestans and to wounding. Plant Mol Biol 46:521–529. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010639225091
Dai X, Zhao PX (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–W159. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr319
Dean C, Schmidt R (1995) Plant genomes: a current molecular description. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:395–418. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.46.060195.002143
Duval M, Hsieh T-F, Kim S-Y, Thomas TL (2002) Molecular characterization of AtNAM: a member of theArabidopsis NAC domain superfamily. Plant Mol Biol 50:237–248
Fang Y, You J, Xie K et al (2008) Systematic sequence analysis and identification of tissue-specific or stress-responsive genes of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Mol Genet Genom 280:547–563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0386-6
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY et al (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D279–D285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Finn RD, Attwood TK, Babbitt PC et al (2017) InterPro in 2017—beyond protein family and domain annotations. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D190–D199. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1107
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Maruyama K et al (2004) A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J 39:863–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02171.x
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R et al (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:1178–1186. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr944
Gray NK, Wickens M (1998) Control of translation initiation in animals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 14:399–458. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.14.1.399
Grillo G, Turi A, Licciulli F et al (2010) UTRdb and UTRsite (RELEASE 2010): a collection of sequences and regulatory motifs of the untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D75–D80. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp902
Guo Y, Gan S (2006) AtNAP, a NAC family transcription factor, has an important role in leaf senescence. Plant J 46:601–612. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02723.x
Guo Y, Cai Z, Gan S (2004) Transcriptome of Arabidopsis leaf senescence. Plant Cell Environ 27:521–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2003.01158.x
Ha Van C, Nasr Esfahani M, Watanabe Y et al (2014) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CaNAC family members in chickpea during development, dehydration and ABA treatments. PLoS One 9:e114107. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114107
He X-J, Mu R-L, Cao W-H et al (2005) AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J 44:903–916. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02575.x
He L, Shi X, Wang Y et al (2017) Arabidopsis ANAC069 binds to C[A/G]CG[T/G] sequences to negatively regulate salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 93:369–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0567-3
Hofmann N (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum–localized transcription factors and mitochondrial retrograde regulation. Plant Cell 25:10–1105
Hu H, Dai M, Yao J et al (2006) Overexpressing a NAM, ATAF, and CUC (NAC) transcription factor enhances drought resistance and salt tolerance in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12987–12992. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604882103
Hu R, Qi G, Kong Y et al (2010) Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol 10:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-145
Hu B, Jin J, Guo A-Y et al (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Ibraheem O, Botha CEJ, Bradley G (2010) In silico analysis of cis-acting regulatory elements in 5′ regulatory regions of sucrose transporter gene families in rice (Oryza sativa Japonica) and Arabidopsis thaliana. Comput Biol Chem 34:268–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2010.09.003
Jansen R-P (2001) mRNA localization: message on the move. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:247–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/35067016
Jensen MK, Hagedorn PH, de Torres-Zabala M et al (2008) Transcriptional regulation by an NAC (NAM-ATAF1,2-CUC2) transcription factor attenuates ABA signalling for efficient basal defence towards Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei in Arabidopsis. Plant J 56:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03646.x
Jeong JS, Kim YS, Baek KH et al (2010) Root-specific expression of OsNAC10 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice under field drought conditions. Plant Physiol 153:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.154773
Jeong JS, Kim YS, Redillas MCFR et al (2013) OsNAC5 overexpression enlarges root diameter in rice plants leading to enhanced drought tolerance and increased grain yield in the field. Plant Biotechnol J 11:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12011
Jin J, Tian F, Yang DC et al (2017) PlantTFDB 4.0: toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D1040–D1045. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw982
John I, Hackett R, Cooper W et al (1997) Cloning and characterization of tomato leaf senescence-related cDNAs. Plant Mol Biol 33:641–651. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005746831643
Kadier Y, Zu Y, Dai Q et al (2017) Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of NAC family of genes in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Plant Growth Regul 83:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-017-0295-y
Kato H, Motomura T, Komeda Y et al (2010) Overexpression of the NAC transcription factor family gene ANAC036 results in a dwarf phenotype in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Physiol 167:571–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.11.004
Kebede H, Subudhi PK, Rosenow DT, Nguyen HT (2001) Quantitative trait loci influencing drought tolerance in grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). TAG Theor Appl Genet 103:266–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220100541
Kharrazi M, Rad M (2002) Evaluation of sorghum genotypes under drought stress conditions using some stress tolerance indices. Afr J Biotechnol 10(61):13086–13089
Kikuchi K, Ueguchi-Tanaka M, Yoshida KT et al (2000) Molecular analysis of the NAC gene family in rice. MGG Mol Gen Genet 262:1047–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00008647
Kim Y-S, Kim S-G, Park J-E et al (2006) A membrane-bound NAC transcription factor regulates cell division in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:3132–3144. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.043018
Kim HS, Park BO, Yoo JH et al (2007) Identification of a calmodulin-binding NAC protein as a transcriptional repressor in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 282:36292–36302. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705217200
Ko J-H, Yang SH, Park AH et al (2007) ANAC012, a member of the plant-specific NAC transcription factor family, negatively regulates xylary fiber development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 50:1035–1048. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03109.x
Kubo M, Udagawa M, Nishikubo N et al (2005) Transcription switches for protoxylem and metaxylem vessel formation. Genes Dev 19:1855–1860. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1331305
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2006) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. October 88:559–566. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbn017.MEGA
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP et al (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Le DT, Nishiyama R, Watanabe Y et al (2011) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the plant-specific NAC transcription factor family in soybean during development and dehydration stress. DNA Res 18:263–276. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsr015
Lee S, Seo PJ, Lee HJ, Park CM (2012) A NAC transcription factor NTL4 promotes reactive oxygen species production during drought-induced leaf senescence in Arabidopsis. Plant J 70:831–844. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04932.x
Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G et al (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2015) SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D257–D260. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku949
Li JQ, Zhang J, Wang XC, Chen J (2010) A membrane-tethered transcription factor ANAC089 negatively regulates floral initiation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Sci China Life Sci 53:1299–1306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-010-4085-2
Li P, Wind JJ, Shi X et al (2011) Fructose sensitivity is suppressed in Arabidopsis by the transcription factor ANAC089 lacking the membrane-bound domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:3436–3441. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1018665108
Lu PL, Chen NZ, An R et al (2007) A novel drought-inducible gene, ATAF1, encodes a NAC family protein that negatively regulates the expression of stress-responsive genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 63:289–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-006-9089-8
Lu M, Ying S, Zhang D-F et al (2012) A maize stress-responsive NAC transcription factor, ZmSNAC1, confers enhanced tolerance to dehydration in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31:1701–1711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-012-1284-2
Lu M, Zhang D-F, Shi Y-S et al (2013) Expression of SbSNAC1, a NAC transcription factor from sorghum, confers drought tolerance to transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 115:443–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0375-2
Ludlow MM, Muchow RC (1990) A critical evaluation of traits for improving crop yields in water-limited environments. Adv Agron 43:107–153
Makita Y, Shimada S, Kawashima M et al (2015) MOROKOSHI: transcriptome database in sorghum bicolor. Plant Cell Physiol 56:e6. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcu187
Mao C, Ding W, Wu Y et al (2007) Overexpression of a NAC-domain protein promotes shoot branching in rice. New Phytol 176:288–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02177.x
Mao X, Zhang H, Qian X et al (2012) TaNAC2, a NAC-type wheat transcription factor conferring enhanced multiple abiotic stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 63:2933–2946. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err462
Mao X, Chen S, Li A et al (2014) Novel NAC transcription factor TaNAC67 confers enhanced multi-abiotic stress tolerances in Arabidopsis. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084359
Martínez-Salas E, Piñeiro D, Fernández N (2012) Alternative mechanisms to initiate translation in eukaryotic mRNAs. Comp Funct Genomics 2012:391546
Menz MA, Klein RR, Unruh NC et al (2004) Genetic diversity of public inbreds of sorghum determined by mapped AFLP and SSR markers. Crop Sci 44:1236. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.1236
Mignone F, Gissi C, Liuni S, Pesole G (2002) Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol 3(3):reviews0004-1
Morishita T, Kojima Y, Maruta T et al (2009) Arabidopsis NAC transcription factor, ANAC078, regulates flavonoid biosynthesis under high-light. Plant Cell Physiol 50:2210–2222. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcp159
Mostafa M, Shahbazi M, Khazaei A (2011) Effect of post-flowering water stress on yield and physiological characters of grain sorghum genotypes. Iran J Plant Physiol 2(1):341–344
Mullet JE, Klein RR, Klein PE (2002) Sorghum bicolor—an important species for comparative grass genomics and a source of beneficial genes for agriculture. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:118–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00232-7
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J et al (2012) NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 1819:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.005
Ning YQ, Ma ZY, Huang HW et al (2015) Two novel NAC transcription factors regulate gene expression and flowering time by associating with the histone demethylase JMJ14. Nucleic Acids Res 43:1469–1484. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1382
Nuruzzaman M, Manimekalai R, Sharoni AM et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene 465:30–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GENE.2010.06.008
Ohbayashi I, Lin C, Shinohara N, Matsumura Y (2017) Evidence for a role of ANAC082 as a ribosomal stress response mediator leading to growth defects and developmental alterations in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00255
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TPLANTS.2004.12.010
Ooka H, Satoh K, Doi K et al (2003) Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res 10:239–247
Ozretić P, Bisio A, Inga A, Levanat S (2012) The growing relevance of cap-independent translation initiation in cancer-related genes. Period Biol 114(4):471–478
Pesole G, Mignone F, Gissi C et al (2001) Structural and functional features of eukaryotic mRNA untranslated regions. Gene 276:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00674-6
Podzimska-Sroka D, O’Shea C, Gregersen P, Skriver K (2015) NAC transcription factors in senescence: from molecular structure to function in crops. Plants 4:412–448. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants4030412
Rachmat A, Nugroho S, Sukma D, Aswidinnoor H (2014) Overexpression of OsNAC6 transcription factor from Indonesia rice cultivar enhances drought and salt tolerance. Emir J Food Agric 26:519–527. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.v26i6.17672
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW et al (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1004402
Ren T (2000) HRT gene function requires interaction between a NAC protein and viral capsid protein to confer resistance to turnip crinkle virus. Plant Cell 12:1917–1926. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.10.1917
Ricachenevsky FK, Menguer PK, Sperotto RA (2013) kNACking on heaven’s door: how important are NAC transcription factors for leaf senescence and Fe/Zn remobilization to seeds? Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2013.00226
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G et al (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5499.2105
Rooney WL, Blumenthal J, Bean B, Mullet JE (2007) Designing sorghum as a dedicated bioenergy feedstock. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefining 1:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.15
Rosenow D, Ejeta G, Clark L, Gilbert M et al (1997) Breeding for pre- and post-flowering drought stress resistance in sorghum. In: Proceedings of the international conference on genetic improvement of sorghum and pearl millet. INSORMIL, Lincoln, pp 400–411
Rushton P, Bokowiec M, Han S et al (2008) Tobacco transcription factors: novel insights into transcriptional regulation in the Solanaceae. Plant physiol 147(1):280–295
Rychlik W (2007) OLIGO 7 primer analysis software. In: PCR primer design. Humana Press, New York, pp 35–59
Sablowski RW, Meyerowitz EM (1998) A homolog of NO APICAL MERISTEM Is an immediate target of the floral homeotic genes APETALA3/PISTILLATA. Cell 92:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80902-2
Saga H, Ogawa T, Kai K et al (2012) Identification and characterization of ANAC042, a transcription factor family gene involved in the regulation of camalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 25:684–696. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-09-11-0244
Sakuraba Y, Kim Y-S, Han S-H et al (2015) The Arabidopsis transcription factor NAC016 promotes drought stress responses by repressing AREB1 transcription through a trifurcate feed-forward regulatory loop involving NAP. Plant Cell 27:1771–1787. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00222
Sanchez AC, Subudhi PK, Rosenow DT, Nguyen HT (2002) Mapping QTLs associated with drought resistance in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Plant Mol Biol 48:713–726. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014894130270
Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ (2008) Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc 3:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Seo PJ, Kim MJ, Park JY et al (2010) Cold activation of a plasma membrane-tethered NAC transcription factor induces a pathogen resistance response in Arabidopsis. Plant J 61:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04091.x
Shang H, Li W, Zou C, Yuan Y (2013) Analyses of the NAC transcription factor gene family in Gossypium raimondii Ulbr.: chromosomal location, structure, phylogeny, and expression patterns. J Integr Plant Biol 55:663–676. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12085
Shiriga K, Sharma R, Kumar K et al (2014) Genome-wide identification and expression pattern of drought-responsive members of the NAC family in maize. Meta Gene 2:407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MGENE.2014.05.001
Singh A, Sharma V, Pal A (2013) Genome-wide organization and expression profiling of the NAC transcription factor family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Dna …
Souer E, van Houwelingen A, Kloos D et al (1996) The No apical meristem gene of petunia is required for pattern formation in embryos and flowers and is expressed at meristem and primordia boundaries. Cell 85:159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81093-4
Sperotto RA, Ricachenevsky FK, Duarte GL et al (2009) Identification of up-regulated genes in flag leaves during rice grain filling and characterization of OsNAC5, a new ABA-dependent transcription factor. Planta 230:985–1002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1000-9
Subudhi PK, Rosenow DT, Nguyen HT (2000) Quantitative trait loci for the stay green trait in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench): consistency across genetic backgrounds and environments. TAG Theor Appl Genet 101:733–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051538
Sudhakar Reddy P, Srinivas Reddy D, Sivasakthi K et al (2016) Evaluation of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.)] reference genes in various tissues and under abiotic stress conditions for quantitative real-time PCR data normalization. Front Plant Sci 7:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00529
Tang Y, Liu M, Gao S et al (2012) Molecular characterization of novel TaNAC genes in wheat and overexpression of TaNAC2a confers drought tolerance in tobacco. Physiol Plant 144:210–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2011.01539.x
Tran LP, Nakashima K, Sakuma Y et al (2004) Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress-inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought-responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 Promoter. Plant Cell 16:2481–2498. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.022699.Shinozaki
Tuinstra MR, Grote EM, Goldsbrough PB, Ejeta G (1997) Genetic analysis of post-flowering drought tolerance and components of grain development in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Mol Breed 3:439–448. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009673126345
Uauy C, Distelfeld A, Fahima T et al (2006) A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science 314:1298–1301. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1133649
Voorrips RE (2002) Computer note MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Walulu RS, Rosenow DT, Wester DB, Nguyen HT (1994) Inheritance of the stay green trait in sorghum. Crop Sci 34:970. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400040026x
Waters BM, Uauy C, Dubcovsky J, Grusak MA (2009) Wheat (Triticum aestivum) NAM proteins regulate the translocation of iron, zinc, and nitrogen compounds from vegetative tissues to grain. J Exp Bot 60:4263–4274. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp257
Willemsen V, Bauch M, Bennett T et al (2008) The NAC domain transcription factors FEZ and SOMBRERO control the orientation of cell division plane in Arabidopsis root stem cells. Dev Cell 15:913–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2008.09.019
Wu X-Y, Hu W-J, Luo H et al (2016) Transcriptome profiling of developmental leaf senescence in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). Plant Mol Biol 92:555–580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-016-0532-1
Xie Q, Frugis G, Colgan D, Chua NH (2000) Arabidopsis NAC1 transduces auxin signal downstream of TIR1 to promote lateral root development. Genes Dev 14:3024–3036. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.852200
Xu W, Subudhi PK, Crasta OR et al (2000) Molecular mapping of QTLs conferring stay-green in grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Genome 43:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1139/g00-003
Xu B, Sathitsuksanoh N, Tang Y et al (2012) Overexpression of AtLOV1 in switchgrass alters plant architecture, lignin content, and flowering time. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047399
Xue G-P, Way HM, Richardson T et al (2011) Overexpression of TaNAC69 leads to enhanced transcript levels of stress up-regulated genes and dehydration tolerance in bread wheat. Mol Plant 4:697–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/MP/SSR013
Yilmaz A, Nishiyama MY, Fuentes BG et al (2009) GRASSIUS: a platform for comparative regulatory genomics across the grasses. Plant Physiol 149:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.128579
You J, Zhang L, Song B et al (2015) Systematic analysis and identification of stress-responsive genes of the NAC gene family in Brachypodium distachyon. PLoS One 10:e0122027. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122027
Zhang L, Zheng Y, Jagadeeswaran G et al (2011) Identification and temporal expression analysis of conserved and novel microRNAs in Sorghum. Genomics 98:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YGENO.2011.08.005
Zhang S, Zhou B, Kang Y et al (2015) C-terminal domains of histone demethylase JMJ14 interact with a pair of NAC transcription factors to mediate specific chromatin association. Cell Discov 1:15003. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2015.3
Zhao C, Avci U, Grant EH et al (2008) XND1, a member of the NAC domain family in Arabidopsis thaliana, negatively regulates lignocellulose synthesis and programmed cell death in xylem. Plant J 53:425–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03350.x
Zhao J, Liu J-S, Meng F-N et al (2016) ANAC005 is a membrane-associated transcription factor and regulates vascular development in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol 58:442–451. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12379
Zhong R, Demura T, Ye Z-H (2006) SND1, a NAC domain transcription factor, is a key regulator of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 18:3158–3170. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.047399
Zhong R, Lee C, Zhou J et al (2008) A battery of transcription factors involved in the regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 20:2763–2782. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.061325
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran (Project Number: 3-03-0305-93122), Education and Extension Organization (AREEO). University of Guilan and the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology are also acknowledged for supporting the project. The authors are grateful for the kind cooperation of Dr. Azim Khazaei and Mr. Mojtaba Jowkar (to plant culture in the field), Dr. Behzad Sorkhi (to provide real-time PCR facility) and Mr. Mohammad Jedari (to create the artworks).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Kan Wang.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanjari, S., Shirzadian-Khorramabad, R., Shobbar, ZS. et al. Systematic analysis of NAC transcription factors’ gene family and identification of post-flowering drought stress responsive members in sorghum. Plant Cell Rep 38, 361–376 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02371-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-019-02371-8