Abstract
Objective
This study aims to evaluate the active and chronic lesions in sacroiliac joints and lumbar spine over a decade of TNFi therapy in patients with AS.
Methods
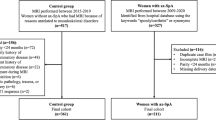
The study enrolled patients with AS under treatment with a TNFi for over a decade. The patients underwent a new MRI scan of their lumbar spine and sacroiliac joint (SIJ). Two readers evaluated all images. Inflammation of SIJ (SIS), SIJ structural damage (SSS) including Fat Metaplasia, Erosions, Backfill and Ankylosis, and Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Bone marrow edema (SPARCC) spine score were recorded.
Results
In the study, 15 patients were included, with 80% being male. The mean age during their first MRI was 38.1 (± 11.9) years old, and the majority (86.7%) tested positive for HLA-B27. While TNFi improved both BASDAI and BASFI scores, there was a noticeable increase in MRI acute lesions in the SIJ over time, where the median score increased from 0 (0–4) to 3 (0–10) after ten years (p = 0.028). After a decade of treatment, the median SPARCC spine score also increased from 0 (0–9) to 5 (0–16), p = 0.093. Finally, it was observed that there was a significant positive correlation between ESR and SIS erosions in cases of chronic lesions (r = 0.819, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
While TNFi have significantly improved the treatment of AS, this study shows that acute lesions can still develop despite treatment. A personalized approach that adapts MRI assessment to each patient’s specific requirements may help detect changes early and enable doctors to intervene promptly to prevent further damage.



Similar content being viewed by others
Open data sharing note
Data from this study are available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Wenker KJ, Quint JM (2023) Ankylosing Spondylitis 2023; in: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL)
Ranganathan V, Gracey E, Brown MA, Inman RD, Haroon N (2017) Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis - recent advances and future directions. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13:359–367
Zhu W, He X, Cheng K et al (2019) Ankylosing spondylitis: etiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Bone Res 7:22
Gran JT, Husby G (1993) The epidemiology of ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 22:319–334
Dean LE, Jones GT, MacDonald AG, Downham C, Sturrock RD, Macfarlane GJ (2014) Global prevalence of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:650–657
Raychaudhuri SP, Deodhar A (2014) The classification and diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis. J Autoimmun 48–49:128–133
Maksymowych WP (2009) MRI in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 21:313–317
Ostergaard M, Lambert RG (2012) Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis 4:301–311
Drosos AA, Venetsanopoulou AI, Voulgari PV (2023) Axial spondyloarthritis: evolving concepts regarding the disease’s diagnosis and treatment. Eur J Intern Med S0953–6205:00221–00222
Inman RD, Davis JC Jr, Dv H et al (2008) Efficacy and safety of golimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial. Arthritis Rheum 58:34
Rudwaleit M, Sieper J (2005) Infliximab for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 5:1095–1109
Venetsanopoulou AI, Voulgari PV, Alamanos Y, Papadopoulos CG, Markatseli TE, Drosos AA (2007) Persistent clinical response of infliximab treatment, over a 4-year period in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 27:935–939
Fröhlich F, Micheroli R, Hebeisen M et al (2023) HLA-B27 as a predictor of effectiveness of treatment with TNF inhibitors in axial spondyloarthritis: data from the Swiss Clinical Quality Management Registry. Clin Rheumatol 42:1267–1274
Leombruno JP, Einarson TR, Keystone EC (2009) The safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor treatments in rheumatoid arthritis: meta and exposure-adjusted pooled analyses of serious adverse events. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1136–1145
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Listing J et al (2008) Persistent clinical efficacy and safety of anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy with infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis over 5 years: evidence for different types of response. Ann Rheum Dis 67:340–345
Maksymowych WP, Inman RD, Salonen D et al (2005) Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada magnetic resonance imaging index for assessment of sacroiliac joint inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 53:703–709
Hu Z, Wang X, Qi J, Kong Q, Zhao M, Gu J (2016) Backfill is a specific sign of axial spondyloarthritis seen on MRI. Joint Bone Spine 83:179–183
Gezer HH, Duruöz MT (2022) The value of SPARCC sacroiliac MRI scoring in axial psoriatic arthritis and its association with other disease parameters. Int J Rheum Dis 25:433–439
Maksymowych WP, Bolce R, Gallo G et al (2022) Ixekizumab in radiographic axial spondyloarthritis with and without elevated C-reactive protein or positive magnetic resonance imaging. Rheumatology (Oxford) 61:4324–4334
van der Heijde D, Baraliakos X, Hermann KA et al (2018) Limited radiographic progression and sustained reductions in MRI inflammation in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: 4-year imaging outcomes from the RAPID-axSpA phase III randomised trial. Ann Rheum Dis 77:699–705
Wang R, Dasgupta A, Ward MM (2022) Predicting Probability of response to Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for individual patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis. JAMA Netw Open 5:e222312
Perrotta FM, Addimanda O, Ramonda R et al (2014) Predictive factors for partial remission according to the Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment Study working group in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with anti-TNFα drugs. Reumatismo 66:208–214
van der Heijde D, Ramiro S, Landewé R et al (2017) 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 76:978–991
Ward MM, Deodhar A, Gensler LS et al (2019) 2019 update of the American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network Recommendations for the treatment of Ankylosing spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 71:1285–1299
Manica SR, Sepriano A, Pimentel-Santos F et al (2020) Effectiveness of switching between TNF inhibitors in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: is the reason to switch relevant? Arthritis Res Ther 22:195
Wick MC, Weiss RJ, Jaschke W, Klauser AS (2010) Erosions are the most relevant magnetic resonance imaging features in quantification of sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 37:622–627
Chen M, Herregods N, Jaremko JL et al (2020) Diagnostic performance for erosion detection in sacroiliac joints on MR T1-weighted images: comparison between different slice thicknesses. Eur J Radiol 133:109352
Nam B, Koo BS, Choi N et al (2022) The impact of smoking status on radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis on anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment. Front Med (Lausanne) 17:9:994797
Baraliakos X, Richter A, Feldmann D et al (2020) Frequency of MRI changes suggestive of axial spondyloarthritis in the axial skeleton in a large population-based cohort of individuals aged < 45 years. Ann Rheum Dis 79:186–192
Dougados M, Maksymowych WP, Landewé RBM et al (2018) Evaluation of the change in structural radiographic sacroiliac joint damage after 2 years of etanercept therapy (EMBARK trial) in comparison to a contemporary control cohort (DESIR cohort) in recent onset axial spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 77:221–227
Braun J, Kiltz U, Baraliakos X (2022) Significance of structural changes in the sacroiliac joints of patients with axial spondyloarthritis detected by MRI related to patients symptoms and functioning. Ann Rheum Dis 81:11–14
Bruckmann NM, Rischpler C, Tsiami S et al (2022) Effects of Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy on osteoblastic activity at sites of Inflammatory and Structural lesions in Radiographic Axial spondyloarthritis: a prospective proof-of-Concept Study using Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints and spine. Arthritis Rheumatol 74:1497–1505
Zochling J, Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Braun J (2007) Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis. CurrO pin Rheumatol 19:346–352
Zhang P, Yu K, Guo R et al (2015) Ankylosing spondylitis: correlations between clinical and MRI indices of sacroiliitis activity. Clin Radiol 70:62–66
Landewé RB, Hermann KG, van der Heijde DM et al (2005) Scoring sacroiliac joints by magnetic resonance imaging. A multiple-reader reliability experiment. J Rheumatol 32:2050–2055
Lukas C, Braun J, van der Heijde D et al (2007) ASAS/OMERACT MRI in AS Working Group. Scoring inflammatory activity of the spine by magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis: a multireader experiment. J Rheumatol 34:862–870
Rudwaleit M, Jurik AG, Hermann KG et al (2009) Defining active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for classification of axial spondyloarthritis: a consensual approach by the ASAS/OMERACT MRI group. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1520–1527
Konca S, Keskin D, Cılız D, Bodur H, Sakman B (2012) Spinal inflammation by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: association with disease activity and outcome parameters. Rheumatol Int 32:3765–3770
Fries P, Runge VM, Kirchin MA, Watkins DM, Buecker A, Schneider G (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine at 3 Tesla. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 12:238–252
Funding
No funding was obtained for this original research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the study: PVV, MIA. Collected the data: ZT, Analyzed and interpreted the data: AZ, NEA. Drafted the manuscript: AIV. Revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content: PVV, LA. Approved the final version of the manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Venetsanopoulou, A.I., Anagnostou, N.E., Tziortzioti, Z. et al. “Long-term MRI findings in Ankylosing spondylitis patients treated with TNF inhibitors for a decade”. Rheumatol Int (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05530-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05530-z