Abstract
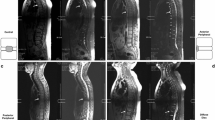
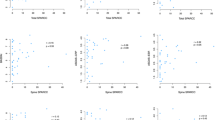
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has major contribution in early diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). As it is difficult to determine disease activity owing to the lack of close relation between laboratory tests, clinical findings and imaging, MRI has been used as an objective outcome measure. The aim of this study is to investigate the relation between spinal MRI findings with disease activity and other outcome measures. Fifty patients fulfilling modified New York criteria for AS were enrolled to the study. All the patients were evaluated with Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS), Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI), Bath AS Metrology Index (BASMI), Bath AS Radiology Index (BASRI) and As Quality of Life. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured as laboratory parameters, and ASspiMR scores were determined by spinal MRI. The median total ASspiMR-a score was 5.2. Spinal inflammation was evaluated in spinal segments, and thoracic segments had the highest mean ASspiMR-a level (3.1 ± 5.94). Cervical and lumbar ASspiMR were correlated with only BASRI, and total ASspiMR score was correlated with BASRI, BASMI and CRP. Thoracic ASspiMR score was correlated with patient’s and doctor’s global assessments, BASFI, BASMI, BASRI, ASDAS A, ASDAS B, ASDAS C, ASDAS D, ESR and CRP (P < 0.05). According to our results, the thoracic spine was the most related region with disease activity parameters and clinical outcome measures, so we suggest thoracic spine MRI evaluation in order to determine the disease activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gensler L (2011) Clinical features of ankylosing spondylitis. In: Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH (eds) Rheumatology, 5th edn. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1129–1134
Braun J, Rudwaleit M, Hermann KG, Rau R (2007) Imaging in ankylosing spondylitis. Z Rheumatol 66:167–178
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W, Brandt J, Rudwaleit M, Listing J, Bollow M, Sieper J, Van Der Heijde D (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum 48:1126–1136
Wendling D, Toussirot E, Streit G, Prati C (2006) Imaging study scores for ankylosing spondylitis. Jt Bone Spine 73:655–660
Rudwaleit M, Khan MA, Sieper J (2005) The challenge of diagnosis and classification in early ankylosing spondylitis: do we need new criteria? Arthritis Rheum 52:1000–1008
Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, Braun J (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 52:1216–1223
Sieper J, Rudwaleit M, Baraliakos X, Brandt J, Braun J (2009) The Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society (ASAS) handbook: a guide to assess spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1–44
Akkoc Y, Karatepe AG, Akar S, Kirazli Y, Akkoc N (2005) A Turkish version of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index: reliability and validity. Rheumatol Int 25:280–284
Yanık B, Gürsel YK, Kutlay S, Ay S, Elhan AH (2005) Adaptation of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index to the Turkish population, its reliability and validity: functional assessment in AS. Clin Rheumatol 24:41–47
Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC (1994) Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS): the Bath AS Metrology Index. J Rheumatol 21:694–698
Madsen OR, Hansen LB, Rytter A, Suetta C, Egsmose C (2009) The bath metrology index as assessed by a trained and an untrained rater in patients with spondyloarthropathy: a study of intra- and inter-rater agreements. Clin Rheumatol 28:35–40
MacKay K, Mack C, Brophy S, Calin A (1998) The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI): a new, validated approach to disease assessment. Arthritis Rheum 41:2263–2270
Tuncay Duruöz LD, Cerrahoglu L, Turan Y, Sari H (2008) Translation and validation of the Turkish version of the ankylosing spondylitis quality of life (ASQOL) questionnaire. Ann Rheum Dis 67(Suppl II):623
Lukas C, Landewé R, Sieper J (2009) Development of an ASAS-endorsed disease activity score (ASDAS) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:18–24
Van der Heijde D, Lie E, Kvien TK, Sieper J, Van den Bosch F, Listing J, Braun J, Landewé R, Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) (2009) ASDAS, a highly discriminatory ASAS-endorsed disease activity score in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1811–1818
Lukas C, Braun J, van der Heijde D, Hermann KG, Rudwaleit M, Østergaard M, Oostveen A, O’Connor P, Maksymowych WP, Lambert RG, Jurik AG, Baraliakos X, Landewé R (2007) Scoring inflammatory activity of the spine by magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis: a multireader experiment. ASAS/OMERACT MRI in AS Working Group. J Rheumatol 34:862–870
Heikkilä S, Viitanen JV, Kautiainen H, Kauppi M (2002) Functional long-term changes in patients with spondyloarthropathy. Clin Rheumatol 21:119–122
Akdeniz O, Alaylı G, Tosun FC, Diren B, Cengiz K, Selçuk MB, Sünter T, Cantürk F (2008) Early spondyloarthropaty: scintigraphic, biological, and clinical findings in MR-positive patients. Clin Rheumatol 27:469–474
Baraliakos X, Davis J, Tsuji W, Braun J (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 52:1216–1223
Baraliakos X, Hermann KG, Landewé R, Listing J, Golder W, Brandt J, Rudwailet M, Bollow M, Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Braun J (2005) Assessment of acute spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis by magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison contrast enhanced T1 and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. Ann Rheum Dis 64:1141–1144
van der Heijde D, Landewé R (2005) Imaging in spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17:413–417
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Golder W, Hermann KG, Listing J, Brandt J, Rudwaleit M, Zuehlsdorf S, Bollow M, Sieper J, van der Heijde D (2004) Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional X rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1046–1055
Sieper J, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Brandt J, Haibel H, Rudwailet M, Braun J (2005) Persistent reduction of spinal inflammation as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis after 2 yrs of treatment with the anti-tumour necrosis factor agent infliximab. Rheumatology 44:1525–1530
Baraliakos X, Landewe R, Hermann KG, Listing J, Golder W, Brandt J, Rudwaleit M, Bollow M, Sieper J, van der Heijde D, Braun J (2005) Inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic description of the extension and frequency of acute spinal changes using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ann Rheum Dis 64:730–734
Pedersen SJ, Sørensen IJ, Hermann KG, Madsen OR, Tvede N, Hansen MS, Thamsborg G, Andersen LS, Majgaard O, Loft AG, Erlendsson J, Asmussen K, Johansen JS, Jurik AG, Møller J, Hasselquist M, Mikkelsen D, Skjødt T, Hansen A, Ostergaard M (2010) Responsiveness of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) clinical and MRI measures of disease activity in a 1-year follow-up study of patients with axial spondyloarthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitors. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1065–1071
Romero-Sánchez C, Robinson WH, Tomooka BH, Londoňo J, Valle-Oňate R, Huang F, Deng X, Zhang L, Yang C, Yu DT (2008) Identification of acute phase reactants and cytokines useful for monitoring infliximab therapy in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 27:1429–1435
Puhakka KB, Jurik AG, Schiottz-Christensen B, Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliitis in early seronegative spondyloarthropathy et al (2004) Abnormalities correlated to clinical and laboratory findings. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:234–237
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konca, Ş., Keskin, D., Cılız, D. et al. Spinal inflammation by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: association with disease activity and outcome parameters. Rheumatol Int 32, 3765–3770 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2248-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2248-5