Abstract
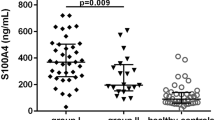
The mechanisms underlying new bone formation in individuals with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) remain unclear; however, low levels of sclerostin (SOST) may be associated with development of syndesmophytes in those with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Expression of fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23), another osteocyte factor, is high in those with osteoporosis and chronic renal failure, but levels in those with axSpA are unknown. To evaluate serum FGF-23 and SOST levels in axSpA patients, and to assess their relationship with inflammation and structural damage. In total, 109 axSpA patients (55 with AS and 54 with non-radiographic axSpA) and 57 healthy control (HC) subjects were included in the analysis. Serum concentrations of FGF-23 and SOST were measured and correlation analysis was performed. The presence of syndesmophytes and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS) were used to assess structural damage. Levels of serum FGF-23 in axSpA patients were significantly higher than those in HCs [median (interquartile range—IQR) FGF-23 level, pg/ml; AxSpA = 144 (82.3–253.2), HC = 107 (63.3–192.8), p = 0.010]; however, there was no difference in SOST levels. FGF-23 levels correlated with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) (r = 0.265, p = 0.006) and serum C-reactive protein (CRP) level (r = 0.229, p = 0.010). In the axSpA, SOST levels correlated negatively with mSASSS (r = − 0.283, p = 0.007), whereas those in the AS group correlated negatively with CRP (r = − 0.426, p = 0.001). Serum FGF-23 levels were high in axSpA patients. Increased FGF-23 was associated with inflammation, but not with SOST levels or disease activity. SOST correlated negatively with both inflammation and structural damage.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poddubnyy D, Sieper J (2017) Mechanism of new bone formation in axial spondyloarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 19:55
Perrotta FM, Ceccarelli F, Barbati C, Colasanti T, De Socio A, Scriffignano S et al (2018) Serum sclerostin as a possible biomarker in ankylosing spondylitis: a case-control study. J Immunol Res 2018:9101964
Swanson C, Shea SA, Wolfe P, Markwardt S, Cain SW, Munch M et al (2017) 24-hour profile of serum sclerostin and its association with bone biomarkers in men. Osteoporos Int 28:3205–3213
Magrey MN, Khan MA (2017) The paradox of bone formation and bone loss in ankylosing spondylitis: evolving new concepts of bone formation and future trends in management. Curr Rheumatol Rep 19:17
Appel H, Ruiz-Heiland G, Listing J, Zwerina J, Herrmann M, Mueller R et al (2009) Altered skeletal expression of sclerostin and its link to radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 60:3257–3262
Ustun N, Tok F, Kalyoncu U, Motor S, Yuksel R, Yagiz AE et al (2014) Sclerostin and Dkk-1 in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Reumatol Port 39:146–151
Korkosz M, Gąsowski J, Leszczyński P, Pawlak-Buś K, Jeka S, Kucharska E et al (2013) High disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis is associated with increased serum sclerostin level and decreased wingless protein-3a signaling but is not linked with greater structural damage. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 14:99
Lories RJ, Haroon N (2014) Bone formation in axial spondyloarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 28:765–777
Tuylu T, Sari I, Solmaz D, Kozaci DL, Akar S, Gunay N et al (2014) Fetuin-A is related to syndesmophytes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a case control study. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 69:688–693
Solmaz D, Uslu S, Kozacı D, Karaca N, Bulbul H, Tarhan EF et al (2018) Evaluation of periostin and factors associated with new bone formation in ankylosing spondylitis: periostin may be associated with the Wnt pathway. Int J Rheum Dis 21:502–509
Penido MGMG, Alon US (2012) Phosphate homeostasis and its role in bone health. Pediatr Nephrol 2:2039–2048
Courbebaisse M, Lanske B (2018) Biology of fibroblast growth factor 23: from physiology to pathology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8:5. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a031260
Isakova T, Wahl P, Vargas GS, Gutiérrez OM, Scialla J, Xie H et al (2011) Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 79:1370–1378
Celik E, Guzel S, Abali R, Guzelant AY, Celik Guzel E, Kuçukyalcin V (2013) The relationship between fibroblast growth factor 23 and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Minerva Med 104:497–504
Mirza MA, Karlsson MK, Mellström D, Orwoll E, Ohlsson C, Ljunggren O et al (2011) Serum fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF-23) and fracture risk in elderly men. J Bone Miner Res 26:857–864
Grabner A, Mazzaferro S, Cianciolo G, Krick S, Capelli I, Rotondi S, Ronco C et al (2017) Fibroblast growth factor 23: mineral metabolism and beyond. Contrib Nephrol 190:83–95
Munoz Mendoza J, Isakova T, Cai X, Bayes LY, Faul C, Scialla JJ, CRIC Study Investigators et al (2017) Inflammation and elevated levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 are independent risk factors for death in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 91:711–719
Francis C, David V (2016) Inflammation regulates fibroblast growth factor 23 production. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 25:325–332
Sato H, Kazama JJ, Murasawa A, Otani H, Abe A, Ito S et al (2016) Serum fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med 55:121–126
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68:777–783
Shi J, Ying H, Du J, Shen B (2017) Serum sclerostin levels in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2017:9295313. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9295313
Zhang L, Ouyang H, Xie Z, Liang ZH, Wu XW (2016) Serum DKK-1 level in the development of ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatic arthritis: a meta-analysis. Exp Mol Med 48:e228
Cortes A, Maksymowych WP, Wordsworth BP, Inman RD, Danoy P, Rahman P et al (2015) Association study of genes related to bone formation and resorption and the extent of radiographic change in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1387–1393
Muntean L, Lungu A, Gheorghe SR, Valeanu M, Craciun AM, Felea I et al (2016) Elevated serum levels of sclerostin are associated with high disease activity and functional impairment in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Lab 62:589–597
Luchetti MM, Ciccia F, Avellini C, Benfaremo D, Guggino G, Farinelli A et al (2018) Sclerostin and antisclerostin antibody serum levels predict the presence of axial spondyloarthritis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Rheumatol 45:630–637
Acknowledgements
This manuscript was edited by pre-peer review service.
Funding
This study was supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Izmir Katip Celebi University. Project number: 2016-TDU-TIPF-0020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All co-authors meet the authorship criteria based on ICMJE. Study design: OG, DS, DK, SA. Acquisition of data: OG, DS, EC, BOI, GA, OB, GK, FET, SA. Analysis and interpretation of data: DS, EC, BOI, GA, OB, GK, FET, DK, SA. Drafting the article or revising: OG, DS, EC, BOI, GA, OB, GK, FET, DK, SA. Final approval of the version of the article to be published: OG, DS, EC, BOI, GA, OB, GK, FET, DK, SA.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None for all authors.
Ethics approval
Ethics approval was obtained from the local ethical committee [Izmir Katip Celebi University Ethics Board, Izmir, Turkey (approval number: 27/2016)]. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gercik, O., Solmaz, D., Coban, E. et al. Evaluation of serum fibroblast growth factor-23 in patients with axial spondyloarthritis and its association with sclerostin, inflammation, and spinal damage. Rheumatol Int 39, 835–840 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04298-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04298-5