Abstract
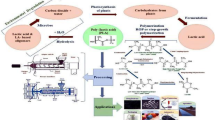
This paper reports effects of acrylic core–shell rubber (CSR) on mechanical and rheological properties of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/CSR blends. The CSR was synthesized via a seeded emulsion polymerization with poly(butyl acrylate) and poly(methyl methacrylate) as core and shell, respectively, and then introduced to PLA using a twin-screw extruder. Toughness of the blends characterized was increased by shear yielding due to micro-voiding formed by de-bonding of CSR. Their shear viscosity, storage, and loss modulus measured using rotational rheometer increased with CSR content. An analysis using Cox–Merz law confirmed that two curves coincided well with each other, while exhibiting shear-thinning behavior.










Similar content being viewed by others

References
Nampoothiri KM, Nair NR, John RP (2010) An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour Technol 101:8493–8501
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly (lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35:338–356
Liu H, Zhang J (2011) Research progress in toughening modification of poly (lactic acid). J Polym Sci Polym Phys 49:1051–1083
Yoo TW, Yoon HG, Choi SJ, Kim MS, Kim YH, Kim WN (2010) Effects of compatibilizers on the mechanical properties and interfacial tension of polypropylene and poly (lactic acid) blends. Macromol Res 18:583–588
Narimissa E, Gupta RK, Choi HJ, Kao N, Jollands M (2012) Morphological, mechanical, and thermal characterization of biopolymer composites based on polylactide and nanographite platelets. Polym Compos 33:1505–1515
Narimissa E, Gupta RK, Kao N, Choi HJ, Jollands M, Bhattacharya SN (2014) Melt rheological investigation of polylactide–nanographite platelets biopolymer composites. Polym Eng Sci 54:175–188
Narimissa E, Gupta RK, Kao N, Choi HJ, Bhattacharya SN (2015) The comparison between the effects of solvent casting and melt intercalation mixing processes on different characteristics of polylactide–nanographite platelets composites. Polym Eng Sci 55:1560–1570
Lee H, Chin I-J (2016) Toughening effect of annealing-induced intermolecular crystallization of PBA-g-PLLA in PLA matrix. Macromol Res 24:515–521
Yao S-S, Pang Q-Q, Song R, Jin F-L, Park S-J (2016) Fracture toughness improvement of poly (lactic acid) with silicon carbide whiskers. Macromol Res 24:961–964
Chen Y, Yuan D, Xu C (2014) Dynamically vulcanized biobased polylactide/natural rubber blend material with continuous cross-linked rubber phase. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3811–3816
Liu GC, He YS, Zeng JB, Li QT, Wang YZ (2014) Fully biobased and supertough polylactide-based thermoplastic vulcanizates fabricated by peroxide-induced dynamic vulcanization and interfacial compatibilization. Biomacromol 15:4260–4271
Yuan D, Chen Z, Xu C, Chen K, Chen Y (2015) Fully biobased shape memory material based on novel cocontinuous structure in poly (lactic acid)/natural rubber TPVs fabricated via peroxide-induced dynamic vulcanization and in situ interfacial compatibilization. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:2856–2865
Valerio O, Pin JM, Misra M, Mohanty AK (2016) Synthesis of glycerol-based biopolyesters as toughness enhancers for polylactic acid bioplastic through reactive extrusion. ACS Omega 1:1284–1295
Chen Y, Wang W, Yuan D, Xu C, Cao L, Liang X (2018) Bio-Based PLA/NR-PMMA/NR ternary thermoplastic vulcanizates with balanced stiffness and toughness:“Soft–Hard” core–shell continuous rubber phase, in situ compatibilization, and properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:6488–6496
Zhao T-H, Yuan W-Q, Li Y-D, Weng Y-X, Zeng J-B (2018) Relating chemical structure to toughness via morphology control in fully sustainable sebacic acid cured epoxidized soybean oil toughened polylactide blends. Macromolecules 51:2027–2037
Mehrabi Mazidi M, Edalat A, Berahman R, Hosseini FS (2018) Highly-toughened polylactide- (PLA-) based ternary blends with significantly enhanced glass transition and melt strength: tailoring the interfacial interactions, phase morphology, and performance. Macromolecules 51:4298–4314
Gramlich WM, Robertson ML, Hillmyer MA (2010) Reactive compatibilization of poly (l-lactide) and conjugated soybean oil. Macromolecules 43:2313–2321
Liu H, Song W, Chen F, Guo L, Zhang J (2011) Interaction of microstructure and interfacial adhesion on impact performance of polylactide (PLA) ternary blends. Macromolecules 44:1513–1522
Bai H, Huang HC, Xiu H, Gao Y, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2012) Toughening of poly (l-lactide) with poly (ε-caprolactone): combined effects of matrix crystallization and impact modifier particle size. Polymer 54:5257–5266
Lee JY, Chin I-J, Choi HJ (2018) Effect of particle size and crosslinking on the toughening of core-shell-type rubber-modified poly(lactic acid) composites. Polym Test 65:440–449
Lu M, Keskkula H, Paul D (1996) Toughening of nylon 6 with core-shell impact modifiers: effect of matrix molecular weight. J Appl Polym Sci 59:1467–1477
Kayano Y, Keskkula H, Paul D (1996) Effect of polycarbonate molecular weight and processing conditions on mechanical behaviour of blends with a core-shell impact modifier. Polymer 37:4505–4518
Bucknall C (2001) Blends containing core-shell impact modifiers part 1. Structure and tensile deformation mechanisms (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 73:897–912
Wu G, Zhao J, Shi H, Zhang H (2004) The influence of core–shell structured modifiers on the toughness of poly (vinyl chloride). Eur Polym J 40:2451–2456
Cho K, Yang J, Park CE (1998) The effect of rubber particle size on toughening behaviour of rubber-modified poly (methyl methacrylate) with different test methods. Polymer 39:3073–3081
Choi HJ, Ray SS (2011) A review on melt-state viscoelastic properties of polymer nanocomposites. J Nanosci Nanotech 11:8421–8449
Jiang L, Wolcott MP, Zhang J (2006) Study of biodegradable polylactide/poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blends. Biomacromol 7:199–207
Afrifah KA, Matuana LM (2010) Impact modification of polylactide with a biodegradable ethylene/acrylate copolymer. Macromol Mater Eng 295:802–811
Dompas D, Groeninckx G, Isogawa M, Hasegawa T, Kadokura M (1995) Cavitation versus debonding during deformation of rubber-modified poly (vinyl chloride). Polymer 36:437–441
Carreau PJ (1997) Rheology of polymeric systems: principles and applications. Hanser Publishers, New York
Dou R, Wang W, Zhou Y, Li L-P, Gong L, Yin B, Yang M-B (2013) Effect of core-shell morphology evolution on the rheology, crystallization, and mechanical properties of PA6/EPDM-g-MA/HDPE ternary blend. J Appl Polym Sci 129:253–262
Karis TE, Kono R-N, Kim CA, Jhon MS, Choi HJ (2003) Nonlinear rheology for a grease. J Ind Eng Chem 9:419–425
Kim TH, Lim ST, Lee CH, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2003) Preparation and rheological characterization of intercalated polystyrene/organophilic montmorillonite nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 87:2106–2112
Cox W, Merz E (1958) Correlation of dynamic and steady flow viscosities. J Polym Sci 28:619–622
Choi H, Park S, Yoon J, Lee HS, Choi S (1995) Rheological study on poly-D (-)(3-hydroxybutyrate) and its blends with poly (ethylene oxide). Polym Eng Sci 35:1636–1642
Sohn J-I, Lee C, Lim S, Kim T, Choi H, Jhon M (2003) Viscoelasticity and relaxation characteristics of polystyrene/clay nanocomposite. J Mater Sci 38:1849–1852
Cui L, Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhou W (2007) Rheological behavior of polypropylene/novolac blends. J Appl Polym Sci 106:811–816
Jang W-Y, Hong K-H, Cho B-H, Jang S-H, Lee S-I, Kim B-S, Shin B-Y (2008) Thermal and rheological properties, and biodegradability of chemically modified PLA by reactive extrusion. Polym Korea 32:116–124
Li J, Ma G, Sheng J (2010) Linear viscoelastic characteristics of in situ compatiblized binary polymer blends with viscoelastic properties of components variable. J Polym Sci Polym Phys 48:1349–1362
Jang K, Lee JW, Hong I-K, Lee S (2013) Effect of supercritical carbon dioxide as an exfoliation aid on bio-based polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified/clay nanocomposites. Korea-Aust Rheol J 25:145–152
Trinkle S, Friedrich C (2001) Van Gurp-Palmen-plot: a way to characterize polydispersity of linear polymers. Rheol Acta 40:322–328
Li R, Yu W, Zhou C (2006) Phase behavior and its viscoelastic responses of poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly (styrene-co-maleic anhydride) blend systems. Polym Bull 56:455–466
You Y-C, Kim Y-C (2011) Study on the talc dispersion and rheological properties of PP/talc compound. J Korea Acad-Ind Soc 12:4261–4266
Kim YH, Kwon SH, Choi HJ, Choi K, Kao N, Bhattacharya SN, Gupta RK (2016) Thermal, mechanical, and rheological characterization of polylactic acid/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites. J Macromol Sci B 55:680–692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.Y., Kwon, S.H., Chin, IJ. et al. Toughness and rheological characteristics of poly(lactic acid)/acrylic core–shell rubber blends. Polym. Bull. 76, 5483–5497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2662-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-018-2662-x