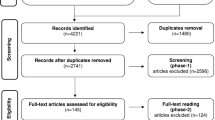
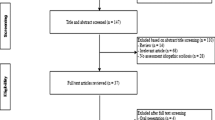
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate aesthetic outcomes in patients with bilateral trapezius hypertrophy treated by botulinum toxin type A (BTxA) injection for aesthetic reconstruction of the upper trapezius.
Methods
From May 2015 to May 2016, 30 women with a short neck shape resulting from bilateral trapezius hypertrophy were treated with botulinum toxin type A (BTxA) injection at the most affected area of the upper trapezius. Pre- and postoperative values of SACDF (irregularly shaped area of the four points A, C, D, and F) and SACDE (irregularly shaped area of the four points A, C, D, and E), responses to patients’ and doctors’ Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) questionnaires for neck aesthetic assessment, as well as reported adverse events, were recorded and analyzed.
Results
Duration of follow-up ranged from 4 to 12 months. Subjects experienced non-severe adverse events and complete recovery after a single BTxA injection. In patients’ GAIS questionnaires, “very much improved” accounted for 53%, “much improved” accounted for 13%, and “improved” accounted for 27%. In doctors’ GAIS questionnaires, “very much improved” accounted for 27%, “much improved” accounted for 33%, “improved” accounted for 33%, and “no change” accounted for 7%. The overall degree of improvement was high. Statistically significant differences were observed with respect to the “very much improved” response to GAIS questionnaires between patients and doctors (P = 0.035).
Conclusion
A single injection of BTxA for aesthetic reconstruction of the upper trapezius is safe and effective in patients with bilateral trapezius hypertrophy.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton FE Jr (2009) Aesthetic surgery of the face and neck. Aesthet Surg J 29:449–463 (quiz 464–446)
Matarasso A (2014) Managing the components of the aging neck: from liposuction to submentalplasty, to neck lift. Clin Plast Surg 41:85–98
Huettner F, Vasconez LO, de la Torre JI (2012) Neck rejuvenation–anatomy and clinical correlation. Facial Plast Surg 28:40–51
Zins JE, Morrison CM (2010) Aesthetic surgery of the aging face and neck. In: Siemionow MZ, Eisenmann-Klein M (eds) Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Springer Specialist Surgery Series. Springer, London, pp 379–392
Abood A, Malata CM (2008) Neck lifts: surgical rejuvenation of the ageing neck. In: Christopher S (ed) The Evidence for Plastic Surgery. TFM Publishing Limited, UK, pp 299–3106
Athanasiou A, Rempelos G (2014) Lore’s fascia a strong fixation point for neck rejuvenation procedures. Clin Plast Surg 41:43–49
Sykes JM (2001) Rejuvenation of the aging neck. Facial Plast Surg 17:99–107
Wu WT (2015) Microbotox of the lower face and neck: evolution of a personal technique and its clinical effects. Plast Reconstr Surg 136:92S–100S
Cuzalina LA, Bailey CE (2011) Cosmetic surgical rejuvenation of the neck. Springer, Berlin
Bilwatsch S, Kramer M, Haeusler G, Schuster M, Wurm J, Vairaktaris E, Neukam FW, Nkenke E (2006) Nasolabial symmetry following Tennison-Randall lip repair: a three-dimensional approach in 10-year-old patients with unilateral clefts of lip, alveolus and palate. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 34:253–262
Hersant B, Abbou R, SidAhmed-Mezi M, Meningaud JP (2016) Assessment tools for facial rejuvenation treatment: a review. Aesthetic Plast Surg 40:556–565
Kane MA (1999) Nonsurgical treatment of platysmal bands with injection of botulinum toxin A. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:656–663 (discussion 664-655)
Guyuron B (2003) Nonsurgical treatment of platysmal bands with injection of botulinum toxin A. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:123S–124S
Esenyel M, Aldemir T, Gursoy E, Esenyel CZ, Demir S, Durmusoglu G (2007) Myofascial pain syndrome: efficacy of different therapies. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 20:43–47
Gobel H, Heinze A, Reichel G, Hefter H, Benecke R, Dysport myofascial pain study g (2006) Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum type A toxin complex treatment (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: results from a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre study. Pain 125:82–88
Zhang T, Adatia A, Zarin W, Moitri M, Vijenthira A, Chu R, Thabane L, Kean W (2011) The efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in managing chronic musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta analysis. Inflammopharmacology 19:21–34
Kwanchuay P, Petchnumsin T, Yiemsiri P, Pasuk N, Srikanok W, Hathaiareerug C (2015) Efficacy and safety of single botulinum toxin type A [Botox(R)] injection for relief of upper trapezius myofascial trigger point: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Med Assoc Thai 98:1231–1236
Sclafani AP, Kwak E (2005) Alternative management of the aging jawline and neck. Facial Plastic Surgery Fps 21:47–54
Matarasso A, Matarasso SL (2003) Botulinum A exotoxin for the management of platysma bands. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:138S–140S
Lowe NJ, Ascher B, Heckmann M, Kumar C, Fraczek S, Eadie N, Botox Facial Aesthetics Study T (2005) Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-response study of the safety and efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in subjects with crow’s feet. Dermatol Surg 31:257–262
Baumann L, Dayan S, Connolly S, Silverberg N, Lei X, Drinkwater A, Gallagher CJ (2016) Duration of clinical efficacy of onabotulinumtoxin A in crow’s feet lines: results from two multicenter, randomized, controlled trials. Dermatol Surg 42:598–607
Ellis DA, Tan AK (1997) Cosmetic upper-facial rejuvenation with botulinum. J Otolaryngol 26:92–96
Matarasso SL (2003) Comparison of botulinum toxin types A and B: a bilateral and double-blind randomized evaluation in the treatment of canthal rhytides. Dermatol Surg 29:7–13 (discussion 13)
Lowe NJ, Lask G, Yamauchi P, Moore D (2002) Bilateral, double-blind, randomized comparison of 3 doses of botulinum toxin type A and placebo in patients with crow’s feet. J Am Acad Dermatol 47:834–840
Levy JL, Pons F, Jouve E (2006) Management of the ageing eyebrow and forehead: an objective dose-response study with botulinum toxin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 20:711–716
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the institutional ethics committee. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, RR., Wu, HL., Zhang, XD. et al. Efficacy and Safety of Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection in Patients with Bilateral Trapezius Hypertrophy. Aesth Plast Surg 42, 1664–1671 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1201-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1201-3