Abstract
Background
Botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA) is a neurotoxin that acts by inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions, thus reducing muscular contractions. Recent evidence suggests that BoNTA can reduce nociceptive activities of sensory neurons in animal models by inhibiting release of certain neuropeptides. Despite the therapeutic benefit of BoNTA in alleviating painful muscle spasms, its efficacy in other musculoskeletal pain conditions is less clear.
Objective
We aim to examine the efficacy of BoNTA in reducing chronic musculoskeletal pain.
Methods
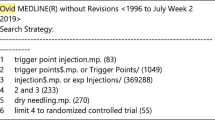
Studies for inclusion in our report were identified using MEDLINE, EMBASE, PUBMED, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, CINAHL, and reference lists of relevant articles. Studies were considered eligible for inclusion if they were randomized controlled trials (RCTs), evaluating the efficacy of BoNTA injections in pain reduction. All studies were assessed and data were abstracted independently by paired reviewers. The outcome measures were baseline and final pain scores as assessed by the patients. The internal validity of trials was assessed with the Jadad scale. Disagreements were resolved through discussions.
Main results
Twenty-one studies were included in the systematic review and 15 of them were included in the final meta-analysis. There was a total of 706 patients in the meta-analysis, represented from trials of plantar fasciitis (n = 1), tennis elbow (n = 2), shoulder pain (n = 1), whiplash (n = 3), and myofascial pain (n = 8). Overall, there was a small to moderate pain reduction among BoNTA patients when compared to control (SMD = −0.27, 95% CI: −0.44 to −0.11). When the results were analyzed in subgroups, only tennis elbow (SMD = −0.44, 95% CI: −0.86 to −0.01) and plantar fasciitis (SMD = −1.04, 95% CI: −1.68 to −0.40) demonstrated significant pain relief. Although not in the meta-analysis, one back pain study also demonstrated positive results for BoNTA. Lastly, BoNTA was effective when used at ≥25 units per anatomical site or after a period ≥5 weeks.
Conclusion
In our meta-analysis, BoNTA had a small to moderate analgesic effect in chronic musculoskeletal pain conditions. It was particularly effective in plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, and back pain, but not in whiplash or shoulder pain patients. However, more evidence is required before definitive conclusions can be drawn. On the other hand, there is convincing evidence that BoNTA lacks strong analgesic effects in patients with myofascial pain syndrome. A general dose-dependent and temporal response with BoNTA injections was also observed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki RK (2003) Evidence for antinociceptive activity of botulinum toxin type A in pain management. Headache 43(Suppl 1):S9–S15
Babcock MS, Foster L, Pasquina P, Jabbari B (2005) Treatment of pain attributed to plantar fasciitis with botulinum toxin A. Am J Phys Med Rebabil 84(9):649–654
Borg-Stein J, Simons DG (2002) Focused review: myofascial pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 83(3 suppl 1):S40–S49
Borodic GE, Acquadro M, Johnson EA (2001) Botulinum toxin therapy for pain and inflammatory disorders: mechanisms and therapeutic effects. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 10:1531–1544
Braker C, Yariv S, Adler R, Badarny S, Eisenberg E (2008) The analgesic effect of botulinum-toxin A on post-whiplash neck pain. Clin J Pain 24(1):5–10
Carroll A, Barnes M, Comiskey C (2008) A prospective randomized controlled study of the role of botulinum toxin in whiplash-associated disorder. Clin Rehabil 22:513–519
Charles PD (2004) Botulinum neurotoxin serotype A: a clinical update on non-cosmetic uses. Am J Health Syst Pharm 61(Suppl 6):S11–S23
Cheshire WP, Abashian SW, Mann DJ (1994) Botulinum toxin in the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome. Pain 59:65–69
Cohen J (1988) Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd edn Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale (NJ)
Compendium of Pharmaceuticals and Specialties (2010) Webcom inc, Toronto 407 –410, Online http://www.e-cps.ca
Cui M, Khanijou S, Rubino J, Aoki KR (2004) Subcutaneous administration of Botulinum toxin A reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 107:125–133
De Andrés J, Cerda-Olmedo G, Valía JC, Monsalve V, Lopez-Alarcon MinguezA (2003) Use of botulinum toxin in the treatment of chronic myofascial pain. Clin J Pain 19(4):269–275
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188
Eccleston C, Crombez G, Aldrich S, Stannard C (1997) Attention and somatic awareness in chronic pain. Pain 72:209–215
Esenyel M, Aldemir T, Gursoy E, Esenyel CZ, Demir S, Durmusoglu G (2007) Myofascial pain syndrome: efficacy of different therapies. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil 20:43–47
Ferrante FM, Bearn L, Rothrock R, King L (2005) Evidence against trigger point injection technique for the treatment of cervicothoracic myofascial pain with botulinum toxin type A. Anaesthesiology 103(2):377–383
Flanders M, Tischler A, Wise J, Williams F, Beneish R, Auger N (1987) Injection of type A botulinum toxin into extraocular muscles for correction of strabismus. Can J Ophtalmol 22(4):212–217
Foster L, Clapp L, Erickson M, Jabbari B (2001) Botulinum toxin A and chronic low back pain. Neurology 56:1290–1293
Francisco GE (2004) Botulinum toxin: dosing and dilution. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 83(suppl):S30–S37
Gobel H, Heinze A, Reichel G, Hefter H, Benecke R (2006) Efficacy and safety of a single botulinum type A toxin complex treatment (Dysport) for the relief of upper back myofascial pain syndrome: results from a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicentre study. Pain 125(1–2):82–88
Guarda-Nardini L, Manfredini D, Salamone M, Salmaso L, Tonello S, Ferronato G (2008) Efficacy of botulinum toxin in treating myofascial pain in bruxers: a controlled placebo pilot study. J Craniomandibular Pract 26(2):126–135
Hallett M (1999) One man’s position: clinical applications of botulinum toxin. N Engl J Med 341:118–120
Hayton MJ, Santini AJA, Hughes PJ, Frostick SP, Trail IA, Stanley JK (2005) Botulinum toxin injection in the treatment of tennis elbow: A double blind, randomized, controlled, pilot study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:503–507
Herr KA, Mobily PR, Smith C (1993) Depression and the experience of chronic back pain: a study of related variables and age differences. Clin J Pain 9:104–114
Jabbari B (2007) Treatment of chronic low back pain with botulinum neurotoxins. Curr Pain Headache Rep 11(5):352–358
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomised controlled trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Kamanli A, Kaya A, Ardicoglu O, Ozgocmen S, Zengin FO, Bayik Y (2005) Comparison of lidocaine injection, botulinum toxin injection, and dry needling to trigger points in myofascial pain syndrome. Rheumatol Int 25(8):604–611
Kurtoglu C, Gur OH, Kurkcu M, Sertdemir Y, Guler-Uysal F, Uysal H (2008) Effect of botulinum toxin A in myofascial pain patients with or without functional disc displacement. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:1644–1651
Lang AM (2000) A pilot study of botulinum toxin type A (Botox), administered using a novel injection technique, for the treatment of myofascial pain. Am J Pain Manag 10:108–112
Lang AM (2003) Botulinum toxin type A therapy in chronic pain disorders. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 84(Suppl 1):S69–S73
Lew MF (2002) Review of the FDA-approved uses of botulinum toxins, including data suggesting efficacy in pain reduction. Clin J Pain 18:S142–S146
Lew HL, Lee EH, Castaneda A, Klima R, Date E (2008) Therapeutic use of botulinum toxin type A in treating neck and upper-back pain of myofascial origin: A pilot study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 89(1):75–80
Magni G, Caldieron C, Rigatti-Luchini S et al (1990) Chronic musculoskeletal pain and depressive symptoms in the general population: an analysis of the 1st national health and nutrition examination survey data. Pain 43:299–307
National Institute of Health (1998) NIH Guide: new directions in pain research I. Sept 4, available from http://www.grants.nih.gov/grants/guide/pa-files/PA-98-102.html
Naumann M, So Y, Argoff CE, Childers MK, Dykstra DD, Gronseth GS, Kaufmann HC, Schurch B, Silberstein SD, Simpson DM (2008) Assessment: botuinum neurotoxin in the treatment of autonomic disorders and pain (an evidence-based review). Neurology 70:1707–1714
Nixdorf DR, Heo G, Major PW (2002) Randomized controlled trial of botulinum toxin A for chronic myogenous orofacial pain. Pain 99:465–473
Odergrena T, Hjaltasona H, Kaakkolab H, Soldersc G, Hankod J, Fehlingd C, Marttilae RJ, Lundhf H, Geding S, Westergreng I, Richardsonh A, Dotth C, Cohenh H (1998) A double blind, randomised, parallel group study to investigate the dose equivalence of Dysport® and Botox® in the treatment of cervical dystonia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 64:6–12
Ojala T, Arokoski JPA, Partanen J (2006) The effect of small doses of botulinum toxin A on neck-shoulder myofascial pain syndrome: a double-blind, randomized, and controlled crossover trial. Clin J Pain 22:90–96
Padberg M, de Bruijn SFTM, Tavy DLJ (2007) Neck pain in chronic whiplash syndrome treated with botulinum toxin. A double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Neurol 254:290–295
Placzeck R, Drescher W, Deuretzbacher G, Hempfing A, Meiss L (2007) Treatment of chronic radial epicondylitis with botulinum toxin A. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:255–260
Porta M (1999) Botulinum toxin type A injections for myofascial pain syndrome and tension-type headache. Eur J Neurol 6(S4):s103–s109
Qerama E, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Kasch H, Bach FW, Jensen TS (2006) A double-blind, controlled study of botulinum toxin A in chronic myofascial pain. Neurology 67:241–245
Review Manager (RevMan) (2008) (Computer program). Version 5.0. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration
Royal MA, Gunyea I, Bhakta B, Movva V, Ward S, Jenson M (2001) Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of refractory myofascial pain (abstract). Neurology 56(Suppl 3):A350
Simons DG, Travell JG, Simons LS (1999) Myofascial pain and dysfunction: The trigger point manual. 2nd edn. Upper half of body, vol. 1, Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore (MD)
Singh G, Triadafilopoulos G (1999) Epidemiology of NSAID induced gastrointestinal complications. J Rheumatol 26(Suppl 56):18–24
Singh JA, Mahowald ML, Noorbaloochi S (2009) Intra-articular botulinum toxin A for refractory shoulder pain: a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Transl Res 153:205–221
Sohling M (2002) Treatment of myofascial pain of the shoulder and neck region with botulinum toxin A. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 365(2):R42
Szczepanska-Szerej A, Stepniak C, Szczepanski L (2003) Clinical evaluation of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of pain in patients with fibromyalgia. Reumatologia 41(4):335–340
Tuzun EH (2007) Quality of life in chronic musculoskeletal pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 21:567–579
Wheeler AH, Goolkasian P (2001a) Open label assessment of botulinum toxin A for pain treatment in a private outpatient setting. J Musculoskeletal Pain 9:67–82
Wheeler AH, Goolkasian P, Gretz SS (1998) A randomized, double-blind, prospective pilot study of botulinum toxin injection for refractory, unilateral, cervicothoracic, paraspinal, myofascial pain syndrome. Spine 23(15):1662–1666
Wheeler AH, Goolkasian P, Gretz SS (2001b) Botulinum toxin A for the treatment of chronic neck pain. Pain 94:255–260
Wiebe N, Vandermeer B, Platt RW, Klassen TP, Moher D, Barrowman NJ (2006) A systematic review identifies a lack of standardization in methods for handling missing variance data. J Clin Epidemiol 59:342–353
Wohlfarth K, Sycha T, Ranoux D, Naver H, Caird D (2009) Dose equivalence of two commercial preparations of botulinum neurotoxin type A: time for a reassessment? Curr Med Res Opin 25(7):1573–1584
Wong SM, Hul ACF, Tong P, Poon DWF, Yu E, Wong LKS (2005) Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with botulinum toxin. Ann Intern Med 143:793–797
Woolf AD, Pfleger B (2003) Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ 81:646–656
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Adatia, A., Zarin, W. et al. The efficacy of botulinum toxin type A in managing chronic musculoskeletal pain: a systematic review and meta analysis. Inflammopharmacol 19, 21–34 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0069-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-010-0069-x