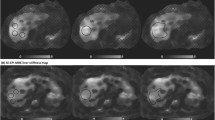
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate performance of 3D magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) using spin-echo echo-planar imaging (seEPI) for assessment of hepatic stiffness compared with 2D gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and 2D seEPI sequences.
Methods
Fifty-seven liver MRE examinations including 2D GRE, 2D seEPI, and 3D seEPI sequences were retrospectively evaluated. Elastograms were analyzed by 2 radiologists and polygonal regions of interests (ROIs) were drawn in 2 different fashions: “curated” ROI (avoiding liver edge, major vessels, and areas of wave interferences) and “non-curated” ROI (including largest cross section of liver, to assess the contribution of artifacts). Liver stiffness measurement (LSM) was calculated as the arithmetic mean of individual stiffness values for each technique. For 3D MRE, LSMs were also calculated based on 4 slices (“abbreviated LSM”). Intra-patient variations in LSMs and different methods of ROI placement were assessed by univariate tests. A p-value of < 0.05 was set as a statistically significant difference.
Results
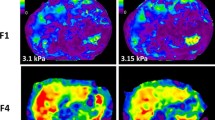
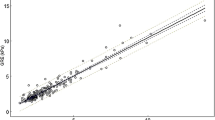
Mean surface areas of the ROIs were 50,723 mm2, 12,669 mm2, 5814 mm2, and 10,642 mm2 for 3D MRE, abbreviated 3D MRE, 2D GRE, and 2D seEPI, respectively. 3D LSMs based on curated and non-curated ROIs showed no clinically significant difference, with a mean difference less than 0.1 kPa. Abbreviated 3D LSMs had excellent correlation with 3D LSMs based on all slices (r = 0.9; p < 0.001) and were not significantly different (p = 0.927).
Conclusion
3D MRE allows more reproducible measurements due to its lower susceptibility to artifacts and provides larger areas of parenchyma, enabling a more comprehensive evaluation of the liver.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials support our published claims and comply with field standards.
Code availability
N/A.
References
Paik JM, Golabi P, Younossi Y, Mishra A, Younossi ZM. Changes in the Global Burden of Chronic Liver Diseases From 2012 to 2017: The Growing Impact of NAFLD. Hepatology. 2020;72(5):1605-16.
Aguilar M, Bhuket T, Torres S, Liu B, Wong RJ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in the United States, 2003-2012. JAMA. 2015;313(19):1973-4.
Shiha G, Ibrahim A, Helmy A, Sarin SK, Omata M, Kumar A, et al. Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) consensus guidelines on invasive and non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: a 2016 update. Hepatol Int. 2017;11(1):1-30.
Dulai PS, Singh S, Patel J, Soni M, Prokop LJ, Younossi Z, et al. Increased risk of mortality by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology. 2017;65(5):1557-65.
Innes H, Morling JR, Aspinall EA, Goldberg DJ, Hutchinson SJ, Guha IN. Late diagnosis of chronic liver disease in a community cohort (UK biobank): determinants and impact on subsequent survival. Public Health. 2020;187:165-71.
Campana L, Iredale JP. Regression of Liver Fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2017;37(1):1-10.
Marcellin P, Gane E, Buti M, Afdhal N, Sievert W, Jacobson IM, et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: a 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet. 2013;381(9865):468-75.
Martinez SM, Foucher J, Combis JM, Metivier S, Brunetto M, Capron D, et al. Longitudinal liver stiffness assessment in patients with chronic hepatitis C undergoing antiviral therapy. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47715.
Gidener T, Ahmed OT, Larson JJ, Mara KC, Therneau TM, Venkatesh SK, et al. Liver Stiffness by Magnetic Resonance Elastography Predicts Future Cirrhosis, Decompensation, and Death in NAFLD. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19(9):1915-24
Mathew RP, Venkatesh SK. Imaging of Hepatic Fibrosis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2018;20(10):45.
Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Loomba R, Wang Z, Sirlin C, Chen J, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a diagnostic accuracy systematic review and individual participant data pooled analysis. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(5):1431-40.
Furlan A, Tublin ME, Yu L, Chopra KB, Lippello A, Behari J. Comparison of 2D Shear Wave Elastography, Transient Elastography, and MR Elastography for the Diagnosis of Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;214(1):W20-W6.
Li J, Venkatesh SK, Yin M. Advances in Magnetic Resonance Elastography of Liver. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2020;28(3):331-40.
Moura Cunha G, Navin PJ, Fowler KJ, Venkatesh SK, Ehman RL, Sirlin CB. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging for chronic liver disease. Br J Radiol. 2021; doi: https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20201377.
Hoodeshenas S, Yin M, Venkatesh SK. Magnetic Resonance Elastography of Liver: Current Update. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;27(5):319-33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0000000000000177.
Idilman IS, Li J, Yin M, Venkatesh SK. MR elastography of liver: current status and future perspectives. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45(11):3444-62.
Yin M, Glaser KJ, Talwalkar JA, Chen J, Manduca A, Ehman RL. Hepatic MR Elastography: Clinical Performance in a Series of 1377 Consecutive Examinations. Radiology. 2016;278(1):114-24.
Wagner M, Besa C, Bou Ayache J, Yasar TK, Bane O, Fung M, et al. Magnetic Resonance Elastography of the Liver: Qualitative and Quantitative Comparison of Gradient Echo and Spin Echo Echoplanar Imaging Sequences. Invest Radiol. 2016;51(9):575-81.
Morisaka H, Motosugi U, Glaser KJ, Ichikawa S, Ehman RL, Sano K, et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracies of two- and three-dimensional MR elastography of the liver. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;45(4):1163-70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25425.
Loomba R, Cui J, Wolfson T, Haufe W, Hooker J, Szeverenyi N, et al. Novel 3D Magnetic Resonance Elastography for the Noninvasive Diagnosis of Advanced Fibrosis in NAFLD: A Prospective Study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(7):986-94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2016.65.
Wang K, Manning P, Szeverenyi N, Wolfson T, Hamilton G, Middleton MS, et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of 2D and 3D hepatic MR elastography with rigid and flexible drivers at end-expiration and end-inspiration in healthy volunteers. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42(12):2843-54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1206-4.
Venkatesh SK, Wells ML, Miller FH, Jhaveri KS, Silva AC, Taouli B, et al. Magnetic resonance elastography: beyond liver fibrosis-a case-based pictorial review. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43(7):1590-611. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1383-1.
RSNA Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Alliance. Magnetic Resonance Elastography of the Liver: Stage 2—Consensus profile. Published May 2, 2018. Available from: https://qibawiki.rsna.org/images/a/a5/MRE-QIBAProfile-2018-05-02-CONSENSUS.pdf. Accessed November 15, 2021
Venkatesh SK, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography of liver. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2014;22(3):433-46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mric.2014.05.001.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-74.
Allen AM, Shah VH, Therneau TM, Venkatesh SK, Mounajjed T, Larson JJ, et al. The Role of Three-Dimensional Magnetic Resonance Elastography in the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Obese Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Hepatology. 2020;71(2):510-21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30483.
Dzyubak B, Venkatesh SK, Manduca A, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL. Automated liver elasticity calculation for MR elastography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43(5):1055-63.
Dillman JR, Franck MD, Gandhi D, Pednekar AS, Tkach JA, Trout AT. Agreement Between Automated and Clinically-Reported Manual ROIBased MR Elastography Liver Stiffness Measurements in Children and Young Adults. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.21.26423.
Serai SD, Dillman JR, Trout AT. Spin-echo Echo-planar Imaging MR Elastography versus Gradient-echo MR Elastography for Assessment of Liver Stiffness in Children and Young Adults Suspected of Having Liver Disease. Radiology. 2017;282(3):761-70.
Kim YS, Jang YN, Song JS. Comparison of gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo-planar imaging MR elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(4):1709-18.. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5149-5.
Wagner M, Corcuera-Solano I, Lo G, Esses S, Liao J, Besa C, et al. Technical Failure of MR Elastography Examinations of the Liver: Experience from a Large Single-Center Study. Radiology. 2017;284(2):401-12. doi: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016160863.
Huwart L, Salameh N, ter Beek L, Vicaut E, Peeters F, Sinkus R, et al. MR elastography of liver fibrosis: preliminary results comparing spin-echo and echo-planar imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(11):2535-41.
Yoshimitsu K, Mitsufuji T, Shinagawa Y, Fujimitsu R, Morita A, Urakawa H, et al. MR elastography of the liver at 3.0 T in diagnosing liver fibrosis grades; preliminary clinical experience. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(3):656-63.
Wang J, Glaser KJ, Zhang T, Shan Q, He B, Chen J, et al. Assessment of advanced hepatic MR elastography methods for susceptibility artifact suppression in clinical patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47(4):976-87. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25818.
Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Wang Z, Miller FH, Motosugi U, Low RN, et al. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13(3):440-51 doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.046.
Acknowledgements
Roger C. Grimm from Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester (MN)
Funding
N/A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Roberta Catania and Amir A. Borhani received Institutional Research Grant from Siemens.
Ethical approval
Waived by our institutional review board due to retrospective design.
Consent to participate
N/A
Consent for publication
N/A
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catania, R., Lopes Vendrami, C., Bolster, B.D. et al. Intra-patient comparison of 3D and 2D magnetic resonance elastography techniques for assessment of liver stiffness. Abdom Radiol 47, 998–1008 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03355-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03355-7