Abstract
Purpose
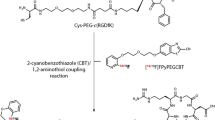
The integrin αvβ3 and aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) play vital roles in the tumor angiogenesis process. They are highly expressed in a variety of tumor cells and proliferating endothelial cells during angiogenesis, which have been considered as highly promising targets for tumor imaging. Arginine-glycine-aspartic (RGD) and asparagine-glycine-arginine (NGR) are two peptides specifically binding to the integrin αvβ3 and CD13, respectively. In this study, we optimized our previously developed probe and preclinically evaluated the new integrin αvβ3 and CD13 dual-targeted probe, NOTA-RGD-NGR (denoted as HX01) radiolabeled with 68Ga, in 10 different subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor models.
Methods
The specific activity and radiochemical purity of [68Ga]Ga-HX01 were identified. The dual-receptor targeting ability was confirmed by a series of blocking studies and partly muted tracers using BxPC-3 xenograft model. The dynamic imaging study and dose escalation study were explored to determine the optimal imaging time point and dosage in the BxPC-3 xenograft model. Next, we established a variety of subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor models including pancreas (BxPC-3), breast (MCF-7), gallbladder (NOZ), lung (HCC827), ovary (SK-OV-3), colorectal (HCT-8), liver (HuH-7), stomach (NUGC-4), and glioma (U87) cancers. All models underwent [68Ga]Ga-HX01 PET/CT imaging about 2 weeks post-inoculation, with a subset of them undergoing [18F]FDG PET/CT scan performed concurrently, and their results were compared. In addition, ex vivo biodistribution studies were also performed for verifying the semi-quantitative results of the non-invasive PET images.
Results
[68Ga]Ga-HX01 significantly outperformed single target probes in the BxPC-3 xenograft model. All blocking and single target groups exhibited significantly descending tumor uptake. The high tumor uptakes were found in BxPC-3, MCF-7, and NOZ subcutaneous tumors (%ID/g > 1.1), while middle uptakes were observed in HCC827, SK-OV-3, HCT-8, and HuH-7 subcutaneous tumor (%ID/g 0.7–1.0). Due to the low background, the tumor-to-muscle and tumor-to-blood ratios of [68Ga]Ga-HX01 were higher than that of [18F]FDG.
Conclusions
[68Ga]Ga-HX01, as a dual target imaging agent, exhibited superior in vivo performance in different subcutaneous and orthotopic mice models of human tumors over [18F]FDG and its respectively mono-receptor targeted agents, which warrants the future clinical translation for tumor imaging.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data and materials are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Rowe SP, Pomper MG. Molecular imaging in oncology: current impact and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:333–52. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21713.
Luo H, Hong H, Yang SP, Cai W. Design and applications of bispecific heterodimers: molecular imaging and beyond. Mol Pharm. 2014;11:1750–61. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp500115x.
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS. Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature. 1997;390:404–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/37126.
Tonini T, Rossi F, Claudio PP. Molecular basis of angiogenesis and cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:6549–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206816.
Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.
Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971;285:1182–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197111182852108.
Shinderman-Maman E, Cohen K, Weingarten C, Nabriski D, Twito O, Baraf L, et al. The thyroid hormone-αvβ3 integrin axis in ovarian cancer: regulation of gene transcription and MAPK-dependent proliferation. Oncogene. 2016;35:1977–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.262.
Yang YSH, Ko PJ, Pan YS, Lin HY, Whang-Peng J, Davis PJ, et al. Role of thyroid hormone-integrin αvβ3-signal and therapeutic strategies in colorectal cancers. J Biomed Sci. 2021;28:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-021-00719-5.
Stucci S, Tucci M, Passarelli A, Silvestris F. Avβ3 integrin: pathogenetic role in osteotropic tumors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2015;96:183–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.05.018.
Barnieh FM, Loadman PM, Falconer RA. Is tumour-expressed aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) structurally and functionally unique? Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876:188641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188641.
Pang L, Zhang N, Xia Y, Wang D, Wang G, Meng X. Serum APN/CD13 as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:77854–64. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12835.
Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhao D, Zhang Z, Zhang S. Expression and clinical significance of aminopeptidase N/CD13 in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015;11:223–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.138007.
Li L, Chen X, Yu J, Yuan S. Preliminary clinical application of RGD-containing peptides as PET radiotracers for imaging tumors. Front Oncol. 2022;12:837952. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.837952.
Zhu L, Ding Z, Li X, Wei H, Chen Y. Research progress of radiolabeled Asn-Gly-Arg (NGR) peptides for imaging and therapy. Mol Imaging. 2020;19:1536012120934957. https://doi.org/10.1177/1536012120934957.
Rubtsov MA, Syrkina MS, Aliev G. RGD-based therapy: principles of selectivity. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22:932–52. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666151209153636.
Judmann B, Braun D, Wängler B, Schirrmacher R, Fricker G, Wängler C. Current state of radiolabeled heterobivalent peptidic ligands in tumor imaging and therapy. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13:173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13080173.
Gai Y, Jiang Y, Long Y, Sun L, Liu Q, Qin C, et al. Evaluation of an integrin αvβ3 and aminopeptidase N dual-receptor targeting tracer for breast cancer imaging. Mol Pharm. 2020;17:349–58. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b01134.
Sun L, Gai Y, Li Z, Li H, Li J, Muschler J, et al. Heterodimeric RGD-NGR PET tracer for the early detection of pancreatic cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022;24:580–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-022-01704-6.
Long Y, Shao F, Ji H, Song X, Lv X, Xia X, et al. Evaluation of a CD13 and integrin αvβ3 dual-receptor targeted tracer 68Ga-NGR-RGD for ovarian tumor imaging: comparison with 18F-FDG. Front Oncol. 2022;12:884554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.884554.
Avraamides CJ, Garmy-Susini B, Varner JA. Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:604–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2353.
Curnis F, Gasparri A, Sacchi A, Cattaneo A, Magni F, Corti A. Targeted delivery of IFNgamma to tumor vessels uncouples antitumor from counterregulatory mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2906–13. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.
Liolios C, Sachpekidis C, Kolocouris A, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Bouziotis P. PET diagnostic molecules utilizing multimeric cyclic RGD peptide analogs for imaging integrin αvβ3 receptors. Molecules. 2021;26:1792. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061792.
Chen X, Tohme M, Park R, Hou Y, Bading JR, Conti PS. Micro-PET imaging of alphavbeta3-integrin expression with 18F-labeled dimeric RGD peptide. Mol Imaging. 2004;3:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1162/1535350041464892.
Zhang J, Niu G, Lang L, Li F, Fan X, Yan X, et al. Clinical translation of a dual integrin αvβ3- and gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-targeting PET radiotracer, 68Ga-BBN-RGD. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:228–34. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.177048.
Li ZB, Wu Z, Chen K, Ryu EK, Chen X. 18F-labeled BBN-RGD heterodimer for prostate cancer imaging. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:453–61. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.107.048009.
Zheng Y, Wang H, Tan H, Cui X, Yao S, Zang J, et al. Evaluation of lung cancer and neuroendocrine neoplasm in a single scan by targeting both somatostatin receptor and integrin αvβ3. Clin Nucl Med. 2019;44:687–94. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000002680.
Liu B, Zhang Z, Wang H, Yao S. Preclinical evaluation of a dual sstr2 and integrin αvβ3-targeted heterodimer [68Ga]-NOTA-3PEG4-TATE-RGD. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019;27:115094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115094.
Liu W, Ma H, Li F, Cai H, Liang R, Chen X, et al. PET imaging of VEGFR and integrins in glioma tumor xenografts using 89Zr labelled heterodimeric peptide. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022;59:116677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116677.
Cheng X, Hübner R, von Kiedrowski V, Fricker G, Schirrmacher R, Wängler C, et al. Design, synthesis, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of heterobivalent SiFAlin-modified peptidic radioligands targeting both integrin αvβ3 and the MC1 receptor-suitable for the specific visualization of melanomas? Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021;14:547. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060547.
Jiang Y, Long Y, Ji H, Qiao P, Liu Q, Xia X, et al. Development and evaluation of a peptide heterodimeric tracer targeting CXCR4 and integrin αvβ3 for pancreatic cancer imaging. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14:1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091791.
Li D, Zhao X, Zhang L, Li F, Ji N, Gao Z, et al. (68)Ga-PRGD2 PET/CT in the evaluation of glioma: a prospective study. Mol Pharm. 2014;11:3923–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp5003224.
Beer AJ, Grosu AL, Carlsen J, Kolk A, Sarbia M, Stangier I, et al. [18F]galacto-RGD positron emission tomography for imaging of alphavbeta3 expression on the neovasculature in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:6610–6. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.
Gao S, Wu H, Li W, Zhao S, Teng X, Lu H, et al. A pilot study imaging integrin αvβ3 with RGD PET/CT in suspected lung cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:2029–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3119-1.
Van Der Gucht A, Pomoni A, Jreige M, Allemann P, Prior JO. 68Ga-NODAGA-RGDyK PET/CT imaging in esophageal cancer: first-in-human imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2016;41:e491–2. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0000000000001365.
Zhang J, Mao F, Niu G, Peng L, Lang L, Li F, et al. 68Ga-BBN-RGD PET/CT for GRPR and integrin αvβ3 imaging in patients with breast cancer. Theranostics. 2018;8:1121–30. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.22601.
Sanz B, Perez I, Beitia M, Errarte P, Fernández A, Blanco L, et al. Aminopeptidase N activity predicts 5-year survival in colorectal cancer patients. J Investig Med. 2015;63:740–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/JIM.0000000000000199.
Faintuch BL, Oliveira EA, Targino RC, Moro AM. Radiolabeled NGR phage display peptide sequence for tumor targeting. Appl Radiat Isot. 2014;86:41–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2013.12.035.
Wood LD, Canto MI, Jaffee EM, Simeone DM. Pancreatic cancer: pathogenesis, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2022;163:386–402. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.03.056.
Xiao Y, Bi M, Guo H, Li M. Multi-omics approaches for biomarker discovery in early ovarian cancer diagnosis. EBioMedicine. 2022;79:104001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104001.
Roa JC, García P, Kapoor VK, Maithel SK, Javle M, Koshiol J. Gallbladder cancer [published correction appears in Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8(1):75]. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2022;8:69. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-022-00398-y.
Jayaprakasam VS, Paroder V, Schöder H. Variants and pitfalls in PET/CT imaging of gastrointestinal cancers. Semin Nucl Med. 2021;51:485–501. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2021.04.001.
Jeng LB, Changlai SP, Shen YY, Lin CC, Tsai CH, Kao CH. Limited value of 18F-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography to detect hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus carriers. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50:2154–6.
Lavanya V, Malik IM, Nallapareddy K, Srivastava M, Valiyaveettil D, Ahmed SF. Correlation of target volumes on magnetic resonance imaging and prostate-specific membrane antigen brain scans in the treatment planning of glioblastomas. Indian J Nucl Med. 2022;37:245–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_189_2.
Jureidini R, da Cunha JE, Takeda F, Namur GN, Ribeiro TC, Patzina R, et al. Evaluation of microvessel density and p53 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016;71:315–9. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2016(06)05.
Haubner R, Weber WA, Beer AJ, Vabuliene E, Reim D, Sarbia M, et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated alphavbeta3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and [18F]Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e70. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020070.
Beer AJ, Pelisek J, Heider P, Saraste A, Reeps C, Metz S, et al. PET/CT imaging of integrin αvβ3 expression in human carotid atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014;7(2):178–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.12.003.
Chen X, Park R, Shahinian AH, Bading JR, Conti PS. Pharmacokinetics and tumor retention of 125I-labeled RGD peptide are improved by PEGylation. Nucl Med Biol. 2004;31:11–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2003.07.003.
Chen H, Jacobson O, Niu G, Weiss ID, Kiesewetter DO, Liu Y, et al. Novel “add-on” molecule based on Evans blue confers superior pharmacokinetics and transforms drugs to theranostic agents. J Nucl Med. 2017;58:590–7. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.182097.
Uehara T, Yokoyama M, Suzuki H, Hanaoka H, Arano Y. A gallium-67/68-labeled antibody fragment for immuno-SPECT/PET shows low renal radioactivity without loss of tumor uptake. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;15(24):3309–16. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0123.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Changyu Shan from Hexin (Suzhou) Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. and Jinquan Han from Wuhan-Britain China School for their help with cell culture and animal model preparing.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81801738 and 82030052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yongkang Gai and Xiaoli Lan: study design and manuscription revision. Xiaoying Lv and Xiangming Song: manuscript writing. Dexing Zeng, Yongkang Gai, Xiaoying Lv, and Xiangming Song: tracer synthesis and identification. Xiaoying Lv, Xiangming Song, and Yu Long: animal experiment, image acquisition, and interpretation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All animal studies were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Competing interests
Dexing Zeng and Yongkang Gai hold the patent of the compound HX01. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, X., Song, X., Long, Y. et al. Preclinical evaluation of a dual-receptor targeted tracer [68Ga]Ga-HX01 in 10 different subcutaneous and orthotopic tumor models. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 51, 54–67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06412-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06412-z